Difference Between Retinol and Tretinoin
Retinol and tretinoin are fat-soluble organic compounds, synthesized from β-carotene. They are both included in the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines and are widely used for medical purposes.
What is Retinol?
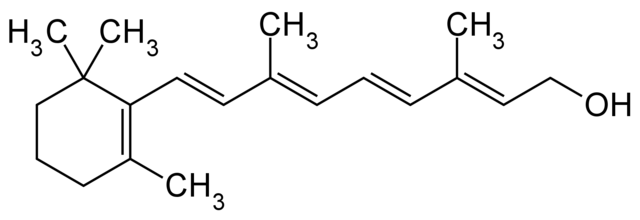
Retinol (vitamin A) is a fat-soluble vitamin. Its chemical formula is C20H30O. It is very important for the human organism and can be found in food and taken as a dietary supplement.
Retinol is synthesized from the breakdown of β-carotene.
Retinol is used for the prophylaxis and treatment of diseases affecting the eyes, skin and mucosal diseases, respiratory diseases such as dry chronic rhinopharyngitis, gastrointestinal tract diseases such as steatorrhea, diarrhea, malabsorption syndrome, chronic pancreatitis. It is also used to support the immune system, as it is involved in maintaining a number of immune cell types – neutrophils, macrophages, T-cells, B-cells, natural killer cells, etc. Retinol affects the synthesis of the growth hormone.
Retinol should not be taken by people, hypersensitive to vitamin A, peanuts, soy, or having hypervitaminosis A, severe liver or kidney diseases.
The possible adverse reactions to retinol include headache, drowsiness, increased nervousness, gum bleeding, dyspnoea, vomiting, diarrhea, hepatosplenomegaly, yellowish and dry skin, menstrual disorders, fever, allergic reactions, anemia, bone and joint pain.
Retinol is a fat-soluble vitamin, essential for many processes in the body.
Alcohol and synthetic retinoids may increase the toxicity of retinol. Oral contraceptives may increase its levels in the body.
The oral dose for adults and adolescents is 2500 IU per day, for children from 1 to 14 years the dose is 1250 IU per day.
What is Tretinoin?
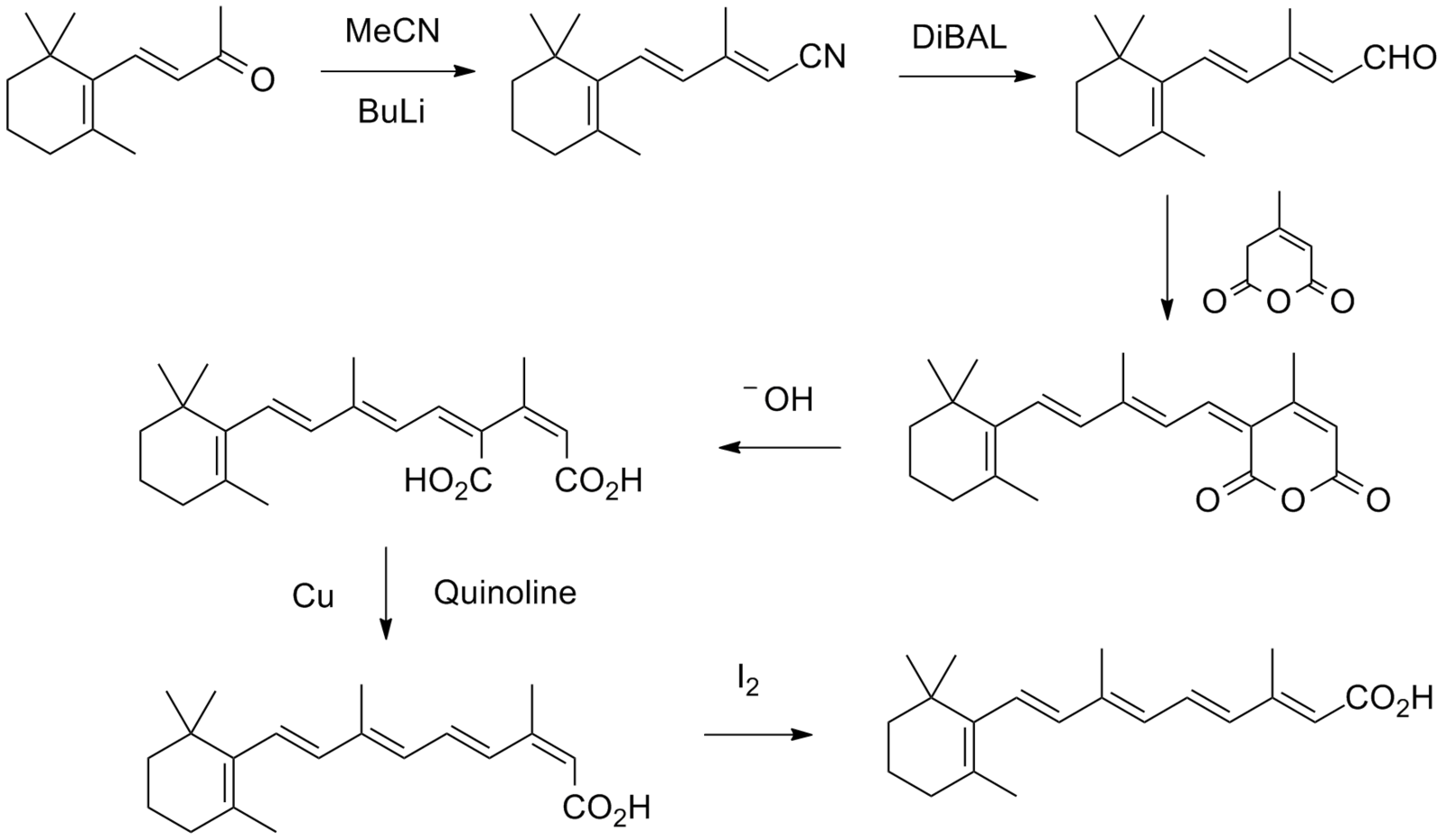
Tretinoin (all-trans retinoic acid) is an acidic form of vitamin A. Its chemical formula is C20H28O2.
