Difference Between Coronavirus and Pneumonia
Coronaviruses (Coronaviridae) are a family of viruses that cause mild to severe diseases in mammals and birds. Infection from Coronavirus can lead to complicated medical condition such as Pneumonia also known as chest infections.
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs, affecting the alveoli and/or the surrounding lung tissue.
Coronavirus infection can lead to pneumonia and therefore both have some common symptoms, however, the two conditions have different etiology and different measures need to be taken in order to avoid complications.
What is Coronavirus?
Coronaviruses (Coronaviridae) are a family of viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. Their name comes from the similarity of the viral particles with the solar corona in an electron microscope examination.
Coronaviruses rank second after rhinoviruses as causative agents of cold and flu. In humans, these viruses cause respiratory infections, which are usually mild, including the common cold. Humans are usually infected with human Coronaviruses 229 E, NL63, OC43, and HKU1. However, there are also more rare forms, causing serious illness. Such are the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS-CoV), the novel Coronavirus (nCoV) which was first reported in humans in China (Wuhan) on December 31, 2019, and the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS-CoV).
Coronaviruses can be transmitted between animals and humans. Surveys have shown that the SARS-CoV has been transmitted to humans from civet cats, the MERS-CoV – from the Arabian camel.
The entrance to infectious particles is the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract. Viruses are spread from person to person mainly through close contact, in particular by airborne droplet (while coughing or sneezing) at a distance of about 2 m. Viral RNA was also found in the feces of infected patients. In a fecal-oral mechanism of transmission of the viruses, gastrointestinal syndrome develops.
Major factors for the transmission of Coronavirus are:
- Secretions from the upper respiratory tract of infected people;
- Contaminated food products;
- Objects from the infected people’s environment;
- Dirty hands.
Coronaviruses are resistant to environmental conditions. At a temperature of 34-36°C, they remain viable for 2-3 days. Disinfectants destroy them within 10 minutes.
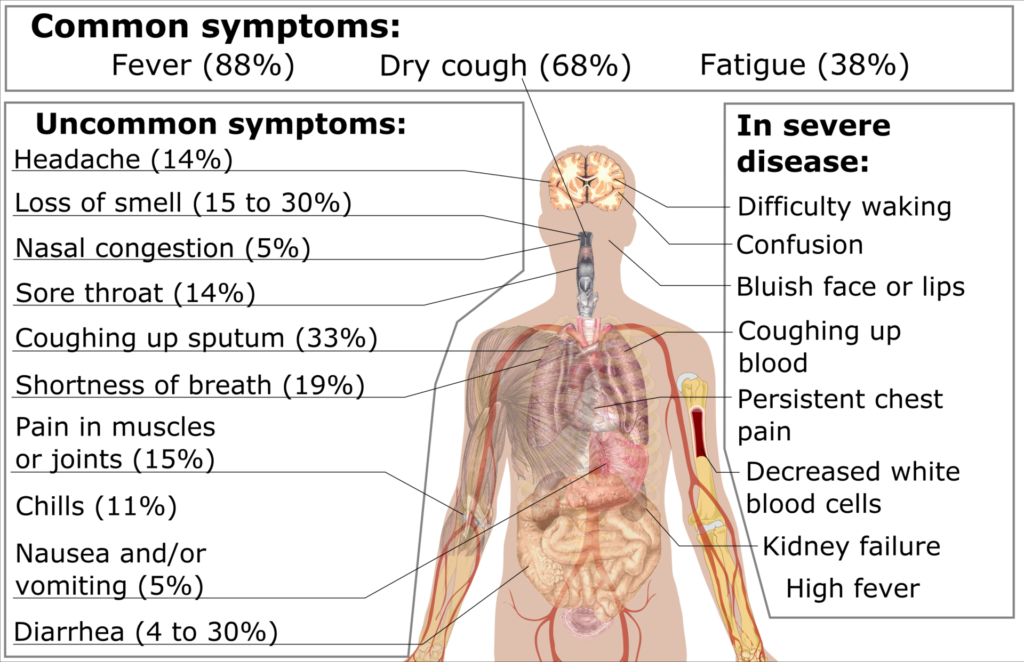
Coronavirus infections are mild to life-threatening acute illness. The symptoms include:
- Fever;
- Cough;
- Sore throat;
- Runny nose;
- Headache;
- Muscle pain;
- Diarrhea (develops in fecal-oral infection).
In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, the following complications may develop:
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome;
- Irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia);
- Cardiovascular shock;
- Severe muscle pain (myalgia);
- Fatigue;
The diagnosis is made based on a medical examination. For microbiological diagnostics can be analyzed:
- Throat secretion;
- Nasal secretion;
- Feces.
