Difference Between Gross Profit and Gross Margin
Gross profit and gross margin are terms used to reflect what a company earns after selling goods and services.
What is Gross Profit?
Gross profit refers to the amount of money that remains after the cost of goods sold has been deducted from the sales revenue.
The cost of goods sold is the amount that is directly related to the products and services which are produced and sold by an enterprise. The amount remaining after deducting direct cost is used in catering for other expenses that are involved in the operations of the company.
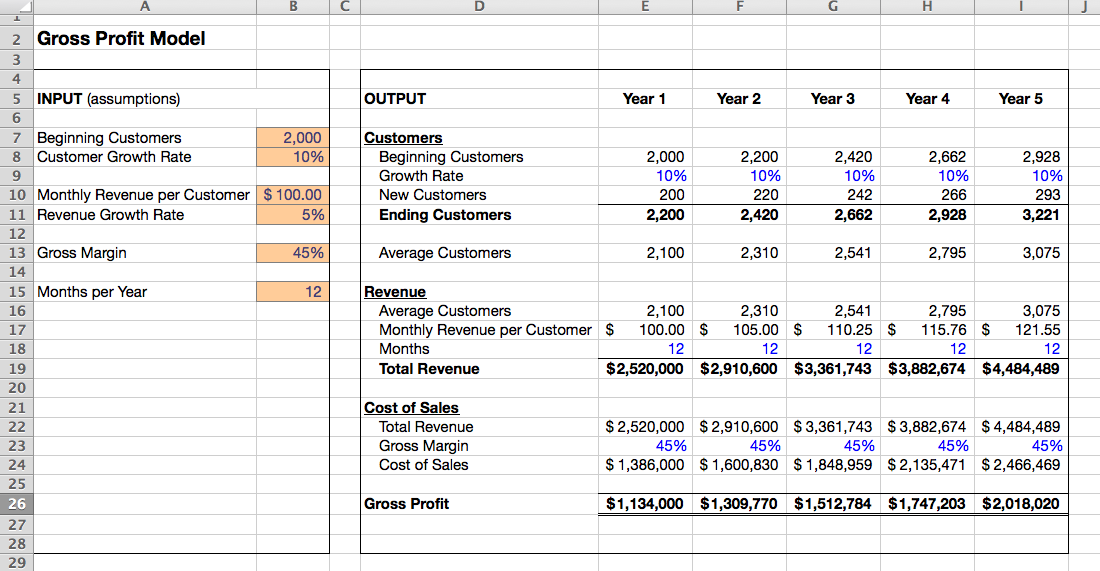
Gross Profit=Net Sales-Cost of Goods Sold
What is Gross Margin?
The term gross margin, sometimes referred to as gross profit margin, is the percentage of the total sales that is retained by the organization after all costs and expenses related with production and selling of goods and services have been deducted.
Gross profit margin mostly focuses on determining the amount of money the company retains regarding profits after selling goods and services worth $1.
Gross Margin=Total Sales Revenue-(Cost of Goods Sold/Total Sales Revenue)
Difference Between Gross Profit and Gross Margin
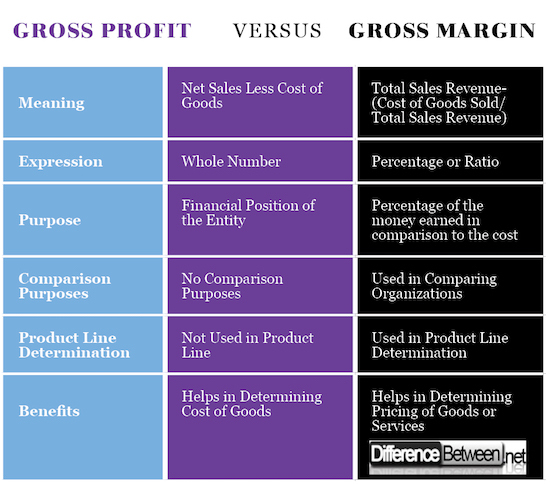
Meaning of Gross Profit and Margin
One of the main difference between gross profit and gross profit margin arises in the meaning of the two terms, which are highly applied when it comes to determining the earnings of the organization after selling company goods and services.
