Difference Between Fear and Phobia
Fear and phobia are both characterized by emotional responses which involve physical reactions such as increased heart, breathing, and pulse rate. These are associated with situations that make individuals feel very uncomfortable. Like phobia, fear can be a learned response because of the association with the aversive stimulus. However, fear is largely an instinct that functions to protect creatures from real danger while phobia is an irrational fear which is characterized by a marked anticipation of a perceived threat. The following discussions further delve into such differences.
What is Fear?
The etymology of “fear” is traced to the German word “Gefahr” which translates to “danger”. Noticeably, this emotional state is evoked by something dangerous. This makes fear a vital response since it helps protect people from actual threats. It is a primitive reaction which was instrumental in the survival of our ancestors.
The following are the two stages of fear:
-
Biochemical Reaction
This is when the body responds to danger by “fight, flight, or freeze”. This is an involuntary response as the physical reactions are governed by the sympathetic system.
-
Emotional Reaction
In this stage, the response is more subjective as most people avoid situations that may lead to fear but some seek this emotion. For instance, “adrenaline junkies” are thrilled when they are in a dangerous situation.
What is Phobia?
“Phobia” came from the Greek word “phobos” which translates to “panic fear” or “terror”. This is a highly intense fear which is out of proportion to the source of threat. Hence, it can significantly interfere with a person’s daily activities and relationships. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM 5) classifies phobia under anxiety disorders with the following diagnostic criteria:
- Significant anxiety regarding an object, animal, or situation such as needles, dogs, or public speaking.
- The source of phobia almost always leads to anxiety and is actively avoided or agonizingly endured
- The fear is markedly out of proportion to the actual danger
- The irrational fear typically lasts for 6 months or more
- The anxiety causes significant impairment in the individual’s areas of functioning
Here are 10 of the common phobias:
- Arachnophobia (fear of spiders)
- Ophidiophobia (fear of snakes)
- Acrophobia (fear of heights)
- Agoraphobia (fear of open/crowded spaces)
- Social Phobia (fear of social interactions/ situations)
- Claustrophobia (fear of enclosed/ narrow spaces)
- Aerophobia (fear of flying)
- Cynophobia (fear of dogs)
- Trypanophobia (fear of needles)
- Glossophobia (fear of public speaking)
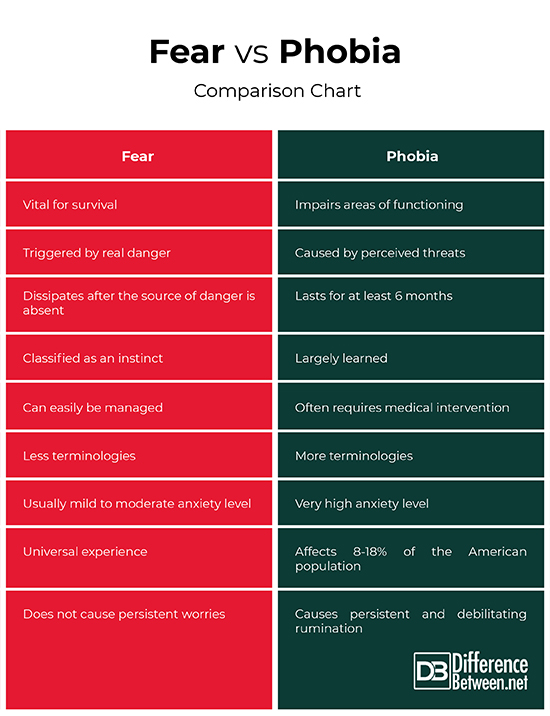
Difference between Fear and Phobia
-
Etymology
Fear is traced to the word “danger” while phobia’s etymology is more emotionally extreme with the word “terror”.
-
Survival
Fear is generally vital for survival as it alerts creatures regarding actual danger. On the other hand, phobia impairs an individual’s occupational, social, and other areas of functioning as the experienced anxiety is inordinate.
-
Danger
Real danger triggers fear while an anticipated threat triggers phobia. People with phobia imagine unnecessary aggravations which may warrant psychiatric intervention.
-
Duration of Emotional Response
Fear dissipates when the source of danger is not present. On the contrary, the anxiety felt in phobia persists for at least six months.
-
Instinct
As compared to phobia, fear is more associated with instincts as it is a primitive emotional response to something aversive or unfamiliar as babies are born with fear responses.
-
Managing the Emotional Response
People who experience fear can easily manage their discomfort as they can still carry on with their daily routine after the threat disappears. However, those suffering from phobia experience debilitating consequences since the fear is often uncontrolled and extreme that they may need the help of a therapist who utilizes various approaches such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), exposure-based therapies, and psychopharmacotherapy.
-
Terminologies
As compared to fear, phobia is more associated with various terminologies as they come in hundreds such as coulrophobia (fear of clowns), sciophobia (fear of shadows), and panophobia (fear of everything).
-
Anxiety Level
Fear is characterized by mild to moderate (sometimes reasonably high) anxiety while phobia is distinguished by a very high anxiety level since it is an anxiety disorder which is coupled with equally very high avoidance and anticipatory behaviors. Moreover, phobia is often associated with having panic attacks.
-
Universality
Fear is a universal experience while phobia affects 8 to 18% of Americans and it is more prevalent among women than men.
-
Rumination
Unlike fear, phobia is characterized by persistent rumination of the threat. It significantly consumes the affected individual’s thoughts in such a way that it notably distracts his focus on more important aspects of his life.
Fear vs Phobia: Comparison Chart
Summary of Fear vs Phobia
- Fear and phobia are both characterized by emotional responses which involve physical reactions such as increased heart, breathing, and pulse rate.
- The etymology of “fear” is traced to the German word “Gefahr” which translates to “danger”.
- The two stages of fear are biochemical and emotional reactions.
- “Phobia” came from the Greek word “phobos” which translates to “panic fear” or “terror”.
- Fear is key for survival while phobia impairs daily functioning.
- Fear is triggered by real danger while phobia is caused by imagined threats.
- Fear dissipates when the danger is over while phobia’s symptoms occur persistently for at least 6 months.
- Fear is largely instinctive while phobia is generally learned.
- As compared to phobia, fear requires no medical intervention.
- Phobia has more terminologies than fear.
- Being an anxiety disorder, phobia is characterized by higher levels of anxiety than fear.
- Unlike phobia, fear is a universal experience.
- Unlike fear, phobia causes debilitating and persistent rumination.
- Difference Between Hematoma and Melanoma - February 9, 2023
- Difference Between Bruising and Necrosis - February 8, 2023
- Difference Between Brain Hematoma and Brain Hemorrhage - February 8, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing, 2013. Print.
[1]Hanh, Thich Nhat. Fear: Essential Wisdom for Getting Through the Storm. New York, NY: Harper Collins, 2012. Print.
[2]Milosevic, Irena and McCabe, Randi. Phobias. Oxford, England: Greenwood, 2015. Print.
[3]Image credit: https://pixabay.com/en/syringe-phobia-fear-blood-sample-1547989/
[4]Image credit: https://www.deviantart.com/rodrigoseroiska/art/Fear-of-the-Dark-130602548