Difference Between Bark Beetle and Termite
• Categorized under Animals,Geography,Nature,Science | Difference Between Bark Beetle and Termite
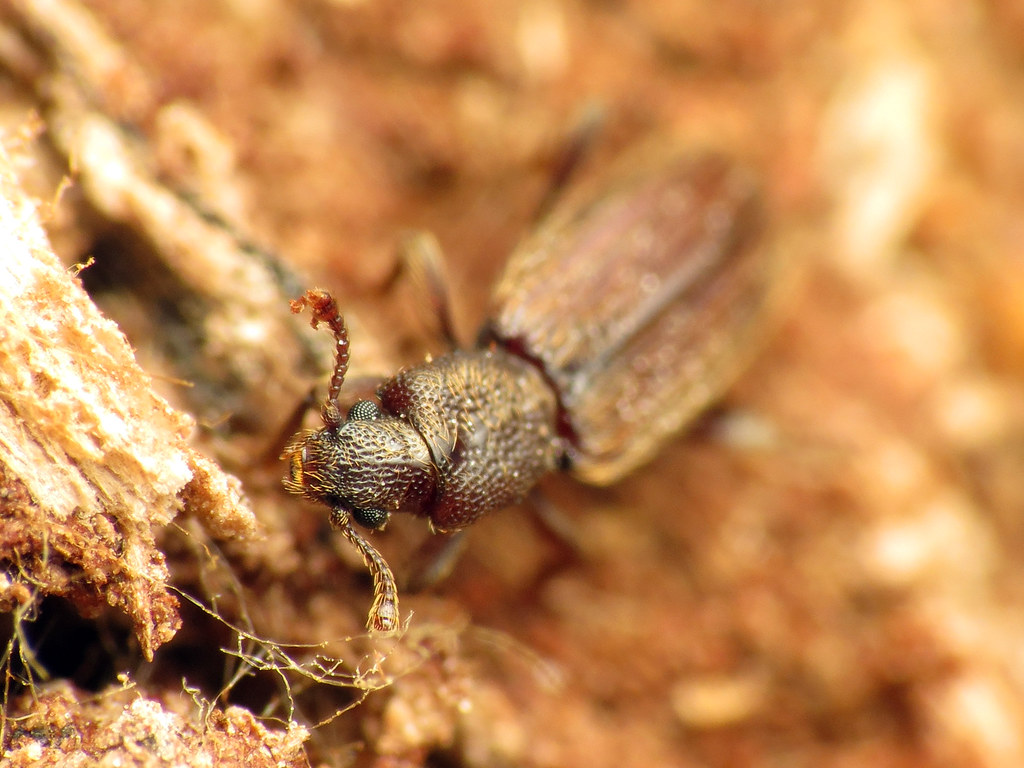
What is Bark Beetle?
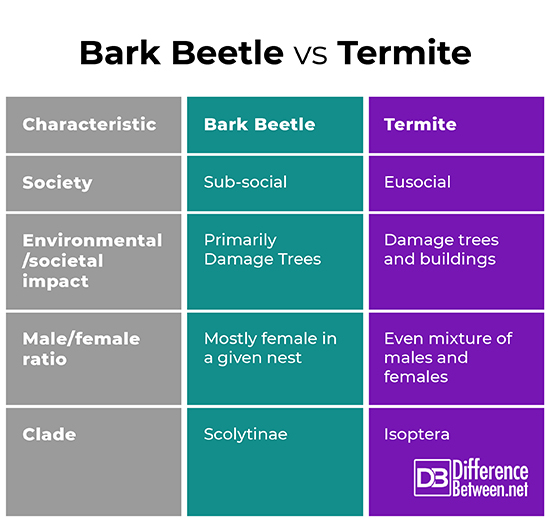
Bark beetles are insects found throughout the world. They are roughly cylinder-shaped and usually no more than 6 mm in length. Bark beetles make nests in trees. Typically, a male and several females will bore into a tree and the females will lay eggs. There can be as many as 60 females for one male.
When the eggs hatch, the larvae bore into the bark of the tree, making tunnels that are very characteristic. Once they make a tunnel, they pupate into adults and emerge from the bark. Bark beetles do not constitute one but over 2,000 species across the world. They are known for causing significant destruction to trees. This destruction has been exacerbated by recent changes in climate, especially in North America.
