Difference Between ZTNA and VPN
ZTNA is a relatively new IT security solution technology that is quickly becoming a growing trend in the cyber security space, replacing the good old VPNs as a more secure way to provide remote connectivity. No wonder enterprises today are looking to adopt ZTNA, as they migrate to multiple cloud providers for redundancy and portability. In the era of cloud computing, ZTNA vendors offer a secure and more effective remote access model than the legacy VPN. Both are undoubtedly great security solutions, but the question is which one is right for you?

ZTNA
Zero Trust Network Access, or ZTNA, is a security strategy based on an adaptive trust model, where trust is never implicit. ZTNA is a set of technologies that adhere to the philosophy that no one inside or outside of the network can be trusted unless they are authenticated and their identification is validated. It is based on the assumption that everyone is compromised and everyone must be verified. This means access to applications and resources are restricted by default. In ZTNA, trust is never assumed by default.

VPN
Virtual Private Network, or VPN, is a secure, encrypted connection over the internet that helps you stay private online. It is a type of network that imitates a private network over a public one. VPN is kind of a security model that protects your internet connection and privacy online. It does that by creating a virtual tunnel between a device and the network, restricting authorized people from eavesdropping on the network traffic. VPNs are widely used in corporate environments where remote employees need to access company’s applications, services and resources from any location at any time they want.
Difference between ZTNA and VPN
Trust
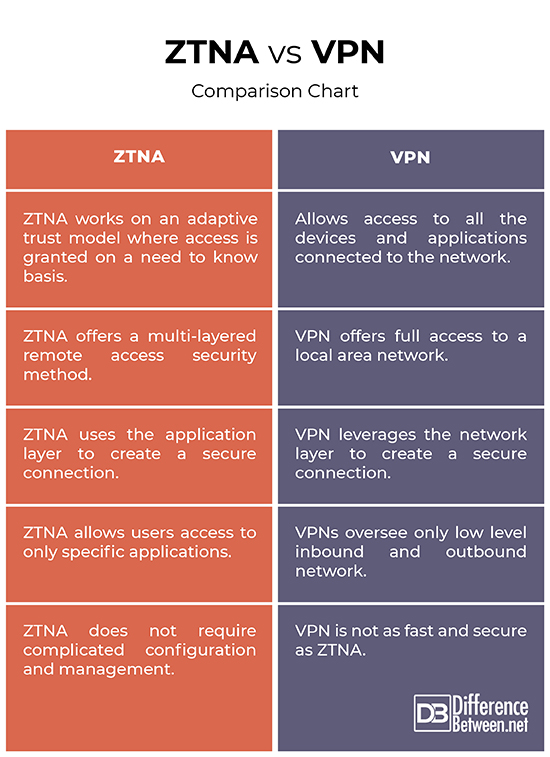
– Both the security models take very different approaches when it comes to accessing corporate applications from remote locations. VPNs work by creating a virtual tunnel between a device and an organization’s network. VPNs allow access to all the devices and applications connected to the network because it works on the assumption that every device and any user connected to the local network is trusted. ZTNA is based on the Zero Trust model so it doesn’t trust anyone.
Authentication
– It first authenticates the user and then creates a secure tunnel to applications or services that user has explicitly granted access to. Unlike VPNs which offer full access to a local area network, ZTNA offers a multi-layered remote access security method that accounts for a more robust authentication system. ZTNA makes sure external users have access to only authorized applications instead of gaining access to the network hosting these applications. Both network and application infrastructure is invisible to unauthorized users.
Access Model
– VPN leverages the network layer to create a secure connection whereas ZTNA uses the application layer to make that connection. VPNs oversee only low level inbound and outbound network. While some VPNs allow you to set rules for which parts of your network will be accessible and to whom, not very harsh security rules can be set because VPNs do not have access to the applications users have access to. ZTNA, on the other hand, allows users access to only specific applications; users do not have access to networks. ZTNA completely isolates application access from network access.
Speed
– Unlike VPNs, ZTNA does not require complicated configuration and management to provide secure, fast direct-to-cloud access to private apps. Additionally, when an organization acquires one or more businesses through mergers and acquisitions, network integration between the organization and the new companies can take years, with overlapping IP addresses. The ZTNA model simplifies this process by reducing the time needed for this effort. This results in quick business value. Another great advantage of ZTNA is that user-accessed resources do not need to be on a local network – they can be on the cloud.
ZTNA vs. VPN: Comparison Chart
Summary
Both VPN and ZTNA are great security solutions to enable remote workers to access services and applications on a corporate network. VPN is an ideal choice when it comes to small businesses because the IT infrastructure is not that robust and the VPN is quite easy to configure and manage. Unlike VPNs which offer full access to a local area network, ZTNA takes a different approach by allowing external users access to only authorized applications instead of the network hosting those applications.
How is ZTNA different from VPN?
Unlike VPNs which offer full access to a local area network, ZTNA security solution chooses not to trust anyone, allowing only access to services that users have explicitly requested.
Is ZTNA better than VPN?
ZTNA allows only trusted devices and users to access specific applications and continually authenticates devices and users. ZTNA offers a secure and more effective remote access model than the legacy VPN.
Does zero trust mean no VPN?
Unlike a traditional VPN where users can access everything once on network, zero trust means all users, whether in or outside the organization, need to be authenticated, authorized and validated before granted access to applications and resources
What is ZTNA and how does it work?
ZTNA stands for zero trust network access and is a security methodology that says you shouldn’t grant implicit access to a user, device or application, based solely around some property about them, such as network location.
Why do I need ZTNA?
ZTNA takes a different approach by allowing external users access to only authorized applications instead of the network hosting those applications. ZTNA is significantly faster than VPNs and also more secure.
What does ZTNA consist of?
ZTNA is a set of technologies that provide secure remote access to services and applications based on defined access control policies. It allows users seamless access to private applications without exposing them.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Griffin, Robert P., et al. ICCWS 2022 17th International Conference on Cyber Warfare and Security. South Oxfordshire, United Kingdom: ACI, 2022. Print
[1]Coombs, Ted. Cloud Security for Dummies. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2022. Print
[2]Devarasetty, Ravi. Zscaler Cloud Security Essentials: Discover how to Securely Embrace Cloud Efficiency, Intelligence, and Agility with Zscaler. Birmingham, United Kingdom: Packt Publishing, 2021. Print