Gross profit represents the amount that the company saves after deducting the cost of goods from the sales revenues of the company. The cost of goods is the amount that is directly related to the production of products in the company.
On the other hand, the gross profit margin is used to refer to the amount that remains after deducting all the costs associated with production and sale of goods and services. It is important to highlight that gross profit margin is expressed in percentage terms.
Expression of Gross Profit and Gross Margin
Both gross margin and gross profits are expressed differently which means that one of the aspects is illustrated as a whole number while the other measurement is expressed regarding percentage or ratio.
Gross profit is expressed regarding dollars or pounds depending on the currency the company is suing in preparing its financial statements. It represents the amount retained after subtracting the cost of goods from sales revenues.
On the other hand, the gross profit margin is expressed regarding percentage or ratios. This is because the amount represented the percentage of the total sales that is retained by the organization after all costs related to production and sales of goods are deducted.
Purpose of Gross Profit and Gross Margin
Gross profit and gross profit margin are used in the statement of financial position to demonstrate how the companies have been performing regarding benefits acquired after sales.
Gross profit is used in the financial statement to show the financial position of the organization as a whole. The amount is realized after deducting all the expenses related to the production of goods and services.
Gross margin shows the percentage of the money earned in comparison to the costs that were incurred. Therefore, the more the gross margin, the higher the capacity of converting much of its sales into profits.
Comparison Purposes
Organizations in the same industry are involved in constant competition with each company focusing on increasing its market share by outdoing other organizations in the same industry so that it can grow its profits.
Therefore, gross margin is highly used in determining which company is operating efficiently in that industry which means that the company is earning more profits as compared to other organizations in the same industry.
Gross margin profits record the amount retained when an organization makes $1 sales. The more the gross margin, the more the efficiency of the company. Therefore, gross margin is highly used to perform industrial benchmarks.
Product Line Determination
Organizations produce several products or services which enables the companies to determine whether the product has been profitable or not. Gross margin helps in identifying and calculating the gross profit margins for each product line.
Calculating the gross margin for each product line or service line helps the company in determining the profitability information for each product.
However, it is difficult to determine the gross profit for each product line or service line, which means that gross profit, does not offer much information when it comes to deciding profitable products.
Benefits of Gross Profit and Gross Margin
Gross profits and gross margin offer specific benefits to the owners of the organization with the ultimate goal of helping them to manage the company in the most efficient method.
Analysis of gross profits helps the company owners to determine the direct costs involved in the sale of goods and services. To increase profits, the owners of the company introduce measures to ensure that they reduce the cost of goods.
On the other hand, gross profit margin benefits the owners of the company in ensuring that the owners use the margin analysis as a measurement technique to ensure the pricing of goods is favorable to all customers while at the same time providing that company achieve its targets.
Difference Between Gross Profit and Gross Margin: Chart
Summary Gross Profit vs. Gross Margin
- Gross profit and gross margin are terms used in the organization to express the income earned by the company after selling goods or services.
- Gross profits are the amount that is retained after the cost of goods, expenses directly involved in the production of products is deducted from the sales revenue.
- Gross margin is the percentage expression of the amount earned after deducting all the costs involved in production and sale of goods or services in the company.
- Other differences between gross profit and gross margin include purpose, benefits, comparison purposes, and product line determination among other factors.
- Difference Between Gross NPA and Net NPA - April 20, 2018
- Difference Between Job Description and Job Specification - April 13, 2018
- Difference Between Yoga and Power Yoga - April 10, 2018
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Bain, Joe S. "Relation of the profit rate to industry concentration: American manufacturing, 1936–1940." The Quarterly Journal of Economics 65.3 (1951): 293-324
[1]Kesavan, Saravanan, Vishal Gaur, and Ananth Raman. "Do inventory and gross margin data improve sales forecasts for US public retailers?" Management Science 56.9 (2010): 1519-1533.
[2]Kwon, Ohio on, and Hongchul Lee. "Calculation methodology for contributive managerial effect by OEE as a result of TPM activities." Journal of Quality in Maintenance Engineering 10.4 (2004): 263-272.
[3]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Simple_Financial_Model.png#/media/File:Simple_Financial_Model.png
[4]Image credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/sampjb/7690683730