Difference Between Vitamin D2 and D3
Vitamin D, also referred to as “calciferol,” is a group of fat-soluble vitamins produced by the body in response to sun exposure. So, vitamin D is also known as the sunshine vitamin. It helps regulate the amount of calcium, magnesium and phosphate in the body. A lack of vitamin D in your body may affect your bones and overall health. Vitamin D exists in two major forms: Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol).
Vitamin D2
Vitamin D2 (also known as “ergocalciferol”) is a type of vitamin D that helps the body absorb calcium and phosphorus. It helps the body to use the calcium found in natural food sources or supplements. When taken as a supplement, it prevents the symptoms of vitamin D deficiency. Ergocalciferol is an inactivated vitamin D analog used to treat calcium disorders and parathyroid disorders. It is used in the treatment of hypoparathyroidism – a rare disorder in which the body produces unusually low levels of parathyroid hormone. It may result in calcium deficiency in the blood called hypocalcemia. Mushrooms, when exposed to UV light, are a great source of vitamin D2. Plants and yeast are main sources of D2.

Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3, also known as cholecalciferol, is another form of vitamin D that is produced by the skin due to sun exposure. Like vitamin D2, it is also found in food sources or else can be taken as dietary supplements. It is important for promoting better bone health and development, and maintaining levels of calcium in the body. The best natural sources of vitamin D3 are flesh of fatty fishes, such as sardines, salmon, trout, tuna, swordfish, etc., and fish liver oil. Egg yolk and cheese contain smaller amounts of vitamin D3. The deficiency of D3 has been attributed to auto-immune problems, depression and osteoporosis. Vitamin D3 plays a key role in maintaining a healthy immune system and suppression of inflammatory cytokines.
Difference between Vitamin D2 and D3
Function
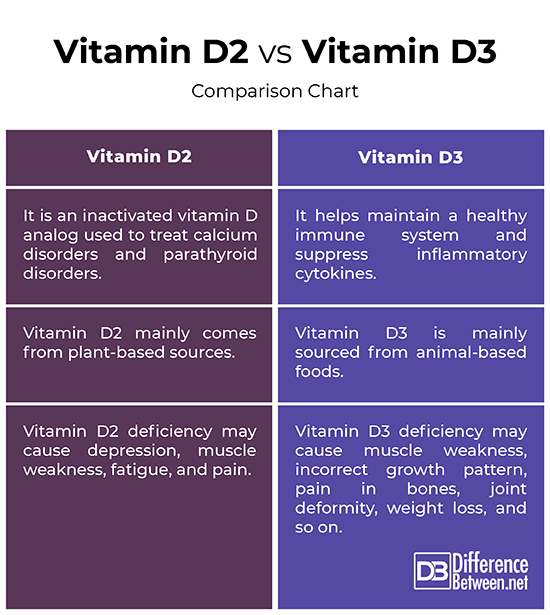
– While both the forms of Vitamin D are naturally synthesized in skin and they are well absorbed in the small intestine, they chemically differ in their side-chain structures. Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) helps the body to use the calcium found in natural food sources or supplements. It helps in maintaining healthy and strong bones. Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is the naturally occurring form of vitamin D that functions as a pro-hormone. It helps in strengthening of bones and muscles, boosting immunity and improving heart function.
Sources
– Vitamin D2 mainly comes from plant-based sources of food whereas vitamin D3 is mainly sourced from animal-based foods. Plants and yeast are main sources of vitamin D2, along with dietary supplements. Fortified foods also contain decent amount of vitamin D2. The main sources of vitamin D3 are flesh of fatty fishes, such as sardines, salmon, trout, tuna, swordfish, etc., and fish liver oil. Egg yolks, butter and cheese contain smaller amounts of vitamin D3.
