Difference Between Anti-Trust and Anti-Competition
Any business person will tell you they have had to deal with the competition of some level in their business. Whether it’s a shop next door with similar products, or another across the street. Either way, the businessman will have to be creative and outsmart his competitors to get and maintain his clients. A little competition is good as it can bring the best out of a service provider. But most people don’t like competition. Did you know some laws govern issues competition between markets? Antitrust and anti-competition laws are such kind. Most people do not differentiate the two. In this article, let’s explore what they are and their differences.

What is Antitrust?
Anti-trust law refers to laws that encourage competition by lowering a company’s market power. Market power refers to the ability to manipulate prices by manipulating the level of supply, demand, or both. The law ensures that companies don’t form monopolies and also breaks up the firms that have become monopolies. They are part of the state and federal laws that are designed to ensure businesses are competing fairly. Anti-trust law is sometimes called competitive law in other nations. It’s also referred to as anti-monopoly law.
It also prevents companies from coming together to form cartels that limit competition through exercises such as price-fixing. It’s a distinct legal law specialization. Those who support these laws argue that competition gives consumers lower prices, higher quality products, and greater innovation.
There are three anti-trust laws namely, the Sherman Act of 1890, the Federal Trade Commission Act, and the Clayton Act both of 1914. The laws are enforced by the Federal Trade Commission and the US Department of Justice and there are penalties for breaking the laws.
Characteristics of Anti-trust Laws
- Market allocation- Market allocation is an agreement by two companies to keep off each other’s geographical location or confined to certain customers. This is referred to as regional monopoly and is prohibited under the anti-trust laws.
- Bid Rigging- This refers to an illegal practice whereby two or more parties conspire to choose who will win or lose a contract. The losing parties purposely make lower bids to allow the winner to succeed in getting the deal. This is a law offense in the US and comes with fines including jail.
- Price fixing- Price fixing happens when the price of a product or service is determined by a business other than letting the market forces determine it naturally. Its also prohibited in the anti-trust law.
- Monopolies- Monopoly refers to dominating an industry by one company while cutting out competition.
- This also is prohibited in the anti-trust law.
- Mergers and Acquisitions- Mergers and acquisitions have to be checked by the FTC to ensure they are not introducing monopoly into the market.

What is Anti-competition?
Anti-competition Laws are laws that have been put in place to stop and prevent unfair business practices that reduce competition and lead to higher prices, reduce quality or bring less innovation. Anti-competition practices include price-fixing, group boycotts, exclusive dealing contracts, or trade association rules.
They are generally classified into two:
- Agreements between competitors
- Monopolization
The competitive law of 1998, the law aims to promote healthy competition and ban anti-competitive practices. Therefore, anticompetitive practices are prohibited by the law.
Characteristics of anti-competition laws
- Anti-competitive conduct- They allow practices, contracts, agreements, that enhance the lessening of competition in the market
- Collective bargaining and boycotts- It’s unlawful to fix prices, restrict outputs, or allocate customers, suppliers, or territories. When the public is bound to benefit though, some exceptions from legal action can be made.
- Exclusive dealing- This happens when a person trading with another imposes restrictions on the other person’s freedom on whom to choose from or in what they deal.
Similarities between Anti-trust and Anti-competitive laws
- Both laws address matters of regulation of competition in the market.
