Difference Between Cytoplasm and Protoplasm
Introduction
Cellular biology studies how the many components that keep life going at the cellular level interact with each other. The cytoplasm and protoplasm are the most important. They play very important roles in the cell. The goal of this article is to explain and simplify the roles and features of both cytoplasm and protoplasm in order to show how important they are to the activities inside cells and to life itself. Through a comparison and analysis of these two parts in great depth, we hope to clarify what makes them different and how they may be similar, which will help you better understand how they play a key role in cell structure and function.
What is Cytoplasm?
Definition
Cytoplasm is a gel-like material that can be found in both animal and plant cells and functions as a medium for cellular components.
Role and Function in the Cell
The cytoplasm plays a crucial role in cell integrity and activity and have the following functions:
- Medium for essential metabolic activities Containing organelles.
- Transports substances.
- Removes waste.
- Transduces signals.
- Promotes intracellular communication and coordination.
Key Components of Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm contains several complex components, including
The cytosol: is mostly water yet rich in proteins, ions, and chemicals, supports organelles.
Organelles: Individual cell structures called organelles fulfill particular roles. Ribosomes, mitochondria, and the endoplasmic reticulum are examples.
The cytoskeleton: supports cell movement, division, and shape.
What is Protoplasm?
Definition
Protoplasm is known as the living material inside the cell. It encompassing all cellular components and it’s the fundamental substance of life because it hosts the vital functions and structure.
Significance and Role in Cellular Activities
The role that protoplasm plays inside the cell is indispensable:
- It acts as the arena for essential biological processes like protein synthesis and energy production.
- Protoplasm facilitates cellular functions like:
Growth, Division, Adaptation and other cellular activities from movement to communication.
Composition of Protoplasm
Most of the protoplasm is made up of:
Water is a solvent that helps molecules move and cellular processes happen.
Proteins: Cells, tissues, and organs are built, work, and are managed by proteins.
Lipids make up cell walls and store energy.
Carbs give cells energy, send signals, and help them find each other.
DNA and RNA are molecules that make proteins and store genetic information so that genes can be passed down.
The composition of protoplasm shows how complicated life is. Understanding protoplasm and how it interacts with other things in the cell and in the body sheds light on the most important processes in life.
Possible Similarities Between Cytoplasm and Protoplasm
In the field of microscopic cell biology, it is very interesting to look at how cytoplasm and protoplasm are related. There are three important things that these two halves have in common, but they are also very different in three important ways.
Important for Cell Life: Cells need both protoplasm and cytoplasm to grow and work properly. They make a huge variety of metabolic processes possible that are needed for growth, reproduction, and responding to outside stimuli.
Being Found in All Cell Types: Cytoplasm, protoplasm, or both are found in all cell types and play important roles, from the simplest bacterial cells to the more complex eukaryotic cells of plants and animals. Its uniformity shows how important it is to cellular biology at its core.
They are made up of water, salts, and organic molecules. Water is an important part of both the protoplasm and the cytoplasm because it dissolves salts, organic substances, and enzymes.
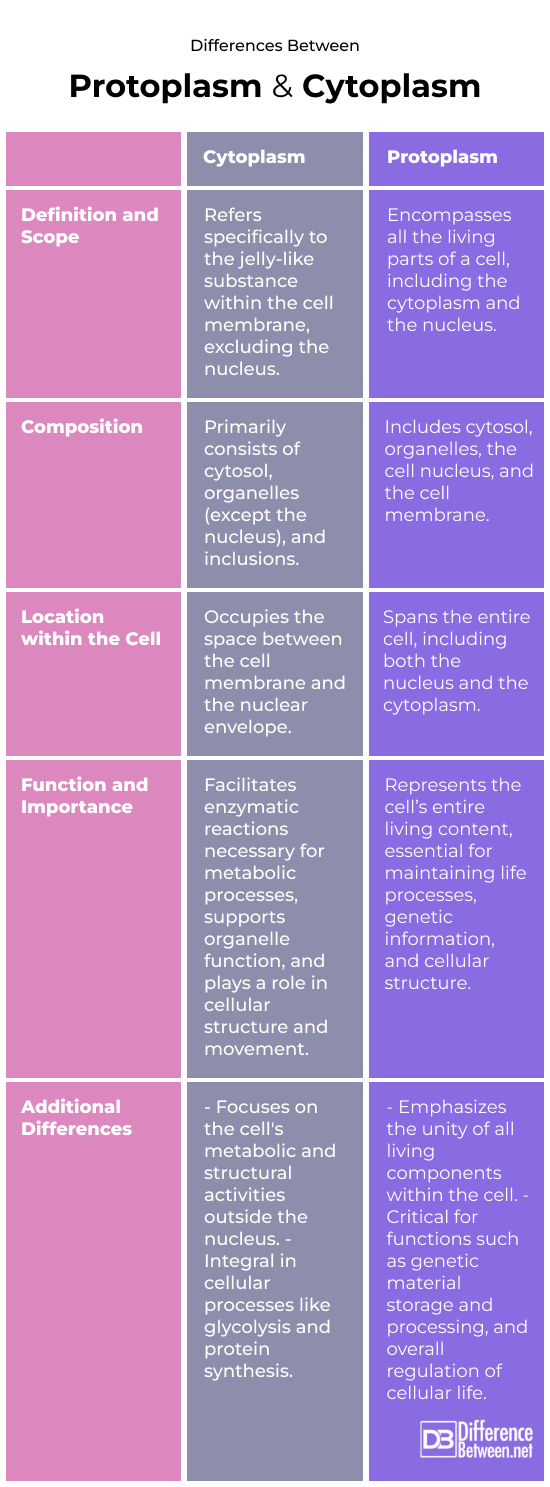
Differences between protoplasm and cytoplasm
In cell biology, “cytoplasm” and “protoplasm” have different meanings. Their significant differences are listed below:
Definition and scope
Cytoplasm is jelly-like substance that fills the cell except for the nucleus. It houses cell organelles and supports many cellular activities.
