Difference Between Neuromodulator Injections and Botox
Neuromodulators are generally chemicals like dopamine, acetylcholine, serotonin, histamine, nitric oxide, norepinephrine and a number of neuropeptides and even include cannabinoids (D. A. Fortin and Levine) as well as the hormones testosterone, vasopressin and oxytocin (Molly J. Crockett and Fehr) that are found in the body and act together with neurotransmitters to excite or inhibit receptor responses. Botox, short for botulinum toxin, is also a neuromodulator, but unlike chemical and hormonal neuromodulators, it is a protein produced by one of the most potent neurotoxins on earth (S Košenina et al.) that causes botulism, a type of life-threatening food poisoning when ingested (MedlinePlus).
Function of Neuromodulators
Neuromodulators potentiate or inhibit the transmission of nerve impulses but are not themselves a means of transmission (Meriam-Webster). Neuromodulation occurs when a given neuron uses chemicals or hormones for the regulation of diverse populations of neurons to bind and initiate a messenger that signals for a cascade to produce a long-lasting signal or inhibit that signal.
Neuromodulators alter synaptic communication by targeting synapses directly or changing neurons’ excitability in the short term or regulation in the long term, and multiple neuromodulators act simultaneously on a neuron in a complex process that involves multiple antagonistic or synergistic pathways (Farzan Nadim and Bucher).
How Botox works
Botox is the trade or brand name of a neuromodulator that can injected for cosmetic or medical treatment reasons. So, while Botox would be life threatening if ingested, when injected under the skin in minute quantities by a qualified medical practitioner, Botox causes flaccid paralysis (D. P. Figgitt and Noble): It inhibits or prevents a muscle from moving temporarily (Mayo Clinic). It is most commonly known for its ability to reduce the appearance of wrinkles, but it is also used to treat excessive sweating, neck spasms, a lazy eye, and bladder dysfunction as well as prevent chronic migraines. When injected, Botox blocks chemical signals from nerves that control the muscles (Cleveland Clinic).
The most common use for Botox is to relax the facial muscles causing wrinkles around the eyes and on the forehead. In cosmetic applications, Botox is regarded as relatively safe and effective (Bagus Komang Satriyasa). In 2018, botulinum toxin injections were the most commonly performed cosmetic operation, and some 7.4 million procedures were performed in the United States (New Plastic Surgery Statistics), and in 2019, 6,271,488 Botulinum Toxin procedures were performed worldwide (“Botulinum Toxin Market”). Injections, generally done by qualified medical practitioner, take between one and three days to work and the effect may last three months or longer (Mayo Clinic).
Side-Effects and Complications
While relatively safe when injected by a qualified doctor, complications such as pain and swelling at the injection site, flu-like symptoms, droopy eyelids, a crooked smile, drooling, and eye dryness or tearing may occur, and in rare instances, more widespread muscle weakness, vision problems, trouble speaking or swallowing and breathing (Mayo Clinic) especially if injected into the wrong muscle group or the toxin spreads from the injection site (P. K. Nigam & Nigam).
While the repeated cosmetic use of Botox is also safe, the long-lasting cosmetic use of Botox can result in permanent changes in facial expression; the person’s face can become expressionless and mask-like (Henryk Witmanowski & Błochowiak). Those breast-feeding or pregnant or with allergies to dairy products are advised to avoid Botox (Mayo Clinic).
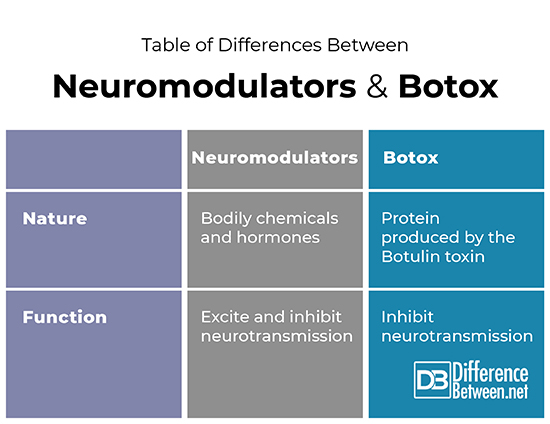
Table of differences between neuromodulators and Botox
Summary
While neuromodulator and Botox injections have the ability to inhibit neurotransmission in common, Boxtox is a toxin rather than chemical or hormone and is most often injected for cosmetic reasons, but Botox can also be used treat excessive sweating, neck spasms, a lazy eye, and bladder dysfunction as well as prevent chronic migraines.
FAQ:
Is Botox a neuromodulator?
Botox is a popular cosmetic neuromodulator and the first FDA-approved botulinum toxin Type A for cosmetic use that blocks nerve receptors, thus softening and preventing lines and wrinkles from forming on the brow and around the eyes. Botox may also be used to treat excessive sweating, neck spasms, a lazy eye, and bladder dysfunction as well as prevent chronic migraines.
How long do neuromodulators last?
The effects of minute amounts of botulinum toxin, known commercially as Botox Cosmetic, typically lasts about three months. When used to treat excessive sweating, the reduction lasts as long as six months, so patients can be treated just twice a year (American Society for Dermatologic Surgery).
Is there anything better than Botox?
