Differences Between Osteomyelitis and Septic Arthritis
What is Osteomyelitis?
Definition:
Osteomyelitis is inflammation of the fatty tissues within a bone caused by a bacterial, fungal, or viral infection.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Osteomyelitis is always the result of an infection, but the infectious agent and routes of infection can vary widely. Bacteria are the most common causes, particularly Staphylococcus aureus, but fungal and viral infections are also potential causes.
Risk factors for infection include severe fractures and puncture wounds, recent joint surgery, intravenous drug use, and orthopedic or prosthetic hardware. Hemodialysis patients are also at risk of infection from the tubing used in dialysis.
Conditions that impair circulation are also potential risk factors, including diabetes, sickle cell disease, and smoking, as are conditions leading to a weakened or suppressed immune system, such as cancer treatment or HIV. Because diabetes both suppresses the immune system and impairs circulation, it is a significant risk factor associated with osteomyelitis.
Diagnosis:
Blood tests and radiography may be useful initial tests, but a definitive diagnosis requires tissue culture from a bone biopsy, combined with histologic examination of the affected bone.
Symptoms:
Symptoms present initially as pain and swelling at the site of infection and fever. Erythema or reddening of the skin surrounding the bone may follow, then necrosis of the surrounding tissue and the formation of purulent wounds and ulcers.
Complications:
Osteomyelitis can impair circulation and lead to bone death if left untreated. Septic arthritis is a risk if the infected bone is adjacent to a joint, as are septicaemia, sepsis, and death. If the infection leads to purulent ulcers or sores, the skin surrounding these is at increased risk for skin cancer.
Treatment:
Treatment of osteomyelitis must begin immediately to avoid serious complications like bone death and permanent joint damage. Intravenous antibiotics are always a component of effective treatment, but treatment must be tailored to the specific infection, making culture from a bone biopsy critical.
If bone death has occurred, surgery will be necessary to remove diseased and necrotic bone, debride the area, and restore blood circulation. Surgery may also be necessary to remove implants if these were vectors for infection.
What is Septic Arthritis?
Definition
Septic arthritis is painful inflammation of a joint caused by an infection in the synovium.
Causes and Risk Factors
Septic arthritis is a complication of infection in a joint, commonly bacterial but occasionally fungal or viral. Staphylococcus aureus accounts for the majority of cases, with Streptococcus pneumonia prevalent but less common.
As with osteomyelitis, risk factors for septic arthritis include immune-suppressing conditions like sickle cell and diabetes, as well as trauma or surgery in a joint and prosthetic or orthopedic implants. Children are at higher risk for septic arthritis, particularly neonates and immunocompromised children.
Diagnosis
Radiography can reveal abnormalities in joints and surrounding tissues, but synovial fluid from the affected joint must be evaluated to establish a diagnosis, and a full tissue culture is needed to identify the infectious agent.
Symptoms
Many symptoms of septic arthritis are common to sterile arthritis, including intense joint pain, difficulty moving or using the affected limb, and redness or swelling at the site of infection. Septic arthritis also presents symptoms of bacterial infection, including fever, chills, and tachycardia.
Complications
Septic arthritis is a serious condition that can be fatal if left untreated. Complications include loss of cartilage and permanent joint damage, infection and osteomyelitis in adjacent bones, bone death, sepsis, and death. Early identification and treatment are needed to prevent complications from arising.
Treatment
Treatment of septic arthritis should start with intravenous antibiotics for 1 to 2 weeks, followed by 1 to 2 weeks of oral antibiotics. Daily aspiration of synoval fluid can reduce swelling and pain in the joint but should be supervised by an orthopedic surgeon. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent permanent joint damage and complications.
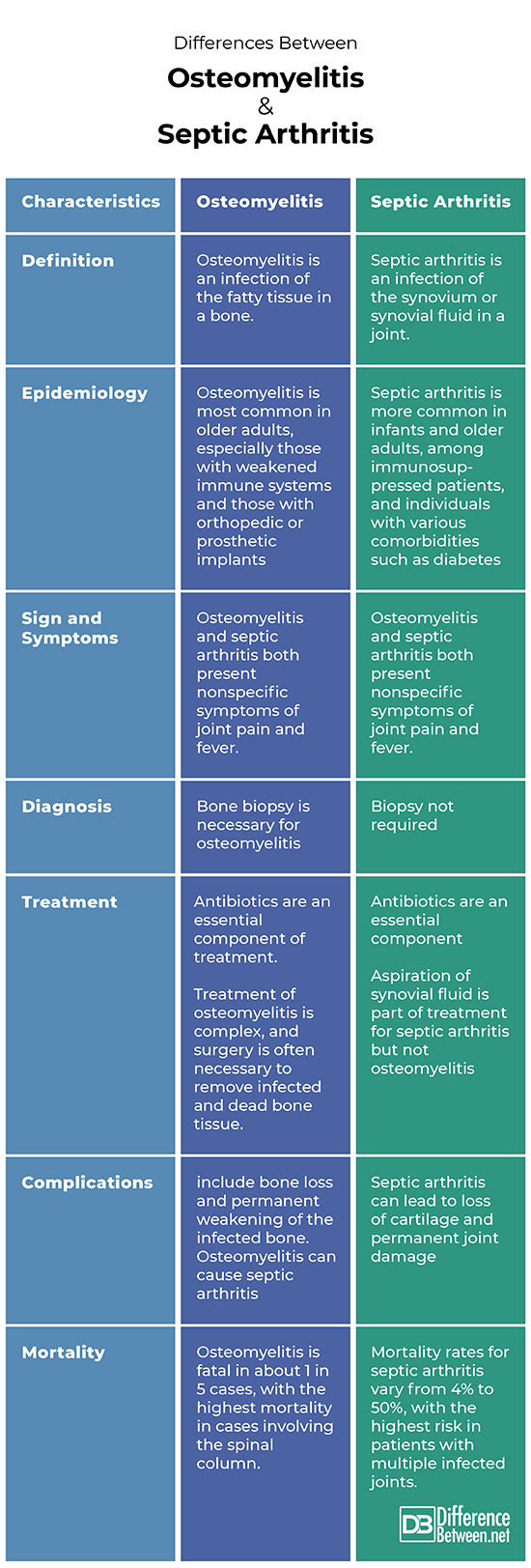
Differences Between Osteomyelitis and Septic Arthritis
Definition
Osteomyelitis is an infection of the fatty tissue in a bone. Septic arthritis is an infection of the synovium or synovial fluid in a joint.
