Difference Between CNG And LPG
Using an alternate fuel is the most effective technique to lower carbon emissions in modern transportation. Natural gas and propane are two of the most popular alternative fuels now in use. The environmental benefits of automobiles fuelled by alternative fuels are well-known.
CNG and LPG differ primarily in the following ways:

CNG
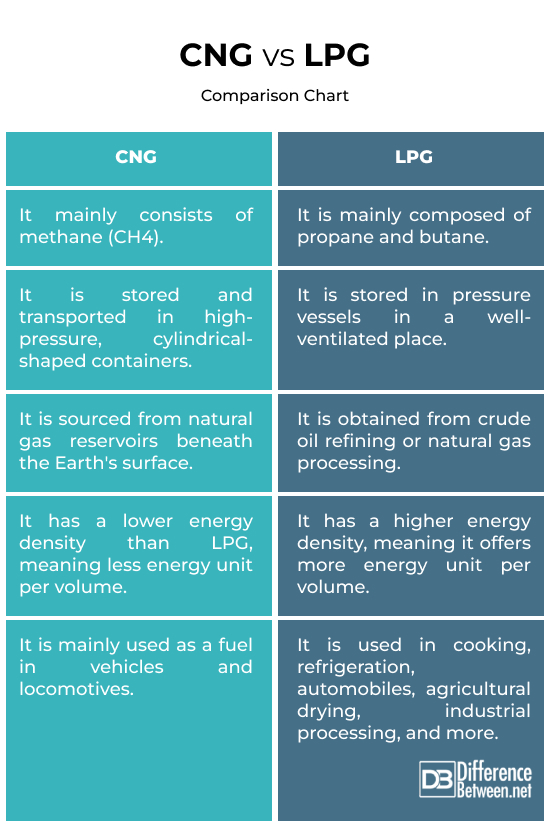
An eco-friendly substitute for fossil fuels like diesel and gasoline is compressed natural gas, more often known as CNG. It comes from natural gas reservoirs and is made of methane (CH4).
It burns more cleanly than conventional gasoline and diesel, releasing less harmful gases including nitrogen oxides (NOx) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Compressed natural gas (CNG) is made by reducing the volume of natural gas to less than 1% at atmospheric pressure. If you’re an individual or a fleet operator looking to cut expenses and emissions, this is a fantastic option to consider.

LPG
The adaptable alternative fuel known as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) is mostly butane (C4H10) and propane (C3H8). Refining crude oil and extracting natural gas are the sources of this material. The safety of storing and transporting LPG is ensured by compressing it into a liquid state under pressure.
It has several uses, including in the kitchen, the fridge, industrial operations, and even cars. Compared to conventional fuels like gasoline or diesel, LPG is better for the environment.
When compared to traditional fuels, LPG is a greener and more environmentally friendly energy choice.
Difference between CNG and LPG
Composition
The principal component of natural gas and the simplest hydrocarbon, methane (CH4), is the main component of compressed natural gas. Different from propane (C3H8), butane (C4H10) is the main ingredient in LPG. Their molecular structures are slightly larger than methane’s, and they are hydrocarbons.
State of Matter
Cylindrical containers designed for high-pressure storage and transportation are used for CNG. Materials such as steel, aluminum, or composites are used to construct these containers. The liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) is kept in sealed containers in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, far from any potential fire hazards. Safe transportation and storage of small amounts is made possible by converting to a liquid state by applying modest pressure.
Storage Volume
Because CNG must be stored at high pressure to keep it compressed, bigger storage volumes are required. However, because LPG is maintained in a liquid state under moderate pressure, it can be more compactly stored, resulting in reduced storage volumes.
Source
Compressed natural gas (CNG) comes from underground gas reserves. Oil wells, bed methane wells, and natural gas wells are the usual places to find them. Nonetheless, there are primarily two places where LPG is sourced. The refining of crude oil or the processing of natural gas are two sources. The methods involve separating the basic ingredients from propane and butane.
Applications
Compressed natural gas vehicles, or CNGVs, are a kind of alternative fuel vehicle. It helps save money and cuts down on carbon emissions as compared to regular fuels. Conversely, liquid propane gas (LPG) has a wide range of industrial uses and is utilized in many different contexts, including transportation, heating, cooking, drying crops, melting metal, and powder coating.
CNG vs. LPG: Comparison Chart
Summary
Compared to more conventional fossil fuels, compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquid propane gas (LPG) are far better for the environment. Compared to LPG, CNG is lighter. For this reason, LPG finds utility in many different settings, including homes, businesses, and factories. However, compressed natural gas has few uses outside of its primary function as a motor fuel.
FAQs
Which is better fuel, LPG or CNG?
LPG is commonly used for cooking, heating, and cars, however compressed natural gas (CNG) is more commonly utilized in vehicles because it produces fewer emissions. Therefore, LPG is more adaptable and has many potential uses. But which fuel is best dependent on the job.
What is the difference between CNG, LPG, and LNG?
Different from CNG, LPG is a liquid at moderate pressure, and LNG is a liquid that has been super-cooled. Different features and purposes give rise to different applications for each.
Are natural gas and CNG the same?
Natural gas is a broader term that includes various gases found naturally, while CNG specifically refers to compressed natural gas, which is mainly composed of methane.
Is CNG highly flammable?
CNG is less likely to auto-ignite because it is lighter than air and disperses quickly in the atmosphere, which reduces the risk of accumulation.
Why LNG is not used for cooking?
LNG is not typically used for cooking due to the need for specialized storage and handling equipment. Rather, it’s more suitable for large-scale industrial and transportation applications.
Why use LNG instead of LPG?
LNG is often preferred for long-distance transportation due to its higher energy density and lower storage volume. LPG, being versatile, is used in cooking, heating, and smaller-scale transportation.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
8 Comments
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Biernat, Krzysztof. Alternative Fuels: Technical and Environmental Conditions. IntechOpen, 2016.
[1]Subic, Aleksandar, et al. Sustainable Automotive Technologies 2012: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference. Springer, 2012.
[2]Durbin, Enoch. Methane: Fuel for the Future. Springer, 2012.
[3]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAEb_iHPd_M-cilinder-with-mixed-gases-tanks-with-compressed-gas-for-industry-liquefied-oxygen-production-factory/
[4]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MADWKXJIzdM-multi-colored-and-different-sized-gas-cylinders-on-the-street-bottles-with-liquefied-petroleum-gas/

its very interesting to know about CNG & LPG ,also their classification
It is very good information and explanation. 🙂
Impressed.
Hi in maharashtra the availability of cng is in mumbai and pune so i jst wanna know when should it will be available in rest of maharashtra cities like karad,satara,kolhapur,ratnagiri,nashik,goa…………..
Very soon
it’s good.
Give some more information
It is very interesting fact about LPG &CNG. It helps to make pollution free india…
Thanks for your superb information
It is very important for fresher engineering student.