Differences between Anti-trust and Anti-competition Laws
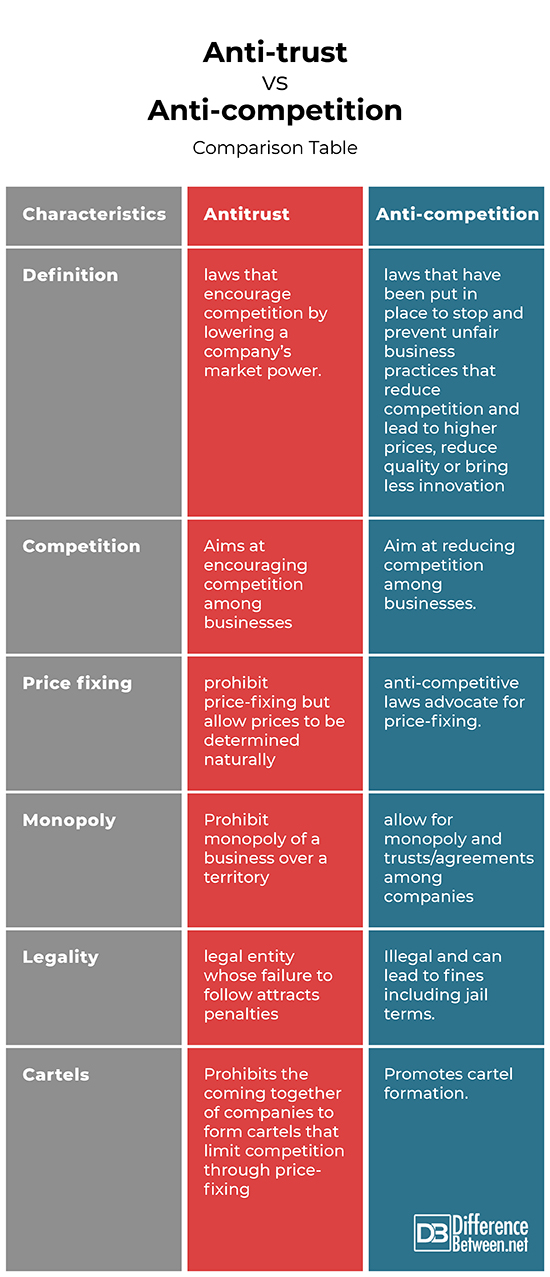
Definition
Anti-trust law refers to laws that encourage competition by lowering a company’s market power. Anti-competition Laws are laws that stop and prevent unfair business practices that reduce competition and lead to higher prices, reduce quality or bring less innovation
Competition
Antitrust laws aim at encouraging competition among businesses, while Anti-competitive laws aim at reducing competition among businesses.
Price fixing
Antitrust laws prohibit price-fixing but allow prices to be determined naturally while anti-competitive laws advocate for price-fixing.
Monopoly
Antitrust laws prohibit the monopoly of a business over territory while anti-competitive laws allow for monopoly and trusts/agreements among companies.
Legality
Antitrust laws are legal entities whose failure to follow attracts penalties, while anti-competitive laws are illegal and can lead to fines including jail terms.
Cartels
Antitrust prohibits the coming together of companies to form cartels that limit competition through price-fixing while anti-competition laws allow cartels to be formed.
Anti-trust vs. Anti-competition: Comparison Table
Antitrust vs. Anti-competition: Conclusion
Now you know the difference between the antitrust and anti-competitive laws. Antitrust encourages competition by lowering the market power and prohibiting trust agreements between companies while anti-competitive laws aim at lowering competition by encouraging trust agreements between companies which leads to monopoly, price-fixing, and cartel formation. As a business person, it’s important to know who you are engaging with so you don’t find yourself entangled in a legal case.
Antitrust vs. Anti-competition: FAQS
What is the difference between antitrust and anti-monopoly?
Anti-trust law refers to laws that encourage competition by lowering a company’s market power. Monopoly refers to dominating an industry by one company while cutting out competition. It’s one of the prohibitions in the antitrust law.
Do antitrust laws protect competition?
Yes.
Is antitrust the same as anti-competitive?
No.
Why is competition law called antitrust?
It prohibits the formation of trusts/agreements between parties. This in turn reduces competition by allowing monopoly and price-fixing among other practices.
What is another word for antitrust?
Competitive Law.
- Difference Between Profit Center and Investment Center - July 2, 2022
- Difference Between Anti-Trust and Anti-Competition - June 6, 2022
- Difference Between Stocktaking and Stock Control - June 6, 2022
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Ariel Ezrachi. Competition and Antitrust Law: a Very Short Introduction. Oxford University Press, 2021. https://books.google.co.ke/books?id=N7o0EAAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover&dq=Difference+between+Anti-trust+and+Anti-competition&hl=en&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjA3czjjbf3AhWH4IUKHR_iAKUQ6AF6BAgEEAI#v=onepage&q=Difference%20between%20Anti-trust%20and%20Anti-competition&f=false
[1]Maher M. Dabbah. The Internationalisation of Antitrust Policy. Cambridge University Press, 2003. https://books.google.co.ke/books?id=cF1LQAUfUFEC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Difference+between+Anti-trust+and+Anti-competition&hl=en&sa=X&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=Difference%20between%20Anti-trust%20and%20Anti-competition&f=false
[2]Marcus Glader. Innovation Markets and Competition Analysis: EU Competition Law and US Antitrust Law. Edward Elgar Publishing, 2006. https://books.google.co.ke/books?id=TsCczKArfcsC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Difference+between+Anti-trust+and+Anti-competition&hl=en&sa=X&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=Difference%20between%20Anti-trust%20and%20Anti-competition&f=false
