Difference Between Antihistamine and Decongestant
An antihistamine is a medicine that blocks the effects of histamine in the body. A decongestant is a medicine that causes blood vessels to become narrower.
What is Antihistamine?
Definition:
An antihistamine is a medication that has been synthesized to reduce the effects of the chemical called histamine, which is produced by immune system cells known as mast cells.
Mode of action:
The way an antihistamine works is that it stops histamine from binding at the cell receptor sites on the cell membrane. The H1 receptor antagonist antihistamines compete with the histamine by occupying the receptors. The H2 receptor antagonists work on receptors found on the parietal cells of the stomach, it blocks these receptors. The histamine is responsible for the symptoms people experience when they have an allergic response. The H2 medicine works because it blocks the histamine which actually causes increased secretion of acid in the stomach.
Uses:
The H1 antihistamines treat conditions of hay fever in which people have an allergic response with symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes. The H2 antihistamines reduce acid secretion in the stomach and so are used to treat conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and stomach or duodenal ulcers.
Side effects from Antihistamine:
H1 antihistamines have the side effect of making you sleepy which can make driving or operating machinery dangerous if you are taking them. The H2 antihistamines may also make you sleepy and in some people, it can cause headaches or diarrhea, and it can interfere with some of the androgen hormones in the body. Blurred vision and dry mouth may be a side effect of some of the antihistamines.
Examples:
Examples of H1 receptor antagonists include diphenhydramine, chlorpheniramine, loratidine, and promethazine. An example of an H2 antagonist is the medication cimetidine.
What is Decongestant?
Definition:
A decongestant is a medication that was developed to shrink the mucous membranes in the nasal cavity by causing vasoconstriction of the blood vessels.
Mode of action for Decongestant:
The decongestant medicines work by decreasing the blood flow to the mucous membranes of the nose. This is achieved by the medicine influencing the alpha-adrenergic receptors (often by binding to them), which then impacts the muscles found in the middle layer of the arterioles and venules. The muscle contraction decreases the amount of blood flowing into capillary beds which results in reduced inflammation of the tissues. Inflammation occurs when immune system cells and their secretions rush to an area that is affected. Thus, decreasing the blood flow decreases the overall immune response and hence the reaction. These drugs are often powerful vasoconstrictors which help alleviate the symptoms related to inflammation, including the swelling of the mucous membranes and the overproduction of mucus in the respiratory passages.
Uses:
Decongestants help by reducing secretions in the nose which tends to occur when a person has a cold or bad allergic response in which there is excessive inflammation resulting in too much mucus being produced from the nasal mucosa. Epinephrine is used for anaphylaxis, which is a severe life-threatening allergic response.
Side effects:
Some of the decongestants are more dangerous than others because they strongly stimulate the sympathetic nervous system. This can cause a rapid heart rate and a dangerous rise in blood pressure. This is why ephedrine is less common today than pseudoephedrine which has less severe side effects. Most have side effects such as increased heart rate and blood pressure. They can cause insomnia and anxiety. Headaches, heart palpitations, and dizziness can also be side effects.
Examples:
Examples of decongestants include epinephrine and ephedrine, but these can cause great anxiety because they stimulate the nervous system. The epinephrine is very strong and so is only used in particular situations such as anaphylaxis. Other examples that are more commonly used to treat colds include pseudoephedrine and phenylephrine.
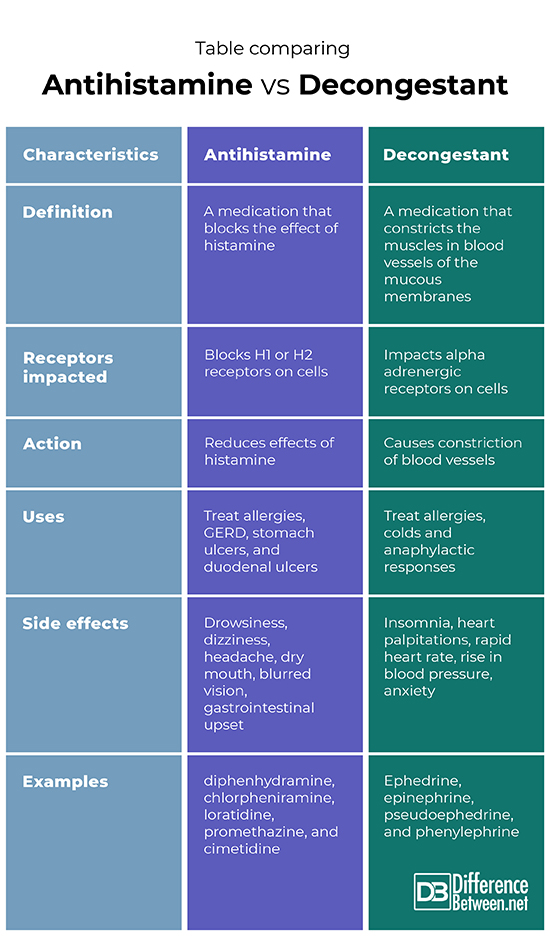
Difference between Antihistamine and Decongestant
Definition
An antihistamine is a medicine that stops histamine from working. A decongestant is a medicine that causes constriction of blood vessels of the mucous membranes.
Receptors impacted
Antihistamines either block H1 cell receptors or they block H2 cell receptors. Decongestants impact the alpha-adrenergic cell receptors.
Action
The antihistamines reduce the effects of histamine on the body. Decongestants cause constriction of the muscles in blood vessels.
Uses
Antihistamine medications are used to treat allergies, and some types are used to treat GERD, ulcers of the stomach, and duodenum. Decongestants are used to treat allergies, colds, and anaphylactic reactions.
Side effects
The side effects of antihistamines include drowsiness, dizziness, headache, dry mouth, blurred vision, and gastrointestinal upset. The side effects of decongestants include Insomnia, heart palpitations, rapid heart rate, rise in blood pressure, and anxiety.
Examples
Examples of antihistamine medications include diphenhydramine, chlorpheniramine, loratidine, promethazine, and cimetidine. Examples of decongestant medications include ephedrine, epinephrine, pseudoephedrine, and phenylephrine.
Table comparing Antihistamine vs. Decongestant
Summary of Antihistamine Vs. Decongestant
- Antihistamines and decongestants are both types of medicine that can be used to treat allergic responses.
- Antihistamines target the histamine that is a chemical which is released by the mast cells of the immune system.
- Decongestants work by targeting the muscle in the blood vessels found near the mucous membranes that are affected by colds and allergies.
- Both decongestant and antihistamine medications treat the symptoms which result from the immune system reacting to a perceived threat and causing an inflammatory response.
- Both antihistamines and decongestants have side effects that a person needs to be aware of when taking these medications.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Church, Martin K., and Diana S. Church. "Pharmacology of antihistamines." Indian journal of dermatology 58.3 (2013): 219.
[1]Image credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/shardayyy/5551457461
[2]Image credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/comedynose/7184518521