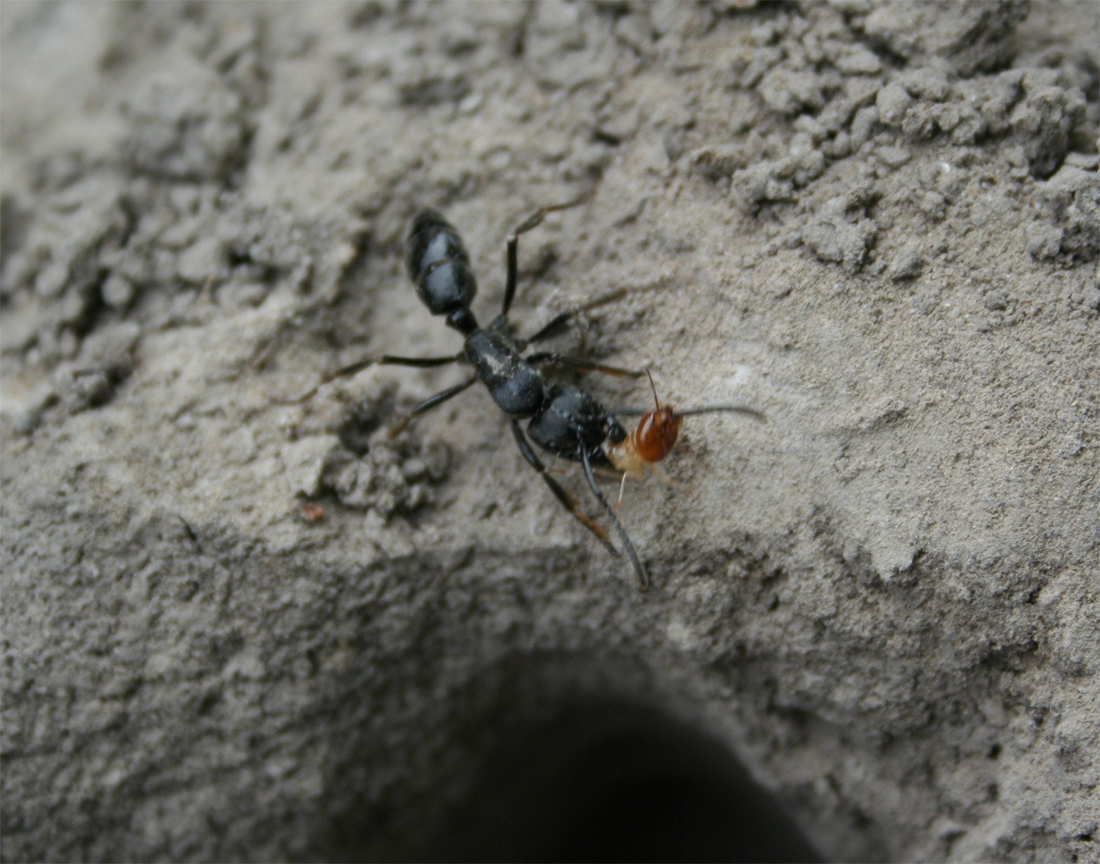
What is Termite?
Termites are social insects found all over the world. They are known for making nests in the trunks of trees and in subterranean chambers which have access to moist soil. Termites are also known for making nests within buildings made of wood and, as a result, are known for being destructive pests. At the same time, they are also very beneficial to the environment since they recycle cellulose into the ecosystem.
Distribution
Termites are generally found in climates that are warm and moist. In North America, their northernmost extant is Vancouver on the Pacific Coast. On the Atlantic Coast, their northernmost extant is Main and the eastern provinces of Canada. In Europe, they generally are not found north of France and are distributed around the Mediterranean region. In eastern Asia, they are found as far north as the islands of Japan and South Korea.
Worldwide shipping has resulted in species of termites being introduced as invasive species all over the world. Termites native to North America have been found in Vienna, Switzerland and termites native to east Asia have been found in Hawaii, California, and the American south.
Invasive species are not as adapted to the local, natural environment. As a result, they tend to take refuge in artificial structures created by humans. For this reason, the most serious pest species of termites tend to be invasive species. Although only 10% of termites are classified as pests, they still cause significant destruction to buildings, other wooden structures, and plant matter important to humans. Significant measures have been taken to curb their advance.
Society
Termites are eusocial and have a complex societal structure consisting of several castes. Each termite colony will consist of a reproductive pair, workers, soldiers, and juvenile termites known as nymphs. Nymphs are termites who have not been differentiated into a particular caste. If there is a need for more termites of one caste, nymphs will develop into workers, soldiers, or reproductives through the mediation of pheromones. Workers and soldiers are sterile, whereas reproductives are capable of reproducing and can start new colonies or replace the current reproductive pair if necessary.
Launching colonies
The reproductive caste consists of the members of the termite colony responsible for producing more termites. Because they must go outside to find a location for a new colony, they have wings which they shed after their initial flight. They also have hardened bodies and large compound eyes. When it is time to establish a new colony, reproductives will be taken to a far corner of the nest and released into the open. Although they can fly short distances, wind carries them most of the journey.
Once they land, a male and female pair up and the new couple finds a good nesting site. Once they have found a spot, they will build a nest and begin to lay eggs. As time goes on, the female’s abdomen will expand until she becomes an enormous egg laying machine capable of laying thousands of eggs per day. The king and queen will continue producing offspring to keep the colony going.