Electron microscopy and immunofluorescence methods are used.
Treatment is directed at relieving symptoms and may include:
- Antiviral medication (not recommended for the new Coronavirus);
- Rest;
- Fluid intake;
- Cough medications;
- Pain killers.
What is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs. The disease affects individually, but more often simultaneously, the alveoli (responsible for the gas exchange between the inhaled air and the blood) and the surrounding lung tissue called interstitium. It disrupts the normal breathing process.
Depending on the size of the affected area, pneumonia is:
- Lobar – affects the entire lobe;
- Segmental – affects one or more lobal segments;
- Lobular – affects separate lobules.
Inflammation can be caused by various chemical and physical agents in a gaseous state (e.g. toxic and irritating gases), from radiation, foreign bodies in the bronchi. However, the most common cause of pneumonia is biological, and depending on the cause the pneumonia is:
- Viral pneumonia;
- Bacterial pneumonia;
- Fungal pneumonia;
- Allergic pneumonia.
In some cases, pneumonia becomes chronic.
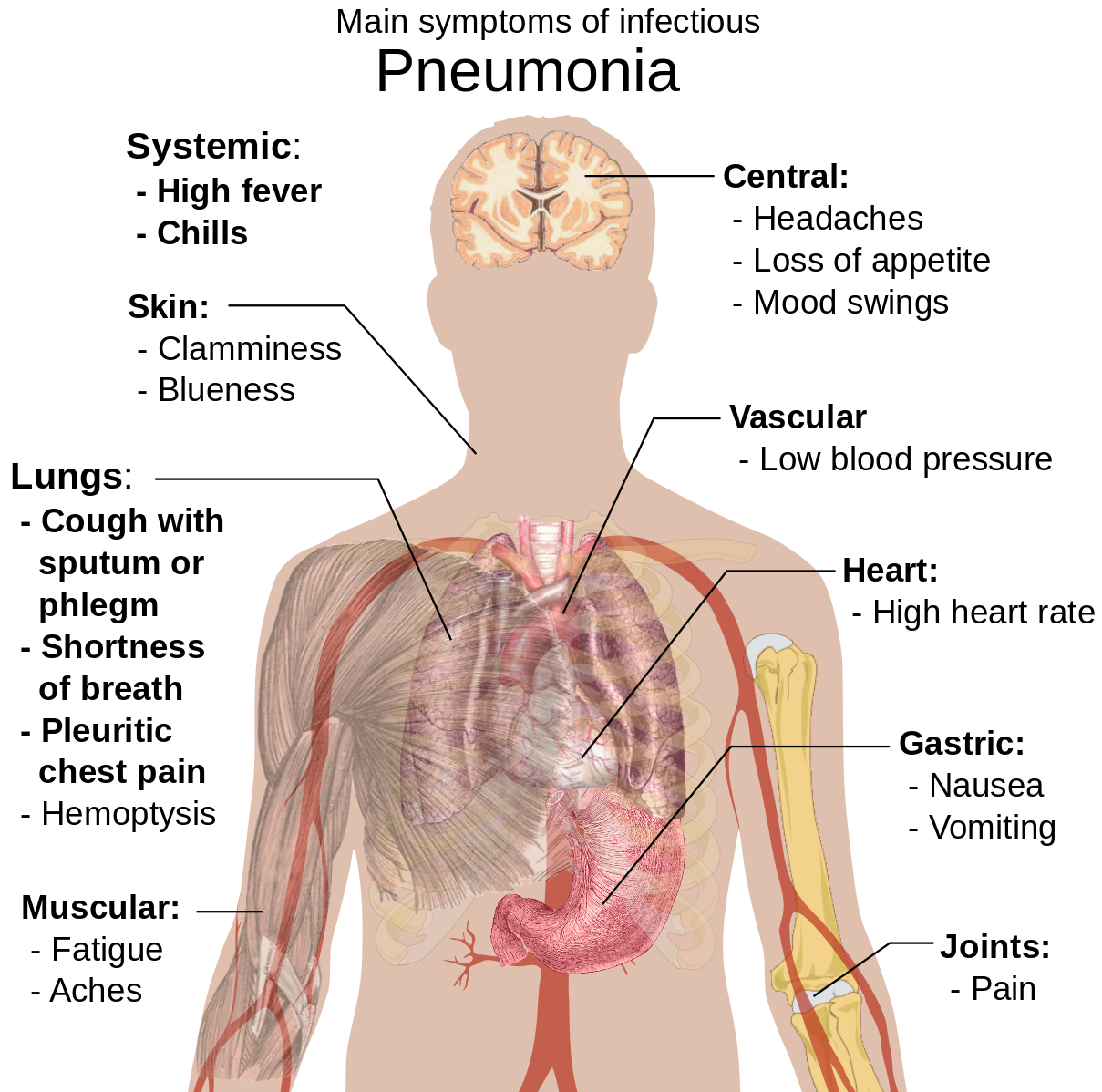
Symptoms of pneumonia include:
- Cough with greenish or yellow phlegm;
- Strong fever, sometimes accompanied by chills;
- Shortness of breath;
- Chest pain;
- Joint or muscle pain;
- Headache;
- Loss of appetite;
- Fatigue.
