Difference Between Fast Metabolism and Slow Metabolism
• Categorized under Food,Health,Science | Difference Between Fast Metabolism and Slow Metabolism
A fast metabolism is when substances are broken down to provide energy at a rapid rate. A slow metabolism is when substances are only broken down slowly in order to provide energy for the cells.
What is Fast Metabolism?
Definition:
A fast metabolism means that substances are catabolized or broken down quickly to provide energy for the cells to use to do work. Catabolism is the process by which biological macromolecules such as sugars are broken down to release energy in the form of ATP through a series of enzymatic reactions.
Why people may have a fast metabolism:
People can have a fast metabolism because of their genetics. Certain stimulant drugs may speed up a person’s metabolism because they speed up the nervous system. For instance, stimulant drugs such as cocaine or methamphetamines can artificially speed up the metabolic rate but they are very dangerous since they can cause heart attacks and people often forget to eat or sleep.
Medical conditions that can cause a fast metabolism:
An unusually fast metabolic rate may also be a sign of some type of physical abnormality such as hyperthyroidism. Hyperthyroidism is the condition in which too many thyroid hormones are secreted causing an increased metabolic rate.
Signs of a fast metabolism in people:
A pathologically abnormally rapid metabolism due to an overactive thyroid gland in humans has certain signs such as irritability, irregular and fast heart rate, weight loss.
Animals that have fast metabolism:
Animals that have a small body size often have a naturally very fast metabolism compared with larger animals. An organism that has a fast metabolic rate has to eat often in order to stay alive and get enough energy. Examples of animals that have a fast metabolism include hummingbirds and mice.
What is Slow Metabolism?
Definition:
A slow metabolism means that substances are catabolized or broken down slowly to provide energy to the cells.
Why people may have a slow metabolism:
Many factors influence a person’s metabolic rate, and one of these is simply ageing. In general, a person’s metabolism slows down with age which is one reason that so many people start to gain more weight after about age 40. Changes in hormones can also be a reason for having a slow metabolism, and in some cases, these changes are normal such as occurs with menopause. A slow metabolic rate can also be caused by certain medications such as anti-seizure medications such as Tegretol.
Medical conditions that can cause a slow metabolism:
In some cases, a pathological condition can cause an unusually slow metabolism. A problem in which too little thyroid hormones are being made is one condition that causes metabolism to be slow. This condition is called hypothyroidism. Cushing’s syndrome is another disease that can cause a person to have an unusually slow metabolic rate because it affects hormones in the body.
Signs of a slow metabolism in people:
The most obvious symptom of a slow metabolism is that the person gains weight, but they also may feel slowed down and hair may become brittle and dry. A person with a very slow metabolism not only gains weight but also often feels slowed down and sluggish.
Animals that have a slow metabolism:
Generally, the larger the animal the slower its metabolic rate, at least this holds true for mammals. This means that the metabolism of an elephant is very slow, particularly when compared with a mouse. Larger mammals have a slower metabolism, but they do have longer life spans than smaller mammals which have a fast metabolism.
Difference between Fast Metabolism and Slow Metabolism?