In the initial stages of the colony’s development, the king and queen will care for the young and tend the nest. Eventually, nymphs and workers will take over these roles and the king and queen will focus on reproducing.
Other castes
The soldiers will typically have either large mandibles for attacking predators or a long narrow snout which shoots chemicals to ward off attackers. Soldiers are primarily responsible for defense of the nest. Workers will have soft bodies and large mandibles for chewing. Workers are responsible for collecting food, building and maintaining the nest, and feeding all the other members of the colony.
Termite nests
Some termites build their nests in wood while other species build them in subterranean chambers. Termite mounds are a common sight in tropical regions. The termite mounds will have their own regulated microclimates with higher temperature and humidity than the surrounding environment.
Other invertebrates, such as flies or beetles, tend to also live in termite mounds because of the shelter that termite mounds provide. Some such guests are dependent on the termites for their survival and secrete substances that the termites need. Termites also raise fungus for food. In this way, termites technically practice a form of domestication.
Similarities between Bark Beetle and Termite
Bark beetles and termites are both insects known for being very destructive to natural and artificial wooden structures.
Differences between Bark Beetle and Termite
Although there are similarities between the bark beetle and the termite, there are also notable differences. These differences include the following.
- Bark beetles do not appear to live in structured societies, whereas termites live in highly structured eusocial hives or colonies.
- Bark beetles are most known for damaging trees, whereas termites are most notorious for the damage that they cause to buildings and other artificial wooden structures.
- Bark beetles appear to be mostly female with an average nest starting out with as many as 60 females to 1 male, whereas termites tend to have a more even sex distribution.
- Bark beetles and termites descend from very different evolutionary lineages.
Bark Beetle vs. Termite
Summary of Bark Beetle vs. Termite
Bark beetles are insects that are known to eat bark matter. They make nests in trees and lay eggs. When the eggs hatch, the larvae bore through the trees. Bark beetle nests can start out with as many as 60 females for 1 male. They are known for causing destruction to trees worldwide. Termites are social insects that live in nests in trees or in subterranean chambers. They have colonies or hives consisting of multiple casts, usually reproductive, worker, soldier, and nymph castes. Termites are very beneficial to the environment because they break down and recycle cellulose structures. They are also known for being destructive because they also cause damage to wooden structures and plant matter that is important to humans. Bark beetles and termites are similar in that they are both insects that are known to live in wood and cause destruction to wooden structures both natural and artificial. They are different however in that termites are eusocial, have an even male/female ratio, and mainly damage buildings. Bark beetles, on the other hand, are more known for the damage they cause to trees and they do not live in societies in the same way that termites live in societies. They also appear to be mostly female. Termites and bark beetles also belong to rather different evolutionary lineages.
Caleb Strom has a B.SC. in earth science from the University of California San Diego and is currently a graduate student in geological sciences at California State Polytechnic University Pomona. He has done scientific research in planetary science at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography and astrophysics at the Center for Astrophysics and Space Science at UC San Diego.Caleb Strom has a B.Sc in Earth Sciences from the University of California San Diego and He is currently a graduate student working on an M.Sc. in geological sciences from California State Polytechnic University, Pomona. His master’s research is in planetary science and he has participated in published research related to cosmochemistry while working at the Scripps Isotope Geochemistry Laboratory. He also has experience with archaeological surveying, excavation, and collections. His skills include satellite remote sensing, geologic mapping, archaeological excavation and surveying, and mass spectroscopy.
Caleb has also published popular articles for magazines related to geology, astronomy, archaeology, anthropology, and history.
- Difference Between Environmental Performance Index and Development - November 24, 2023
- Difference Between Environmental Intervention and Development - November 8, 2023
- Difference Between Eco Efficiency and Eco Effectiveness - September 18, 2023
Sharing is caring!
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Cite
APA 7
Strom, C. (2020, May 1). Difference Between Bark Beetle and Termite. Difference Between Similar Terms and Objects. http://www.differencebetween.net/science/difference-between-bark-beetle-and-termite/.
MLA 8
Strom, Caleb. "Difference Between Bark Beetle and Termite." Difference Between Similar Terms and Objects, 1 May, 2020, http://www.differencebetween.net/science/difference-between-bark-beetle-and-termite/.
Leave a Response
Written by : Caleb Strom. and updated on 2020, May 1
References :
[0]Image credit: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Matebele_ant%2Btermite.jpg
[1]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/7891/47453653622_1b5bf4db33_b.jpg
[2]Morris, Jesse L., et al. "Bark beetles as agents of change in social–ecological systems." Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 16.S1 (2018): S34-S43. https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/fee.1754
[3]The Editors of Encyclopedia Britannica. “Bark Beetle.” Encyclopedia Britannica. Encyclopedia Britannica, Inc. 2017. https://www.britannica.com/animal/bark-beetle
See more about : Bark Beetle, Termite