Difference Between Space Probes and Rovers
Space exploration is the human endeavor to explore and understand the vast, mysterious realm beyond our planet, which we call space. It involves sending spacecraft, such as satellites, probes, and rovers, to various celestial bodies like the Moon, Mars, and distant planets. Space probes and rovers are crucial tools in space exploration. These robotic explorers provide valuable insights into the composition, geology, and atmospheres of other worlds.
In this article, we’ll talk about them in brief and highlight the key differences between space probes and rovers in detail. Read on to learn more!

What is a space probe?
A space probe is an unmanned device designed to travel through space and collect data about celestial bodies such as planets, moons, comets, and asteroids. These probes are equipped with various scientific instruments and sensors to gather information and transmit it back to Earth. Unlike crewed missions, space probes are typically one-way journeys, as they do not carry astronauts and are often left to operate autonomously.
Probes have been used for missions to study the planets in our solar system, explore comets and asteroids, and even venture beyond our solar system to gather data on interstellar space.
Some well-known space probes include the Voyager spacecraft, which have left the solar system and continue to send data from interstellar space, and the Mars rovers like Curiosity and Perseverance, which explore and study the Martian surface.

What is a rover?
Rovers are small, mobile robots designed to explore and study the surfaces of other celestial bodies, primarily planets and moons. Unlike space probes, rovers are equipped with wheels or legs that allow them to move around on the surface. This allows them to investigate multiple locations and conduct experiments in different areas.
Rovers are built to be mobile, so they can traverse rough terrain, collect samples, and travel significant distances on the celestial body they are exploring. They carry a suite of scientific instruments, cameras, and sensors to study the local geology, climate, and chemistry.
One of the most famous rover missions is NASA’s Mars rovers, including Spirit, Opportunity, Curiosity, and Perseverance. These rovers have explored the Martian surface, searching for signs of past or present life and studying the planet’s geology and climate.
Key Differences between Space Probes and Rovers
Mobility
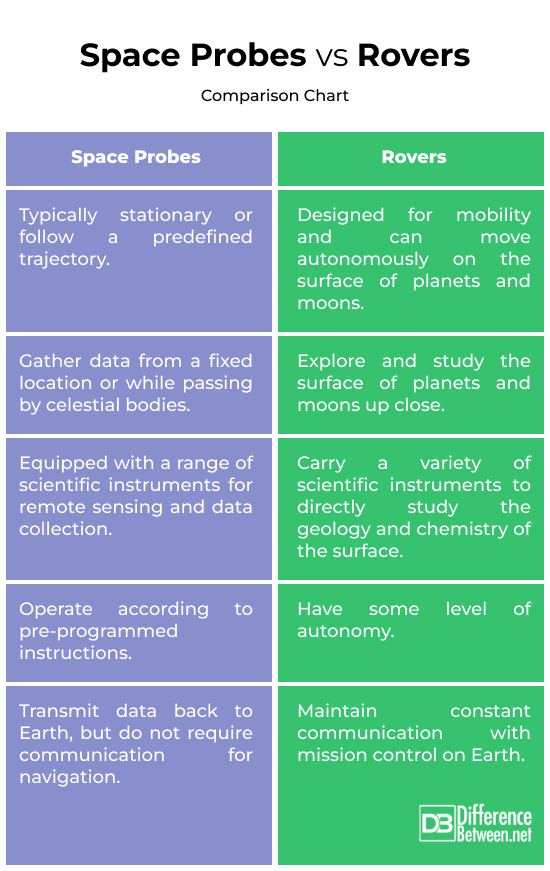
Probes are typically stationary or follow a predefined trajectory without the ability to move on the surface of celestial bodies. Rovers, on the other hand, are designed for mobility and can move autonomously on the surface of planets and moons, allowing them to explore different locations. Unlike space probes, rovers are equipped with wheels or legs that allow them to move around on the surface.
Surface Exploration
Space probes gather data from a fixed location or while passing by celestial bodies but do not explore the surface. They do not land on the surface of celestial bodies but gather data from a distance. Rovers are specifically built to explore and study the surface of planets and moons up close. They are equipped with wheels or legs that allow them to move across the terrain and investigate different locations.
Scientific Instruments
Probes are equipped with a range of scientific instruments for remote sensing and data collection. They are more focused on obtaining data from the vicinity of the probe’s orbit or trajectory. Rovers carry a variety of scientific instruments, including cameras, spectrometers, and drills, to directly study the geology and chemistry of the surface.
Autonomy
Probes operate according to pre-programmed instructions without making autonomous decisions about their activities. Rovers have a level of autonomy, allowing them to adapt their movements and experiments based on real-time data and conditions on the surface.
Communication
Probes transmit data back to Earth but do not require communication for navigation. Their missions are typically one-way, with limited adjustments made after launch. Rovers maintain constant communication with mission control on Earth, receiving commands and transmitting data during their missions. This ongoing connection allows for real-time adjustments to their movements and activities.
Space Probes vs. Rovers: Comparison Chart
Summary
In a nutshell, space probes and rovers serve distinct roles. Space probes, like Voyager, are stationary or on predefined trajectories, collecting data remotely without surface exploration using instruments designed for distant observations. In contrast, rovers, exemplified by Mars rovers Curiosity and Perseverance, are mobile robots engineered for on-the-ground exploration. They possess wheels or legs, directly interact with and investigate planetary surfaces, and are equipped with tools such as drills and analyzers to study geology and chemistry.
FAQs
What is a rover space probe?
A rover space probe is a robotic spacecraft designed for surface exploration on celestial bodies like planets and moons, equipped with mobility for close-up investigation.
What is the difference between a rover and an orbiter?
Rovers are designed for on-the-ground exploration, while orbiters typically study celestial bodies from orbit without direct surface interaction.
What is the difference between a probe and a rocket?
A rocket is a launch vehicle used to propel payloads, including probes, into space. Probes are spacecraft sent into space to gather data from celestial bodies.
Is the Curiosity Rover a space probe?
The Curiosity Rover is not a space probe but a rover designed for surface exploration on Mars, capable of on-site analysis and mobility.
Why does NASA use rovers?
NASA uses rovers for their unique capability to explore and study planetary surfaces up close, conducting experiments, collecting samples, and transmitting valuable data back to Earth. Rovers provide hands-on insights that orbiters or probes cannot, contributing to a deeper understanding of other worlds.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Schaefer, Lola M. Explore Space Probes. Lerner Publishing Group, 2022.
[1]Matloff, Gregory L. Deep Space Probes: To the Outer Solar System and Beyond. Springer Science and Business Media, 2006.
[2]Collins, Ailynn. Probe Power: How Space Probes Do What Humans Can’t. 2020.
[3]Owen,Ruth. Rovers. Rosen Publishing, 2014.
[4]Ellery, Alex. Planetary Rovers: Robotic Exploration of the Solar System. Springer, 2015.
[5]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAE4ICyr8wQ-space-probe-orbiting-saturn-3d-rendering/
[6]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAEe0th9skI-3d-render-mars-rovers-landed-illustration/