In contrast, “protoplasm” is broader. The nucleus and cytoplasm are included. Why is it called the “living part” of the cell? It’s everything inside the cell membrane.
Composition
Organelles, salts, water, enzymes, and chemicals make up the cytoplasm. Cell metabolism occurs in this crowded environment.
The protoplasm is made up of the nucleus, which contains the cell’s DNA, and the cytoplasm. In addition to metabolic activities, the protoplasm stores genetic information and regulation.
Location within the cell
Cytoplasm surrounds the cell’s organelles outside the nucleus.
The nucleus and other cell membrane contents are called protoplasm. It contains all cell life.
Function and importance
The cytoplasm helps the cell maintain its structure, motility, and metabolism.
Protoplasm is important to cell life and houses metabolic, genetic, and reproductive activities.
Differences between protoplasm and cytoplasm
Summary
We discovered the complicated link between protoplasm and cytoplasm. This shows how they cooperate to sustain cells. Both are essential for life at the cellular level, although they perform distinct functions:
– The cytoplasm, packed with chemicals and organelles is where metabolism and other cellular activities occur.
– Protoplasm refers to the nucleus, cytoplasm, and overall cell life.
The chemical molecules, salts, and water that make them up may appear similar. But deeper analysis displays their varied responsibilities and places in the cell. Understanding these distinctions helps us comprehend cells and advances health, medicine, and life science as well as school. The complicated relationships between protoplasm and cytoplasm give rise to life.
FAQs:
What is the difference between cytoplasm and protoplasm on Brainly?
- Cytoplasm refers to the jelly-like substance inside the cell that contains organelles, excluding the nucleus. Protoplasm includes the cytoplasm and the nucleus, representing the entire content of the cell’s living material.
What is the difference between the cytoplasm and the chloroplast?
- The cytoplasm is the fluid that fills the cell and supports the organelles. The chloroplast, on the other hand, is an organelle within the cytoplasm of plant and algae cells that conducts photosynthesis.
What is the difference between the cytoplasm and the cytosol?
- The cytoplasm encompasses the cytosol and the organelles within a cell, except for the nucleus. The cytosol is the liquid part of the cytoplasm, which does not include organelles.
What is the difference between cytoplasm and hyaloplasm?
- Hyaloplasm, often synonymous with cytosol, is the clear, fluid portion of the cytoplasm. It’s where the cell’s organelles are suspended. Cytoplasm includes both this fluid and the organelles.
What is the difference between cytoplasm and protoplasm & what is the function of the mitochondria?
- Cytoplasm is the part of the protoplasm that lies outside the nucleus, while protoplasm is the entire content within a cell, including the nucleus. The mitochondria, often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell, generates most of the cell’s supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy.
What does cytoplasm do?
- The cytoplasm plays a crucial role in supporting cellular functions by providing a platform for most of the biochemical reactions that occur within the cell. It helps in the transport of materials, holds organelles in place, and is involved in cell division and growth.
- Difference Between Psychopath and Sociopath - April 2, 2024
- Difference Between IQ and EQ - April 2, 2024
- Difference Between Good Carbs and Bad Carbs - April 2, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
24 Comments
Leave a Response
References :
[0]http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/00/Eastern_equine_encephalitis.jpg
[1]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAEEWsnnmUg-plasmodesma-plant-cytoplasm/
[2]Image credit; https://www.canva.com/photos/MADVZLWfda4-a-protoplasmic-left-and-a-fibrous-astrocyte-protoplasmic-astrocytes-occur-in-the-gray-matter-fibrous-astrocytes-in-the-white-matter-of-the-branh-/
[3]Oberling, C. (1959). The structure of cytoplasm. In International Review of Cytology (Vol. 8, pp. 1-31). Academic Press
[4]Claude, A. (1943). The constitution of protoplasm. Science, 97(2525), 451-456.
[5]Oberling, C. (1959). The structure of cytoplasm. In International Review of Cytology (Vol. 8, pp. 1-31). Academic Press.
[6]Oberling, C. (1959). The structure of cytoplasm. In International Review of Cytology (Vol. 8, pp. 1-31). Academic Press.
[7]Oberling, C. (1959). The structure of cytoplasm. In International Review of Cytology (Vol. 8, pp. 1-31). Academic Press.
[8]Claude, A. (1943). The constitution of protoplasm. Science, 97(2525), 451-456.
[9]Claude, A. (1943). The constitution of protoplasm. Science, 97(2525), 451-456.
[10]Claude, A. (1943). The constitution of protoplasm. Science, 97(2525), 451-456.

simple language but can be made be more interesting by more images
Yaa u r right anamika
Yes you are right amamika
Thanks . For Focusing on only useful details
This airticle was very helpful and it really heloed me to clear my doubts. Thank you
Great and lucid explanation
This article is very brilliant
Thanks for the information
This text is 100.100 % helpful for me thanks
Thnx for the answer
It was very helpful
Not so good it should be in a systematic manner and should be in tabulate manner ahhh I should go to another website
Thank you very much
Beautiful summary explained
Very nice
Very bad . It should be in a systematic manner.
Clear understanding I really apreciated
Hello… please how do you understand that cause it seems it’s talking more on the same particular difference. Please can you further clarify…
If prptoplasm consists of cell membrane, nucmeus and cytoplasm..then what is the difference between cell and protoplasm as the cell is having the same constituent??
That was very helpful . Thank you
Not nice not much knowledge full
Nice presentation
Sandar explanation
Simplified and detailed
Nice