Epidemiology
Septic arthritis is more common in infants and older adults, among immunosuppressed patients, and individuals with various comorbidities such as diabetes. 56% of patients with septic arthritis are male. Bacterial Septic Arthritis is commonly described as either gonococcal or nongonococcal. Osteomyelitis is most common in older adults, especially those with weakened immune systems and those with orthopedic or prosthetic implants.
Symptoms
Osteomyelitis and septic arthritis both present nonspecific symptoms of joint pain and fever. Purulent wounds or ulcers are frequently symptomatic of osteomyelitis but not septic arthritis.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of either condition requires evaluation of affected tissue: bone for osteomyelitis, synovial fluid for septic arthritis. Bone biopsy is necessary for osteomyelitis but not septic arthritis.
Treatment
Antibiotics are an essential component of treatment of either disease. Treatment of osteomyelitis is complex, and surgery is often necessary to remove infected and dead bone tissue. Aspiration of synovial fluid is part of treatment for septic arthritis but not osteomyelitis.
Complications
Septic arthritis can lead to loss of cartilage and permanent joint damage. Complications of osteomyelitis include bone loss and permanent weakening of the infected bone. Osteomyelitis can cause septic arthritis, and vice versa.
Mortality
Osteomyelitis is fatal in about 1 in 5 cases, with the highest mortality in cases involving the spinal column. Mortality rates for septic arthritis vary from 4% to 50%, with the highest risk in patients with multiple infected joints.
Differences Between Osteomyelitis and Septic Arthritis
FAQs
Does osteomyelitis cause septic arthritis?
Yes, rarely. Osteomyelitis can occur in any bone, but when it is present in a joint, there is a risk that pus from the infection will enter the joint tissue or synovial fluid, which can cause septic arthritis.
What is the difference between septic arthritis and inflammatory arthritis?
Septic arthritis is a type of inflammatory arthritis, to the extent that arthritis is by definition inflammation of a joint or joints. What distinguishes septic arthritis from sterile arthritis (lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.) is an infectious etiology, usually bacterial.
Is osteomyelitis the same as sepsis?
No. Sepsis is systemic and affects the entire body. Osteomyelitis is limited to bone tissue. However, the underlying infectious agent responsible for osteomyelitis can also cause sepsis if left untreated.
What bacteria are the most common cause of both septic arthritis and osteomyelitis?
Both septic arthritis and osteomyelitis are most commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus, but infections from Group B species of Streptococcus are also frequent.
What are the two types of osteomyelitis?
Osteomyelitis can present as chronic or acute. Treatment of the underlying cause of infection is the same in either type (antibiotics), but chronic osteomyelitis may also require surgical removal of dead bone fragments.
What are the two most common causes of osteomyelitis?
Osteomyelitis is either hematogenous or direct. Hematogenous osteomyelitis is caused by bacteria introduced via the bloodstream, but bacteria can also be introduced directly or adjacent to the site of infection, either through trauma or surgery.
What is the gold standard for diagnosing osteomyelitis?
Only a tissue culture from a bone biopsy is definitive of osteomyelitis, ideally informed by histopathology tests of the affected bone. Radiography and culture of wounds or ulcers are useful supplements but may give false negatives or otherwise misleading results.
What is the most common site of osteomyelitis?
The vertebrae are the most common sites of infection in adults, followed by the bones of the limbs, pelvis, and clavicles.
Can bone scans detect septic arthritis?
No. Bone scans can identify the site of inflammation but cannot distinguish infectious inflammation from age-related or autoimmune inflammation. Only an analysis of the synovial fluid can establish an infectious pathology.
- Difference Between Vascular Cambium and Cork Cambium - November 1, 2023
- Difference Between DevOps and Developer - September 10, 2023
- Difference Between Acute Gastritis and Chronic Gastritis - April 3, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Ferrand, J, El Samad, Y, Brunschweiler, B, Grados, F, Dehamchia-Rehailia, N, Séjourne, A, Schmit, J-L, Gabrion, A, Fardellone, P, Paccou, J. Morbimortality in adult patients with septic arthritis: a three year hospital-based study. BMC Infectious Diseases vol. 16 issue 239, 2016. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4888402/
[1]Fritz, JM & McDonald, JR. Osteomyelitis: approach to diagnosis and treatment. Physical Sports Medicine vol. 36 issue 1, 2008. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2696389/#:~:text=The%20gold%20standard%20for%20the,until%20bone%20biopsy%20is%20performed.
[2]Marsh, JL, Watson, PA & Crouch, CA. “Septic arthritis aused by chronic osteomyelitis.” Iowa Orthopedic Journal vol. 17, 1997, pp. 90-95. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2378102/
[3]Momodu, II & Savaliya, V. “Septic arthritis.” National Library of Medicine, 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538176/
[4]NORD Rare Disease Database. “Osteomyelitis.” 2019. https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/osteomyelitis/#symptoms