It is synthesized from β-carotene.
It is applied dermally, for the treatment of heavy forms of acne vulgaris (Stage II-III) in which papules and pustules predominate, and orally, for the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia.
Tretinoin should not be used by people, hypersensitive to the drug or any of its excipients, with acute inflammatory skin processes, acute eczema, rosacea, photoallergy, or during pregnancy.
When tretinoin is applied to the skin to treat acne, adverse drug reactions include transient erythema, burning, and itching. The oral admission may lead to the retinoic acid syndrome, leukocytosis, thrombosis, benign intracranial hypertension in children, hypercholesterolemia and/or hypertriglyceridemia, liver damage, etc.
Tretinoin has a strong comedonolytic, exfoliative, and keratolytic effect. Its local application reduces adherence between follicular epithelial cells, which reduces the formation of microcomedones.
The concurrent use with topical agents containing sulfur, resorcinol, and salicylic acid has to be avoided.
Tretinoin is usually applied to the skin once daily, at bedtime. The effect is observed after 2-6 weeks. Continuous use results in a long-lasting therapeutic effect. If severe erythema and itching develop, treatment should be stopped.
The oral dose is 45 mg daily, administered in 2 evenly divided doses.
Difference Between Retinol and Tretinoin
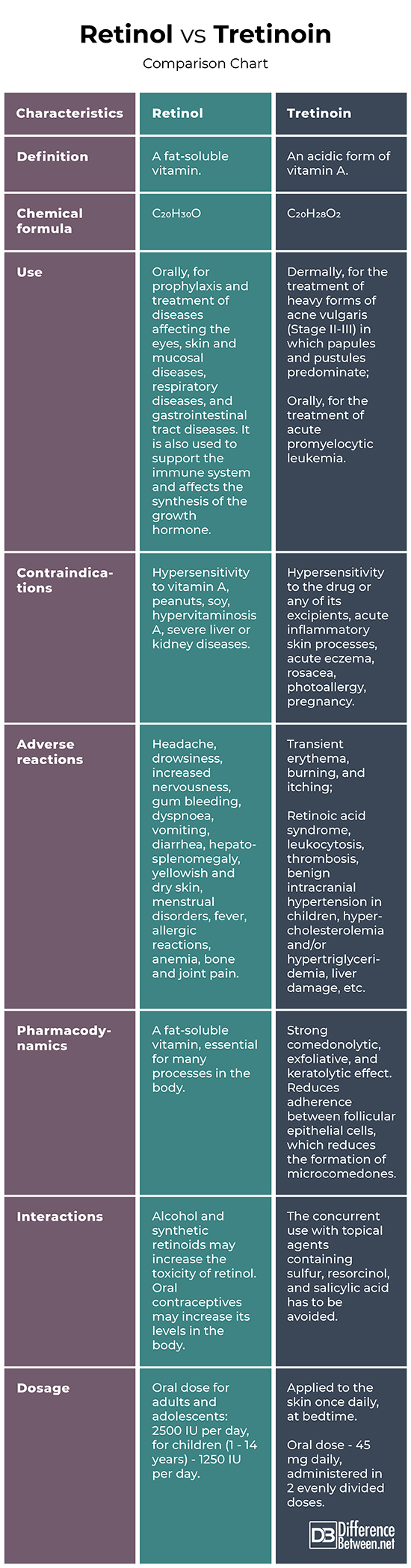
Definition
Retinol: Retinol (vitamin A) is a fat-soluble vitamin.