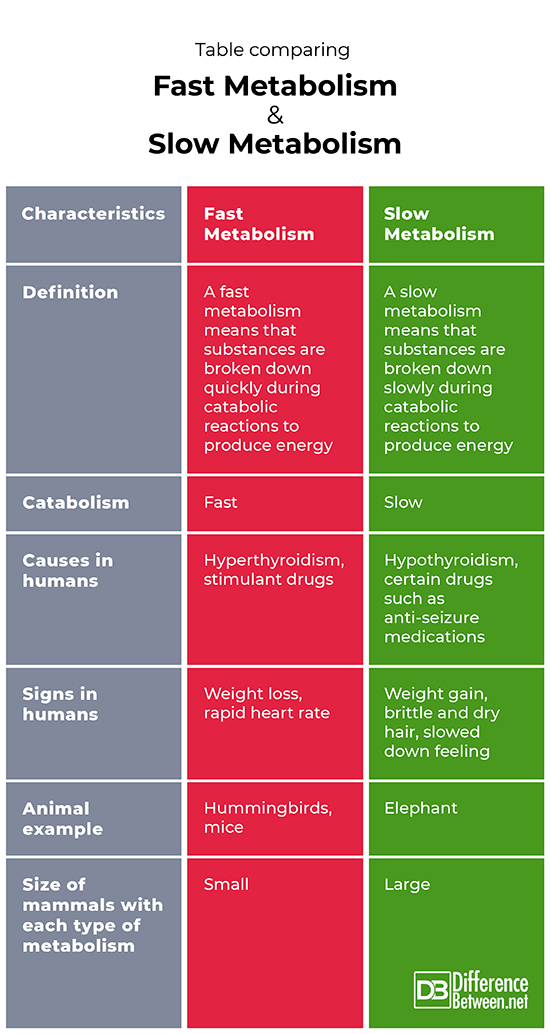
Definition
A fast metabolism is when catabolic reactions in which substances are broken down, proceed rapidly. A slow metabolism is when the breakdown of substances occurs at a slow pace, and energy is provided slowly to the cells.
Catabolism
Catabolism is rapid in the case of a fast metabolism. Catabolism is slower in cases of slow metabolism.
Causes in humans
In people, an unusually fast metabolism can be caused by stimulant drugs or by having the disorder hyperthyroidism. In people, an unusually slow metabolism can be due to the effect of drugs such as anti-seizure medication, due to ageing, or due to hypothyroidism.
Signs in humans
People who have an unusually fast metabolism have symptoms such as weight loss and a rapid heart rate. People with unusually slow metabolism tend to gain weight and they also may show signs such as brittle and dry hair and feel slowed down and sluggish.
Animal example
Animals that have a naturally fast metabolism include mice and hummingbirds. Animals that are known to have a naturally slow metabolism include elephants.
Size of mammals with each type of metabolism
Small mammals tend to have a fast metabolism. Large mammals tend to have slow metabolism.
Table comparing Fast Metabolism and Slow Metabolism
Summary of Fast Metabolism Vs. Slow Metabolism
- A fast metabolism is when the rate at which molecules are broken down in the body to provide energy is very rapid.
- A slow metabolism is the opposite thing to fast metabolism and involves a slow breakdown or catabolism of substances to release energy.
- Genetics and drugs can impact a human’s metabolic rate, with stimulants speeding up metabolism.
- Medical conditions involving the thyroid gland also impact the metabolic rates of people.
- In general, large animals have a naturally slow metabolism while small animals have a fast metabolism.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Sharing is caring!
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Cite
APA 7
Osborn, D. (2020, January 6). Difference Between Fast Metabolism and Slow Metabolism. Difference Between Similar Terms and Objects. http://www.differencebetween.net/science/health/difference-between-fast-metabolism-and-slow-metabolism/.
MLA 8
Osborn, Dr. Rae. "Difference Between Fast Metabolism and Slow Metabolism." Difference Between Similar Terms and Objects, 6 January, 2020, http://www.differencebetween.net/science/health/difference-between-fast-metabolism-and-slow-metabolism/.
Leave a Response
Written by : Dr. Rae Osborn. and updated on 2020, January 6
References :
[0]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Glucose_metabolism.svg
[1]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/3/31/Weight_cycle.jpg
[2]Jones, James R., William F. Caul, and James O. Hill. "The effects of amphetamine on body weight and energy expenditure." Physiology & behavior 51.3 (1992): 607-611.
[3]Kleiber, Max. "Body size and metabolic rate." Physiological reviews 27.4 (1947): 511-541.
[4]Pearson, Oliver P. "The metabolism of hummingbirds." The Condor 52.4 (1950): 145-152.
See more about : Fast Metabolism, Slow Metabolism