Some rare forms of pneumonia can cause other symptoms. For example, Legionella-induced pneumonia can lead to abdominal pain, and diarrhea; Pneumocystis-induced pneumonia can only lead to weight loss and night sweats. Children with pneumonia can develop the listed symptoms, but in many cases, they are just sleepy or with reduced appetite.
The potential complications of pneumonia include:
- Bacteria in the bloodstream (bacteremia);
- Accumulation of fluid around the lungs;
- Lung abscess;
- Difficulty breathing.
Pneumonia is usually diagnosed by medical examination and radiography of the lungs.
Treatment includes:
- Antibiotics;
- Analgesics;
- Rest;
- Fluids.
However, people who have other illnesses, the elderly or those who have significant breathing difficulties may need more serious care.
Difference Between Coronavirus and Pneumonia
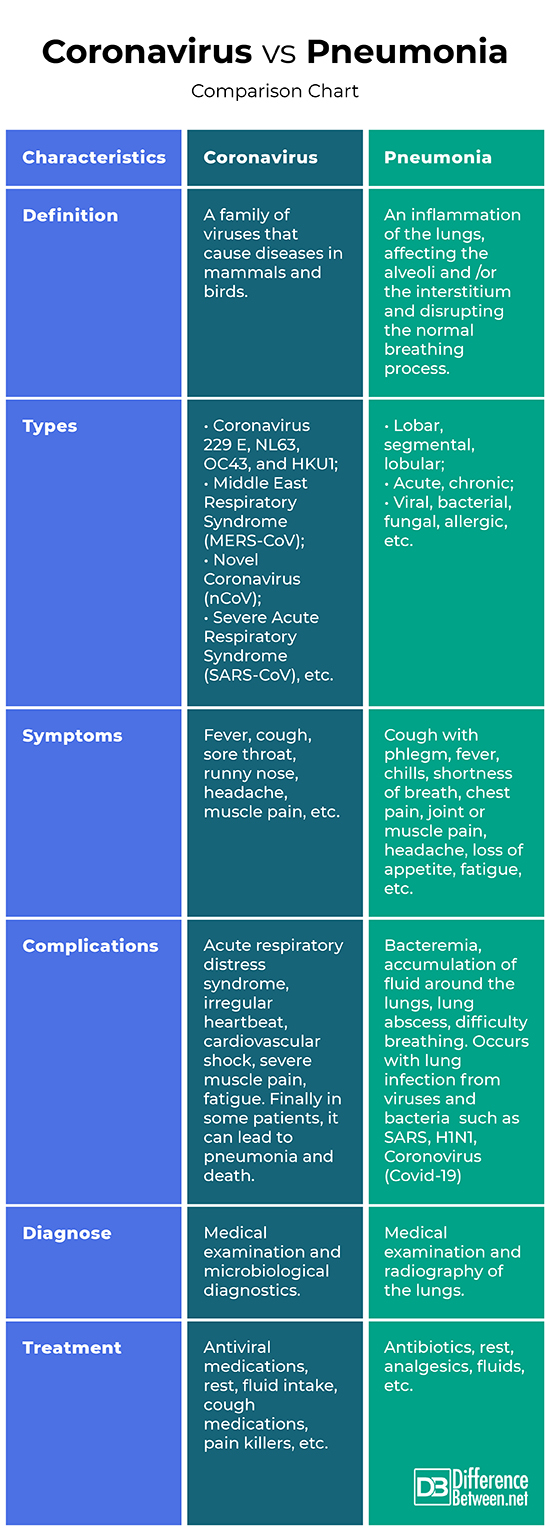
Definition
Coronavirus: Coronaviruses are a family of viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds, and in some cases it can lead to pneumonia for patients with other cormorbidity.
Pneumonia: Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs, affecting the alveoli and /or the interstitium and disrupting the normal breathing process.
