Difference Between Hallucinations and Illusions
Hallucinations and Illusions are popular terms in connection with the concept of perception. The key difference is the presence of a stimulus which only exists in the latter. A hallucination is an error in perception that is why it is often associated with mental health issues; whereas an illusion is merely a misperception which is often used in magic tricks.
What is Hallucination?
Hallucination came from the Latin word “hallucinat” which means “gone astray in thought”. Indeed, a hallucination is a false perception as the pertinent external stimuli is actually absent. As the supposed stimuli is only internally present, a person going through this sees or hears something that cannot be perceived by others. Hence, the perceptual event is not consistent with reality. This is the reason why prolonged states of hallucination is closely linked with psychological illnesses such as schizophrenia.
The following are the different kinds of hallucinations:
- Visual Hallucination – seeing something which is not actually there like seeing strange insects on somebody’s face
- Auditory Hallucination (“paracusia”) – hearing voices or sounds without any external stimuli
- Command Hallucination- hearing or being impressed with certain commands which are erroneously perceived to be from somebody else
- Olfactory Hallucination (phantosmia)– smelling something which is not there
- Tactile Hallucination- having the feeling that something is crawling under one’s skin or any related sensation involving touch
- Gustatory Hallucination- tasting something without the pertinent external stimulus such as feeling that something which is usually eaten has a very odd taste
- General Somatic Sensations- having the erroneous perception that one’s body is being mutilated
What is Illusion?
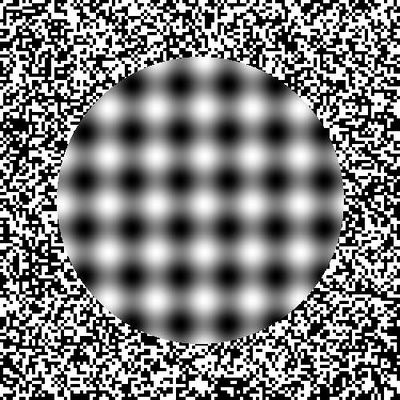
Illusion came from the Latin word, “illusio” which means “to mock”. Rightly so, it occurs when something seems to be different from what it actually is. With the alteration of the stimulus, people experience “misperception”. This happens when the brain tries to fill in gaps in the organized sensory information. Though illusions are usually related with visual processes as it dominates the others, they are also associated with the other senses.
The following are the different kinds of illusions:
- Optical illusion- makes use of visually deceptive illustrations like the Ebbinghaus and Hermann Grid illusions
- Auditory illusion- characterized by sounds which are not actually present or improbable such as those in psychoacoustic tricks
- Tactile illusion- this involves deceptions via touch such as the phantom limb wherein a patient still perceives pain in a leg which has already been amputated
- Temporal illusion- concerned with the perception distortion of time like when minutes seem to significantly slow down to hours
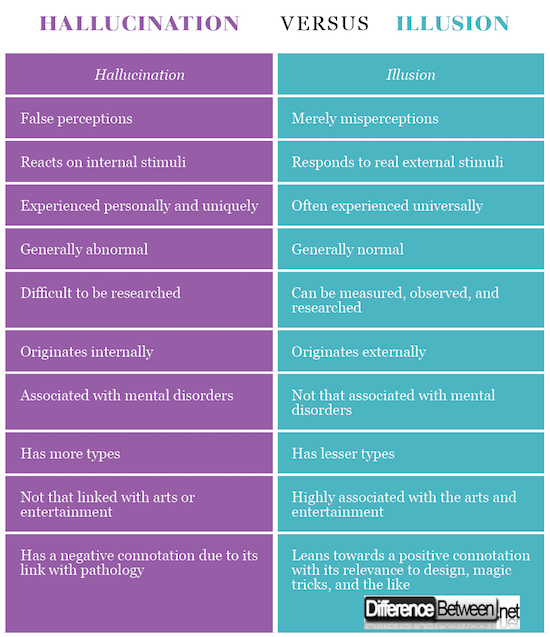
Difference between Hallucination and Illusion
-
Perception
Hallucinations are false perceptions while illusions are merely misperceptions. For instance, a hallucinating individual is arguing with someone who cannot be seen or heard by others while someone who is having an illusion interprets a straight line as broken.
-
External Stimuli
A person who is having illusions perceives certain existing external stimuli. On the other hand, an individual who is having hallucinations react on internal stimuli which only exists in his mind.
-
Universal
As compared to hallucinations, the experience of illusions is universal as they can be perceived by most, if not all, of those who are present. For instance, different groups of people at different times who are looking at an illusion will perceive the same thing. However, a person’s hallucination is highly personal as it is uniquely experienced.
-
Normal
Experiencing illusions is normal while having hallucinations is not normal as the perceptual event does not correspond with reality.
-
Research
Unlike illusions, it is harder to conduct research on hallucinations as they are private and highly internal events. As illusions can be manipulated, it is easier to study them.
-
Experience and Origin of Perception
The origin of an illusion is a real external stimulus and is rightly experienced so. However, the source of a hallucination is from the individual’s own mind but it is also experienced as something from the environment.
-
Mental Disorder
Hallucinations are typically associated with mental disorders such as schizophrenia and dementia. For instance, more than 70% of people with schizophrenia experience hallucinations. On the other hand, illusions are merely associated with minor illnesses such as migraines.
-
Types
There are more types of hallucinations as compared to illusions.
-
Art
Unlike hallucinations, illusions are employable in artistic work such as visual designs, magic tricks, and architecture.
-
Impact
Generally, the impact of hallucination is negative as it is highly associated with pathology. On the contrary, illusion is mainly linked with positive and entertaining experiences.
Hallucination vs Illusion
Summary of Hallucination vs Illusion
- Both hallucination and illusion are related with perceptual processes.
- Hallucination came from the Latin word “hallucinat” which means “gone astray in thought”.
- Illusion came from the Latin word “illusio” which means to mock.
- A hallucination is a false perception as the pertinent external stimuli is actually absent.
- An illusion occurs when something seems to be different from what it actually is.
- The usual types of hallucination include visual, auditory, command, gustatory, tactile, olfactory, gustatory, and general somatic sensations.
- The usual types of illusion include optical, auditory, tactile, temporal, and olfactory.
- Hallucinations are false perceptions while illusions are misperceptions as the former merely reacts to nonexistent external stimuli while the latter involves actual stimuli.
- Unlike illusions, it is difficult to conduct researches on hallucinations due to its uniquely experienced nature.
- As hallucinations are generally abnormal, they receive more negative connotations as compared to illusions which is largely associated with the arts and entertainment.
- Difference Between Hematoma and Melanoma - February 9, 2023
- Difference Between Bruising and Necrosis - February 8, 2023
- Difference Between Brain Hematoma and Brain Hemorrhage - February 8, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Anderson, John. Cognitive Psychology and Its Implications. Basingstoke: Worth Publishers, 2014. Print.
[1]Grondin, Simon. Psychology of Perception. Switzerland: Springer, 2016. Print.
[2]Sloman, Steven and Fernbach, Philip. The Knowledge Illusion. New York: Riverhead Books, 2017. Print.
[3]Image credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/makoy13/4262525851
[4]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/90/Hallucinations_MET_241726.jpg/616px-Hallucinations_MET_241726.jpg


Well educative, well explained and easily understood. Thank you.