Deficiency
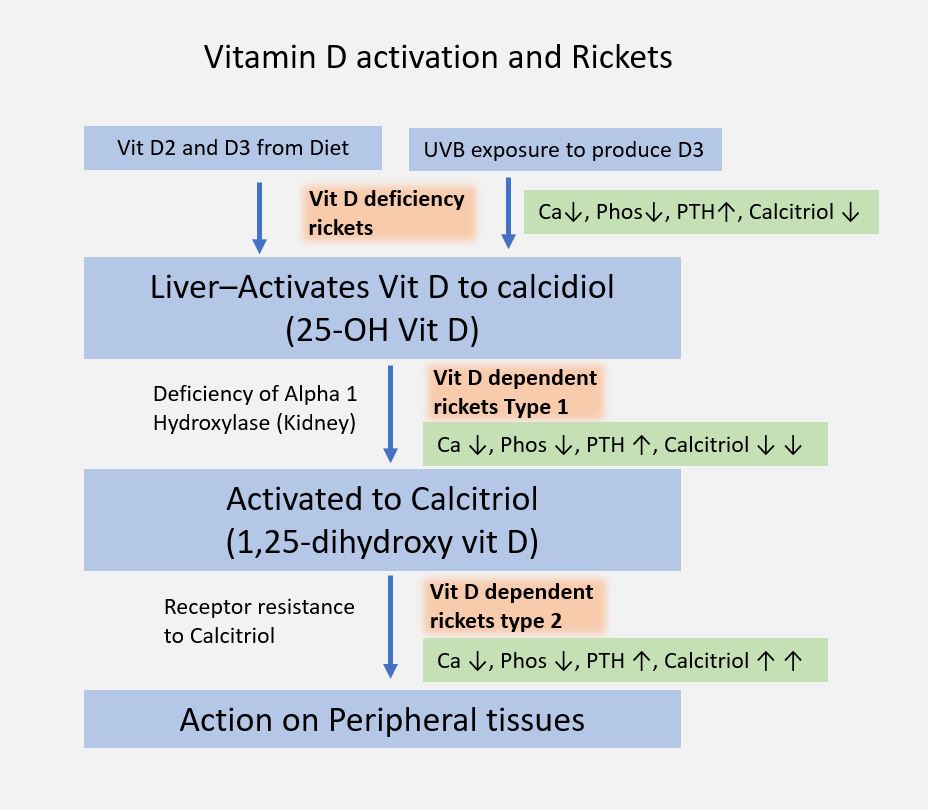
– Vitamin D2 is used to treat rickets, a common vitamin D deficiency that cause softening of bones, or hypophosphatemia, a condition that marginally reduces the levels of phosphate in the blood. Vitamin D2 deficiency may cause other symptoms such as depression, muscle weakness, fatigue, and pain. If the levels of vitamin D3 are low, it may cause muscle weakness, incorrect growth pattern, pain in bones, joint deformity, weight loss, mood swings, and so on.
Vitamin D2 vs. Vitamin D3: Comparison Chart
Summary
Both vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 are the main forms of vitamin D that help regulate the amount of calcium, magnesium and phosphate in the body. They basically play the same role in the body, but they differ in their molecular structures. One of the main differences between the two is that vitamin D2 mainly comes from plant-based sources, whereas vitamin D3 is sourced from animal-based foods. Plant and yeast are the main sources of vitamin D2, whereas the main sources of vitamin D3 are flesh of fatty fish and fish liver oil.
Why do doctors prescribe vitamin D2 instead of D3?
Vitamin D2 is used to treat rickets, a common vitamin D deficiency that cause softening of bones, or hypophosphatemia, a condition that marginally reduces the levels of phosphate in the blood. Vitamin D3, on the other hand, is mostly preferred for dietary supplementation.
Is vitamin D2 or D3 better for immune system?
Vitamin D3 offers many health benefits, including boosting immunity and improving heart function.
Which vitamin D is best?
Vitamin D3 is the naturally occurring form of vitamin D that the boy makes from sunlight. Studies suggest vitamin D3 supplements are better in raising the vitamin D stores in the body. But, choosing the best vitamin D supplement is the key to a better health.
Which is more potent D2 or D3?
Vitamin D3 is considered more potent than vitamin D2 – about 87% more potent in maintaining and raising serum 25(OH)D concentrations. It is also capable of producing greater storage of vitamin D.
When should I take vitamin D morning or night?
There is very limited research to prove whether taking vitamin D in the morning or at night may be more effective.
Is it OK to take vitamin D3 every day?
Most health experts recommend no more than 4,000 IU of vitamin a day. In the right amount, it is important for building and maintaining strong bones. Please refer to your healthcare professional for daily doses.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Watson, Ronald Ross. Handbook of Vitamin D in Human Health: Prevention, Treatment and Toxicity. Wageningen, Netherlands: Wageningen Academic Publishers, 2013. Print
[1]Hewison, Martin, et al. Vitamin D: Volume 1: Biochemistry, Physiology and Diagnostics. Massachusetts, United States: Academic Press, 2017. Print
[2]Spedding, Simon. Vitamin D and Human Health. Basel, Switzerland: MDPI, 2019. Print
[3]Gowder, Sivakumar. A Critical Evaluation of Vitamin D: Clinical Overview. London, United Kingdom: InTech Open, 2017. Print
[4]Image credit: https://world.openfoodfacts.org/images/products/009/661/939/3916/front_en.3.full.jpg
[5]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Vitamin_D_activation_and_rickets.jpg