Types
Coronavirus: Common human Coronaviruses include 229 E, NL63, OC43, and HKU1. The more rare forms, causing serious illness include the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS-CoV), novel Coronavirus (nCoV), Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS-CoV).
Pneumonia: Depending on the size of the affected area, pneumonia is lobar, segmental or lobular. Depending on the causative agent it can be viral, bacterial, fungal, allergic, etc.
Symptoms
Coronavirus: The symptoms of Coronavirus may be from mild to life-threatening and include fever, cough, sore throat, runny nose, headache, muscle pain, etc.
Pneumonia: The symptoms of pneumonia include cough with greenish or yellow phlegm, strong fever, sometimes accompanied by chills, shortness of breath, chest pain, joint or muscle pain, headache, loss of appetite, fatigue.
Complications
Coronavirus: In the absence of timely and adequate treatment of the Coronavirus complications may develop, including acute respiratory distress syndrome, irregular heartbeat, cardiovascular shock, severe muscle pain, fatigue.
Pneumonia: The potential complications of pneumonia include bacteria in the bloodstream, accumulation of fluid around the lungs, lung abscess, difficulty breathing.
Diagnose
Coronavirus: The diagnosis of Coronavirus is made based on a medical examination. For microbiological diagnostics can be analyzed throat secretion, nasal secretion, feces.
Pneumonia: Pneumonia is usually diagnosed by medical examination and radiography of the lungs.
Treatment
Coronavirus: The treatment of Coronavirus is directed at relieving symptoms and may include antiviral medication (not recommended for the new Coronavirus), rest, fluid intake, cough medications, pain killers.
Pneumonia: The treatment of pneumonia includes antibiotics, rest, analgesics, fluids.
Coronavirus Vs. Pneumonia: Comparison Chart
Summary of Coronavirus and Pneumonia
- Coronaviruses (Coronaviridae) are a family of viruses that cause pneumonia in mammals such as human and birds.
- Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs due to any bacteria or virus infection, affecting the alveoli and /or the interstitium, disrupting the normal breathing process.
- The common human Coronaviruses include 229 E, NL63, OC43, and HKU1. The more rare forms, causing serious illness include the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS-CoV), novel Coronavirus (nCoV), Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS-CoV).
- Depending on the size of the affected area, pneumonia is lobar, segmental or lobular. Depending on the causative agent it can be viral, bacterial, fungal, allergic, etc.
- The symptoms of Coronavirus may be from mild to life-threatening and include fever, cough, sore throat, runny nose, headache, muscle pain, etc. The symptoms of pneumonia include cough, fever, chills, shortness of breath, chest pain, joint or muscle pain, headache, loss of appetite, fatigue.
- The potential complications of Coronavirus include acute respiratory distress syndrome, irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia), cardiovascular shock, severe muscle pain (myalgia), fatigue. The potential complications of pneumonia include bacteria in the bloodstream, accumulation of fluid around the lungs, lung abscess, difficulty breathing.
- The diagnosis of Coronavirus is made based on a medical examination. For microbiological diagnostics can be analyzed throat secretion, nasal secretion, feces. Pneumonia is usually diagnosed by medical examination and radiography of the lungs.
- The treatment of Coronavirus is directed at relieving symptoms and may include antiviral medication, rest, fluid intake, cough medications, pain killers. The treatment of pneumonia includes antibiotics, rest, analgesics, fluids.
- Difference Between Gallstones and Cholecystitis - September 5, 2021
- Difference Between Constipation and Cramping - August 4, 2021
- Difference Between Whole Genome Sequencing and Microarray - May 6, 2021
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Sun, K., J. Chen, C. Viboud. Early epidemiological analysis of the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak based on crowdsourced data: a populationlevel observational study. Lancet Digital Health 2020. 2020. Online.
[1]Warrell, D., T. Cox, J. Firth. Oxford Textbook of Medicine, Vol. 2. Oxford: Oxford University Press. 2010. Print.
[2]Yankova, Z. New Guide to Pulmonary Diseases and Tuberculosis. Sofia: Medical University Press. 2012. Print.
[3]Image credit: https://media.defense.gov/2020/Mar/15/2002264851/780/780/0/200315-F-ZZ999-0001.JPG
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Symptoms_of_pneumonia.svg
[5]https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Symptoms_of_coronavirus_disease_2019_3.0.png

I am now making extra $19k or more every month from home by doing very simple and easy job online from home. I have received exactly $20845 last month from this home job. Join now this job and start making extra cash online by follow instruction on the given website….apaybro.com