Difference Between Manned and Unmanned Space Missions
Humans have been studying and exploring space for thousands of years. Space exploration has always captivated our imagination. Going back to about 1600, scientists used telescopes to look at the objects in the sky. In recent decades, we have accomplished so much and are sending humans into space to get a closer look at the moon and other bodies.
Whether it’s sending humans or robots into the vast cosmos, each approach has its own unique advantages and challenges. In this article, we’ll explore the key distinctions between manned and unmanned space missions.

What is a manned space mission?
A manned space mission, often referred to as a human spaceflight, involves sending a crew of passengers or astronauts into space aboard a spacecraft. The crew often operates the spacecraft and can provide real-time data and make complex decisions on-site. They are responsible for piloting the spacecraft, conducting scientific research, and performing spacewalks if necessary.
Manned spacecraft are equipped with life support systems to provide astronauts with the necessary oxygen, food, and waste management capabilities. These systems ensure the crew’s survival in the vacuum of space.

What is an unmanned space mission?
Unmanned space missions, on the other hand, involve sending spacecraft, probes, rovers, or other automated vehicles into space. The objective remains the same, which is to explore and gather data but without the presence of a human crew on board. The spacecraft is operated automatically or remotely from Earth.
Unmanned space missions are typically launched for many reasons, including:
- Exploring the moon and other planets
- Sending communications satellites into orbit
- Launching weather satellites
- Testing new technologies
Difference between Manned and Unmanned Space Missions
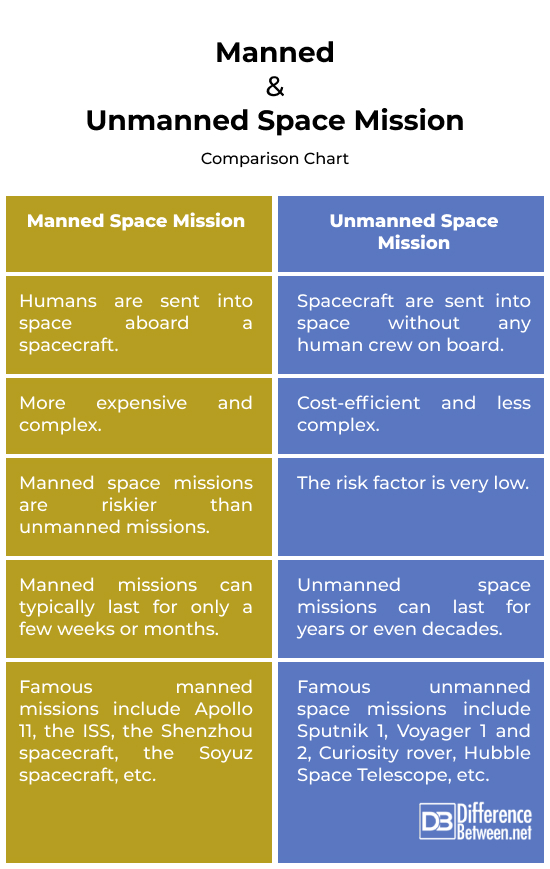
Humans vs. Robots – Manned space missions involve sending passengers or astronauts into space aboard a spacecraft. The spacecraft is often operated directly by the onboard human crew. Unmanned space missions, as the name suggests, involve sending spacecraft into space without any human crew on board. The spacecraft is operated automatically or remotely from Earth.
Cost Factor – Manned missions are more expensive because of the cost involved in developing and maintaining the necessary life support systems, as well as astronaut training and safety measures. In terms of cost, unmanned missions offer a significant advantage over manned missions but require extensive planning and automation.
Risk Factor – Manned space missions are riskier than unmanned missions because they involve human lives and require life support systems. Astronauts may face potential hazards such as space radiation, equipment failures, and life-threatening emergencies. Robotic missions can be carried out remotely without these concerns.
Duration – Manned missions are limited by life support resources and can typically last for only a few weeks or months. Also, humans need to return to Earth to replenish their food, water, and oxygen supplies. On the flip side, unmanned space missions can last for years or even decades, exploring distant planets. So, unmanned missions typically have an edge over manned missions on this front.
Flexibility – Manned missions can adapt to unforeseen challenges. Humans can make decisions and take necessary actions in real-time. Unmanned space missions follow pre-programmed instructions, while manned missions are constrained by the availability of life support resources and the need for astronaut safety.
Manned vs. Unmanned Space Missions: Comparison Chart
Summary
When it comes to space exploration, both manned and unmanned missions play crucial roles. Manned missions offer real-time decision-making but come at a higher cost and risk. Unmanned missions, while cost-effective and risk-averse, excel at long-term exploration and precise tasks. Whether humans or robots, our collective quest to explore the final frontier continues to push the boundaries of knowledge.
FAQs
What are some advantages of unmanned missions to space compared to manned missions?
Advantages of unmanned missions to space over manned missions include cost efficiency, reduced risk, extended operational duration, and the ability to withstand harsh environments.
What is manned and unmanned space?
Manned space missions involve sending astronauts into space, whereas unmanned missions use robotic spacecraft or vehicles without human crews.
What is the difference between human and robotic space exploration?
Human space exploration involves sending astronauts into space aboard a spacecraft, while robotic space exploration involves sending spacecraft, probes, rovers, or other automated vehicles into space without any human crew.
What are the disadvantages of manned space missions?
Manned space missions are typically more expensive and present a greater risk to human life. Additionally, such missions are less flexible and limited due to resource constraints and the need for complex life support systems.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using unmanned air vehicles?
Unmanned air vehicles (UAVs) offer advantages such as cost-effectiveness, remote operation, and endurance. However, they may face limitations in terms of decision-making, adaptability, and the ability to handle complex tasks when compared to manned aircraft.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Hamilton, Tracy Brown. All About Spacecraft. Encyclopaedia Britannica, 2016.
[1]Van Pelt, Michel. Space Invaders: How Robotic Spacecraft Explore the Solar System. Springer Science and Business Media, 2010.
[2]Impey, Chris, and Holly Henry. Dreams of Other Worlds: The Amazing Story of Unmanned Space Exploration - Revised and Updated Edition. Princeton University Press, 2016.
[3]Slakey, F., and P. D. Spudis. “Robots Vs. Humans: Who Should Explore Space?” Scientific American Reports, vol. 18, no. 1, Springer Nature, Feb. 2008, pp. 26–33. https://doi.org/10.1038/scientificamerican0208-26sp.
[4]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAFIoNcx2po-astronaut-man-in-a-space-suit-and-a-lunar-rover-exploring-the-su/
[5]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAEx3ESYKts-rocket-lift-off-space-shuttle-with-smoke-and-blast-takes-off-in/
