Difference Between Raynaud’s Disease and Frostbite

Difference between Raynaud’s disease and frostbite
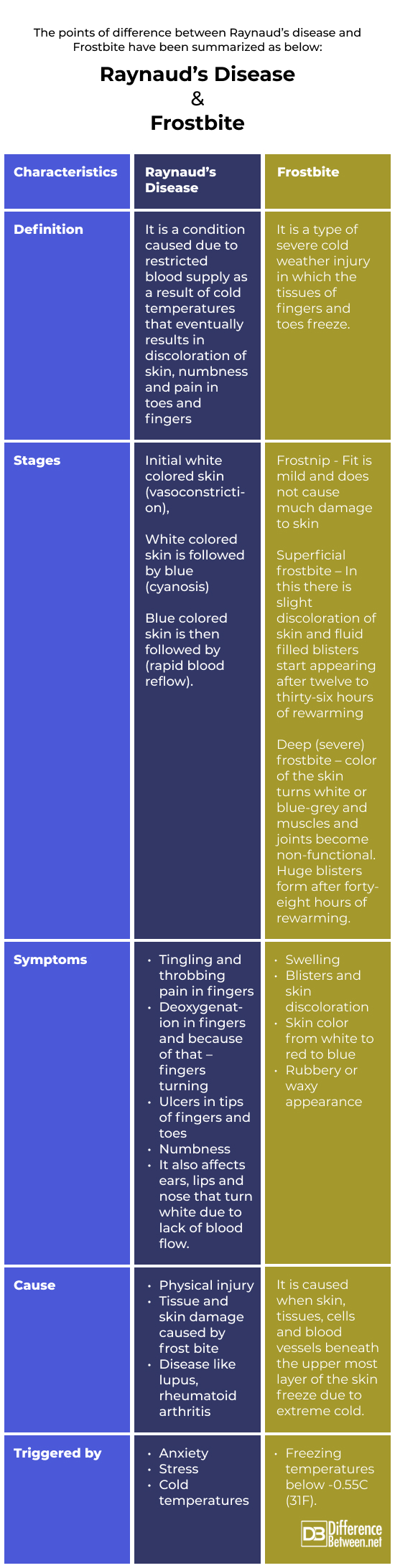
Though both Raynaud’s disease and frostbite exhibit similar symptoms, the two conditions are different from each other. Raynaud’s disease is caused by vascular changes where some parts of the body feel numb and cold either due to extreme cold or due to restricted blood supply in that body part. While as frostbite is caused when bare feet and hands are subjected to below freezing temperatures. Due to extreme cold, the tissues of the skin of fingers and toes freeze resulting in frostbite.

Similarity
Both show symptoms like numbness, pain, burning, discoloration of skin and pins and needles
Raynaud’s disease
Also termed as Raynaud phenomenon, this condition causes restricted blood flow to toes, fingers, nose, and knees due to colder temperatures or due to blood vessels going into temporary spasms. It affects one in twenty people in the United States of America. The symptoms ae episodic and include pins and needles feeling, tingling and throbbing feeling, numbness and skin discoloration.
Frostbite
When skin is exposed to freezing temperatures like -0.55C, the tissues just beneath the skin freezes and this condition is called frostbite. The symptoms include stinging sensation, blisters, reduced sensation of touch, rubbery or waxy appearance.
Difference between Raynaud’s Disease and Frostbite
Definition
Raynaud’s disease
Raynaud’s disease, typically happens when the skin is subjected to cold and affects the blood circulation in the fingers and toes.
Frostbite
When subjected to freezing low temps skin injury, swelling and burning happens and this condition is called Frostbite. It typically affects the nose, ears, cheeks, chin, fingers and toes.
Symptoms
Raynaud’s disease
- Spasm in small blood vessels
- Feeling warmth, tingling or throbbing
- Skin ulcers and gangrene
Frostbite
- Numbness
- Hard or waxy looking skin
- Blistering after rewarming
Diagnosis
Raynaud’s disease
- Antinuclear antibody (ANA) test
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test
- Urinalysis: Urine test that checks for a range of conditions.
- Pulse volume recording: Non-invasive test that checks blood flow in your arms and legs.
- Rheumatoid factor (RF) test: Blood test that checks for autoimmune diseases.
Frostbite
There are no specific tests done to diagnose frostbite. Your doctor will look at your symptoms, and may advise an X-ray to check if there’s any concerning damage to bone or muscle.
Treatment
Raynaud’s disease
- Lifestyle changes
- Medications like
- Calcium-channel blockers
- Alpha-blockers – norepinephrine to increase blood supply
- Nitroglycerin skin ointment – heals skin ulcers
Frostbite
- Put frostbitten parts in warm water for about 30 minutes
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (acetaminophen or ibuprofen)
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy that increases blood-oxygen levels in the affected body parts
Summary
The points of difference between Raynaud’s disease and Frostbite have been summarized as below:
FAQ:
Can Raynaud’s be caused by frostbite?
Yes, tissues and cells of skin damaged by frostbite can also lead to Raynaud’s disease.
What can be mistaken for Raynaud’s syndrome?
The look of cyanosis, which may result from deoxygenated blood (low partial pressure of oxygen) from venous pooling, can be mistaken for Raynaud disease.
Is it Raynaud’s disease or just cold?
Many people experience having cold hands and feet, this is not caused by the Raynaud’s disease unless the skin tissues have turn white or blue during extreme cold. Nailfold capillary microscopy (sensitive and inexpensive morphological analysis) is a technique that separates primary from secondary Raynaud’s.
How can you tell the difference between chilblains and Raynaud’s?
Chilblains, also termed as pernio, is a skin condition that happens from frequent and repeated exposure to cold, damp but not freezing conditions. On the other hand, Raynaud’s is caused by extreme cold conditions and this condition involves blocking of blood flow in the fingers and toes.
What do your fingers look like when you have frostbite?
Bruises on fingers, spotty patches or purple areas on the skin of the fingers.
What is the life expectancy of someone with Raynaud’s disease?
Symptoms of this condition usually do not get worse with age. It is not serious and can last for a lifetime.
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Baumhäkel, M., & Böhm, M. (2010). Recent achievements in the management of Raynaud’s phenomenon. Vascular health and risk management, 6, 207.
[1]Bowling, J. C. R., & Dowd, P. M. (2003). Raynaud's disease. The Lancet, 361(9374), 2078-2080.
[2]Handford, C., Thomas, O., & Imray, C. H. (2017). Frostbite. Emergency Medicine Clinics, 35(2), 281-299.
[3]Handford, C., Buxton, P., Russell, K., Imray, C. E., McIntosh, S. E., Freer, L., ... & Imray, C. H. (2014). Frostbite: a practical approach to hospital management. Extreme physiology & medicine, 3(1), 1-10.