Tretinoin: Tretinoin (all-trans retinoic acid) is an acidic form of vitamin A.
Chemical formula
Retinol: The chemical formula of retinol C20H30O.
Tretinoin: The chemical formula of tretinoin is C20H28O2.
Use
Retinol: Retinol is used for the prophylaxis and treatment of diseases affecting the eyes, skin and mucosal diseases, respiratory diseases, and gastrointestinal tract diseases. It is also used to support the immune system and affects the synthesis of the growth hormone.
Tretinoin: Tretinoin is applied dermally for the treatment of heavy forms of acne vulgaris (Stage II-III) in which papules and pustules predominate, and orally, for the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia.
Contraindications
Retinol: Retinol should not be taken by people, hypersensitive to vitamin A, peanuts, soy, or having hypervitaminosis A, severe liver or kidney diseases.
Tretinoin: Tretinoin should not be used by people, hypersensitive to the drug or any of its excipients, with acute inflammatory skin processes, acute eczema, rosacea, photoallergy, or during pregnancy.
Adverse reactions
Retinol: The possible adverse reactions to retinol include headache, drowsiness, increased nervousness, gum bleeding, dyspnoea, vomiting, diarrhea, hepatosplenomegaly, yellowish and dry skin, menstrual disorders, fever, allergic reactions, anemia, bone and joint pain.
Tretinoin: When tretinoin is applied to the skin to treat acne, adverse drug reactions include transient erythema, burning, and itching. The oral admission may lead to the retinoic acid syndrome, leukocytosis, thrombosis, benign intracranial hypertension in children, hypercholesterolemia and/or hypertriglyceridemia, liver damage, etc.
Pharmacodynamics
Retinol: Retinol is a fat-soluble vitamin, essential for many processes in the body.
Tretinoin: Tretinoin has a strong comedonolytic, exfoliative, and keratolytic effect. Its local application reduces adherence between follicular epithelial cells, which reduces the formation of microcomedones.
Interactions
Retinol: Alcohol and synthetic retinoids may increase the toxicity of retinol. Oral contraceptives may increase its levels in the body.
Tretinoin: The concurrent use with topical agents containing sulfur, resorcinol, and salicylic acid has to be avoided.
Dosage
Retinol: The oral dose for adults and adolescents is 2500 IU per day, for children from 1 to 14 years the dose is 1250 IU per day.
Tretinoin: Tretinoin is usually applied to the skin once daily, at bedtime. The oral dose is 45 mg daily, administered in 2 evenly divided doses.
Retinol vs. Tretinoin: Comparison Chart
Summary of Retinol vs. Tretinoin:
- Retinol (vitamin A) is a fat-soluble vitamin.
- Tretinoin (all-trans retinoic acid) is an acidic form of vitamin A.
- The chemical formula of retinol is C20H30O. The chemical formula of tretinoin is C20H28O2.
- Retinol is used for the prophylaxis and treatment of diseases affecting the eyes, skin and mucosal diseases, respiratory diseases, and gastrointestinal tract diseases. Tretinoin is applied dermally for the treatment of heavy forms of acne vulgaris, and orally, for the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia.
- Retinol should not be taken by people, hypersensitive to vitamin A, peanuts, soy, or having hypervitaminosis A, severe liver or kidney diseases. Tretinoin should not be used by people, hypersensitive to the drug or any of its excipients, with acute inflammatory skin processes, acute eczema, rosacea, photoallergy, or during pregnancy.
- Adverse reactions to retinol include headache, drowsiness, increased nervousness, gum bleeding, dyspnoea, vomiting, diarrhea, hepatosplenomegaly, yellowish and dry skin, menstrual disorders, fever, allergic reactions, anemia, bone and joint pain. Adverse drug reactions to tretinoin include transient erythema, burning, itching, retinoic acid syndrome, leukocytosis, thrombosis, hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, liver damage, etc.
- The concurrent use of retinol with alcohol and synthetic retinoids, and of tretinoin with topical agents containing sulfur, resorcinol, and salicylic acid has to be avoided.
- Difference Between Gallstones and Cholecystitis - September 5, 2021
- Difference Between Constipation and Cramping - August 4, 2021
- Difference Between Whole Genome Sequencing and Microarray - May 6, 2021
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tretinoin_synthesis.png
[1]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Retinol.png
[2]Arun, B., B.S. Bahl. A Textbook of Organic Chemistry. New Delhi: S. Chand Publishing. 2016. Print.
[3]Anderson, J. L. RETIN-A (Tretinoin): Treats Acne (Promotes Peeling of Affected Skin Areas and Unclogs Pores). 2015. Print.
[4]Nau, H., B. William (Eds.). Retinoids. The Biochemical and Molecular Basis of Vitamin A and Retinoid Action. Berlin: Springer. 1999. Print.