Difference Between Acute and Chronic Osteomyelitis
Infection of the bone leading to inflammation describes the condition of Osteomyelitis. Any bacterial, fungal, or mycobacterial infection can cause Osteomyelitis. This gives rise to severe pain in the patient, ultimately causing bone decay and degeneration.

What is Osteomyelitis?
Definition:
Osteomyelitis is a bacterial infection that affects the bones and bone marrow. Symptoms may include fever, chills, bone pain, and swelling, and treatment involves antibiotics and surgery.
Causes and risk factors:
Various bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Escherichia coli, can cause Osteomyelitis. The infection can be spread through contact with infected blood, skin, or bone marrow or from a wound that becomes infected. Risk factors for Osteomyelitis include diabetes, intravenous drug use, and a weakened immune system.
Diagnosis:
Osteomyelitis is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests, such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans.
Symptoms:
Osteomyelitis symptoms include pain in the affected area, swelling, redness and warmth to the touch, fever, chills, fatigue, difficulty moving the affected limb, and drainage of pus from the affected area.
Complications:
Complications of osteomyelitis may include sepsis, meningitis, and abscess formation. It damages the bone and soft tissue, causing long-term pain and disability. In some instances, it can lead to amputation as well.
Treatment:
Antibiotic therapy is typically given intravenously (IV) in the hospital for at least 4-6 weeks, followed by oral antibiotics for several weeks or months, depending on the severity of the infection. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove dead or infected bone and promote healing. Physical therapy may also be recommended to help regain strength and mobility in the affected limb after treating the infection.
What is Chronic Osteomyelitis?
Definition:
Chronic osteomyelitis is a persistent or recurrent infection in the bone that often occurs when the blood supply to the affected area is poor. This can make it difficult for antibiotics to reach the site of the infection and prevent it from healing completely. Usually, osteomyelitis becomes chronic when the infection persists for more than six weeks.
Causes and risk factors:
Chronic osteomyelitis can be caused by various bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Escherichia coli. The infection can be spread through contact with the infected. The risk factors include poor blood flow, weak immune system, previous injury or surgery, and chronic diseases.
Diagnosis:
The diagnosis of chronic osteomyelitis may involve a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Sometimes, bone biopsies may also be necessary for accurate diagnosis.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of chronic osteomyelitis can vary depending on the severity and duration of the infection. However, they may include pain in the affected limb, swelling associated with redness and tenderness, limited movement of the limb, drainage from the affected limb, fever due to infection, and weakness.
Complications:
Chronic osteomyelitis can cause several complications, including the spread of the infection, damage to the affected bone, abscess formation, development of sinus tract, osteonecrosis or bone death, and in some cases, amputation.
Treatment:
Treatment for chronic osteomyelitis typically involves a combination of antibiotics, surgery, and rehabilitation. The specific treatment plan may vary depending on the extent and severity of the infection and any underlying conditions or risk factors. In some cases, a combination of these treatments may be necessary to treat chronic osteomyelitis and prevent recurrence effectively.
Difference between Osteomyelitis and Chronic Osteomyelitis
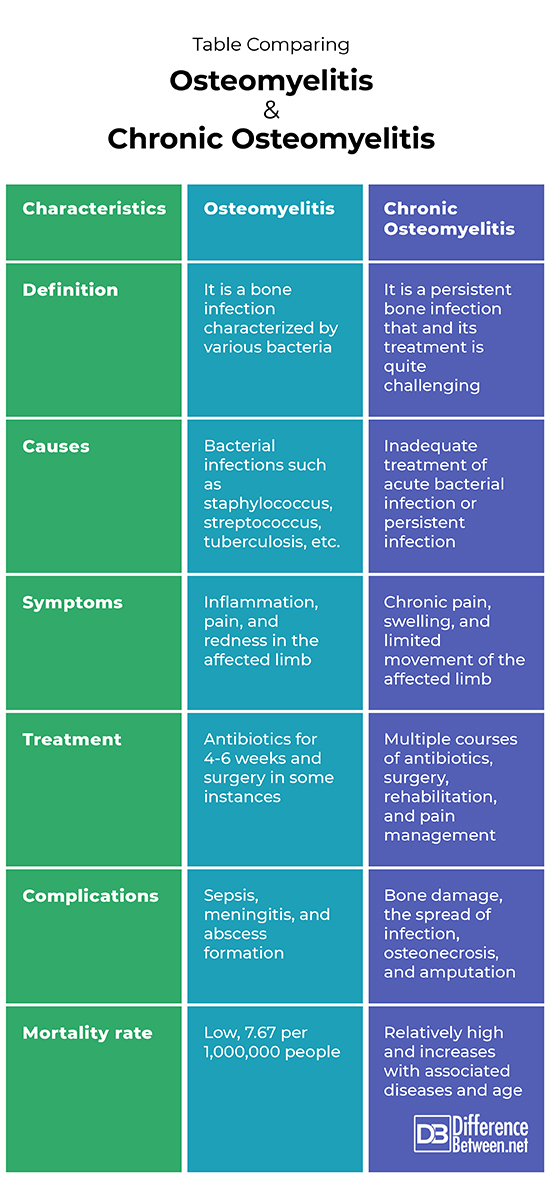
Definition
Osteomyelitis refers to an infection of the bone, which a variety of bacteria, including staphylococcus and streptococcus, can cause. Chronic osteomyelitis, on the other hand, is a form of osteomyelitis that persists over time and is quite challenging to treat.