While Botox was the first neurotoxic injection to be approved by the FDA and for that reason is better known, Dysport, also a neurotoxin, has emerged as popular and provides many of the same benefits. Dysport can create visible results within just two days, whereas Botox takes five to seven days to produce visible effects. Jeuveau, another alternative, is a slightly different form of botulinum toxin: It contains prabotulinumtoxinA rather than onabotulinumtoxinA and is reported to have longer lasting cosmetic effects (What is Jeuveau). Still another option is Xeomin, a powerful botulinum Type A drug approved by the FDA in 2010 that targets frown lines specifically (Ife Rodney, 2021).
What is the best neuromodulator?
What is considered the best neuromodulator would depend on the purpose for which it being used. For example, Jeuveau may give longer-lasting cosmetic results than does Botox, while Dysport shows visible effects more quickly. However, some people might consider Cannabinoids the best neuromodulator for entirely different reasons, such as the treatment of nausea and vomiting induced by chemotherapy (Mellar Davis et al.).
Is 50 too late for Botox?
No upper age limit exists for Botox treatments, but it is best to start when one first notices lines on one’s face when the face is in a relaxed state. It is also FDA approved for the treatment of children over the age two who suffer from spasticity (Brian Park).
What is Botox’s competitor?
Botox has three primary competitors, Dysport, which is also FDA-approved for cosmetic use, Jeuveau, which has a longer-lasting effect, and Xeomin, which was approved for use by the FDA in 2010 and is used to soften frown lines.
- Difference Between Ecchymosis and Erythema - August 15, 2022
- Difference Between Autobiographical Memory and Episodic Memory - August 1, 2022
- Difference Between Biological Drive and Social Motive - July 30, 2022
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]American Society for Dermatologic Surgery. Neuromodulators, 2022. https://www.asds.net/skin-experts/skin-treatments/neuromodulators#:~:text=A%20minute%20amount%20of%20the,typically%20last%20about%20three%20months.
[1]“Botulinum Toxin Market”. Fortune Business Insights. Jan 2022. https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/botulinum-toxin-market-100996
[2]Cleveland Clinic. Botox (Botulinum Toxin), 2022. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/8312-botulinum-toxin-injections
[3]Crockett, Molly J, and Ernst Fehr. “Social brains on drugs: tools for neuromodulation in social neuroscience.” Social cognitive and affective neuroscience vol. 9, no. 2, 2014, pp. 250-4. https://doi.org.10.1093/scan/nst113.
[4]Davis M. et al. The emerging role of cannabinoid neuromodulators in symptom management. Support Care Cancer, Vol. 15, no. 1, Jan 2007, pp. 63-71. https://do.org.10.1007/s00520-006-0180-0.
[5]Figgitt, D. P. and S. Noble S. “Botulinum toxin B: a review of its therapeutic potential in the management of cervical dystonia.” Drugs, vol. 62, no. 4. 2002, pp. 705–722. https://doi.org.10.2165/00003495-200262040-00011.
[6]Fortin D. A. and E. S. Levine “Differential effects of endocannabinoids on glutamatergic and GABAergic inputs to layer 5 pyramidal neurons”. Cerebral Cortex, vol. 17, no. 1, 2007, pp. 163–74. https://doi.org.10.1093/cercor/bhj133.
[7]Košenina S., et al. “Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the Weissella oryzae botulinum-like toxin.” FEBS Letters, vol. 593, no. 12, June 2019, pp. 1403–1410. https://doi.org.10.1002/1873-3468.13446
[8]Mayo Clinic. Botox injections, 2 Feb 2021. htpps://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/botox/about/pac-20384658
[9]MedlinePlus. Botox. 2021. https://medlineplus.gov/botox.html
[10]Nadim, Farzan, and Dirk Bucher. “Neuromodulation of neurons and synapses.” Current opinion in neurobiology vol. 29, 2014, pp. 48‒56. https://doi.org.10.1016/j.conb.2014.05.003
[11]Merriam-Webster.com Medical Dictionary. “Neuromodulator.” Merriam-Webster, n.d. https://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/neuromodulator. Accessed 23 Apr. 2022.
[12]“New plastic surgery statistics reveal trends toward body enhancement.” Plastic Surgery. 11 March 2019. https://web.archive.org/web/20190312062815/https:/www.plasticsurgery.org/news/press-releases/new-plastic-surgery-statistics-reveal-trends-toward-body-enhancement
[13]Nigam, P. K. and A. Nigam “Botulinum toxin.” Indian Journal of Dermatology, vol. 55, no. 1, pp. 8–14. https://doi.org.10.4103/0019-5154.60343.
[14]Parks, Brian. “FDA expands use of Botox and Dysport for spasticity in pediatric patients.” MPR. 13 July 2020. https://www.empr.com/home/news/fda-expands-use-of-botox-and-dysport-for-spasticity-in-pediatric-patients/
[15]Rodney, Ife. “Botox vs Xeomin: Which should I choose?” Eternal Dematology +Aesthetics. 2021. https://eternaldermatology.com/botox-vs-xeomin/
[16]Satriyasa, Bagus Komang. “Botulinum toxin (Botox) A for reducing the appearance of facial wrinkles: a literature review of clinical use and pharmacological aspect.”. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology, vol. 12, 10 April 2019, pp. 223–228. https://doi.org.10.2147/CCID.S202919.
[17]What is Jeuveau and can it better than Botox? Faces, PLLC. 2022. https://www.facesdr.com/what-is-jeuveau-and-can-it-beat-botox/
[18]Witmanowski, Henryk and Katarzyna Błochowiak “The whole truth about botulinum toxin ‒ a review.” Postepy dermatologii i alergologii vol. 37, no. 6, 2020, pp. 853-861. https://doi.org.10.5114/ada.2019.82795