Causes
Different bacterial infections, including staphylococcus and streptococcus, can cause osteomyelitis or bone infection. Chronic osteomyelitis can occur due to an inadequately treated acute or persistent infection that was not fully treated.
Symptoms
Osteomyelitis infection can cause inflammation, pain, and redness in the affected limb. In contrast, chronic osteomyelitis is often accompanied by chronic pain, swelling, and limited movement in the affected limb.
Treatment
Osteomyelitis is mainly treated with antibiotics, and surgery may sometimes be required. Chronic osteomyelitis requires a longer course of multiple antibiotics, with surgery, rehabilitation, and pain management in various cases.
Complications
Osteomyelitis involves complications such as sepsis, meningitis, and abscess formation. Chronic osteomyelitis mainly includes bone damage, infection spread, osteonecrosis, and amputation in some patients.
Mortality rate
The death rate from osteomyelitis is relatively low, at approximately 7.67 per 1,000,000 people in the US. Chronic osteomyelitis has a significantly higher risk for mortality, mainly when associated with other diseases like diabetes, and it increases with age.
Table comparing Osteomyelitis and Chronic Osteomyelitis
Summary of Osteomyelitis and Chronic Osteomyelitis
- Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone caused by a number of bacterial species.
- Chronic osteomyelitis is a form of osteomyelitis occurring due to persistent infection that is difficult to treat.
- Chronic osteomyelitis is more severe and painful than osteomyelitis, potentially increasing the complications associated with the disease.
FAQ
What is the difference between acute and subacute osteomyelitis?
Acute osteomyelitis is a severe and rapidly spreading infection that requires prompt treatment to prevent damage to the bone and surrounding tissues. Subacute osteomyelitis is a less severe infection that progresses more slowly and may not cause as severe symptoms.
When does osteomyelitis become chronic?
Osteomyelitis becomes chronic when the infection persists for an extended period, often several weeks or more, despite appropriate treatment. Chronic osteomyelitis is more challenging to treat and may cause long-term damage to the affected bone and surrounding tissues.
What are the different types of osteomyelitis?
According to the illness duration, osteomyelitis is categorized into acute, subacute, and chronic. Based on the mechanism of infection, osteomyelitis can either be hematogenous or contiguous.
Which distinguishing characteristic is most commonly seen in cases of chronic osteomyelitis?
One of the most common distinguishing characteristics of chronic osteomyelitis is the sinus tract, a narrow channel or tunnel connecting the infected bone to the surface of the skin.
What is the most common cause of chronic osteomyelitis?
The most common cause of chronic osteomyelitis is an infection with bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics, also known as antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
- Difference Between Vascular Cambium and Cork Cambium - November 1, 2023
- Difference Between DevOps and Developer - September 10, 2023
- Difference Between Acute Gastritis and Chronic Gastritis - April 3, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Lew, Daniel P, and Waldvogel, Francis A. "Osteomyelitis". The Lancet 364.9431 (2004): 369-379.
[1]Momodu, Ifeanyi I. "Osteomyelitis". Stat Pearls, 2023, https://www.statpearls.com/ArticleLibrary/viewarticle/26397
[2]Huang JF, Wu QN, Zheng XQ, Sun XL, Wu CY, Wang XB, Wu CW, Wang B, Wang XY, Bergman M, Wu AM. "The Characteristics and Mortality of Osteoporosis, Osteomyelitis, or Rheumatoid Arthritis in the Diabetes Population: A Retrospective Study". International Journal of Endocrinology 8821978 (2020): 1-11.
[3]Osborn, Rae. “What is Osteomyelitis?”. Myacare, 2022, https://myacare.com/blog/what-is-osteomyelitis#:~:text=Osteomyelitis%20is%20a%20serious%20condition,treatment%20is%20not%20started%20rapidly
