Difference Between Somatic Hypermutation and Affinity Maturation
Somatic hypermutation is when mutation occurs in the variable region of the B lymphocyte antibodies. Affinity maturation is when B lymphocytes develop a greater affinity for certain antigens.

What is Somatic Hypermutation?
Definition:
This is the condition where point mutations occur in the part of the antibody that’s known as the variable region (V region).
Causes:
The process of somatic hypermutation (SHM) is triggered by the action of an enzyme known as activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID). Somatic hypermutation occurs during the process of B-cell activation.
Pros:
Somatic hypermutation is a process that is important for affinity maturation. It plays a role in improving the immune response because it is an adaptive response to new antigens. It increases the diversity in mature B cells of the immune system, which can be beneficial.
Cons:
The process of somatic hypermutation can produce antibodies that are nonfunctional or do not function in the way that they are supposed to. This can have a detrimental affect on the immune response. In very rare cases, somatic hypermutation can impact the occurrence and function of oncogenes. The oncogenes can result in the development of cancerous malignancies.

What is Affinity Maturation?
Definition:
Affinity maturation is the process in which the B cells of the immune system develop a stronger response (affinity) to a foreign antigen.
Causes:
The cause of affinity maturation is a combination of somatic hypermutation and then clonal selection of the B cells. This increases the affinity of the B cells to a specific foreign antigen.
Pros:
Affinity maturation, due to the selection of better binding sites, can improve the immune response to a particular antigen. This is because the process results in longer-lasting plasma cells, which then contribute to the person’s humoral immune response. This is advantageous since the plasma cells create a memory for the immune system, making it easier to attack pathogens that the system has been exposed to previously.
Cons:
There is a limitation to how much affinity maturation can occur because it depends on how much the immunoglobulin genes can mutate.
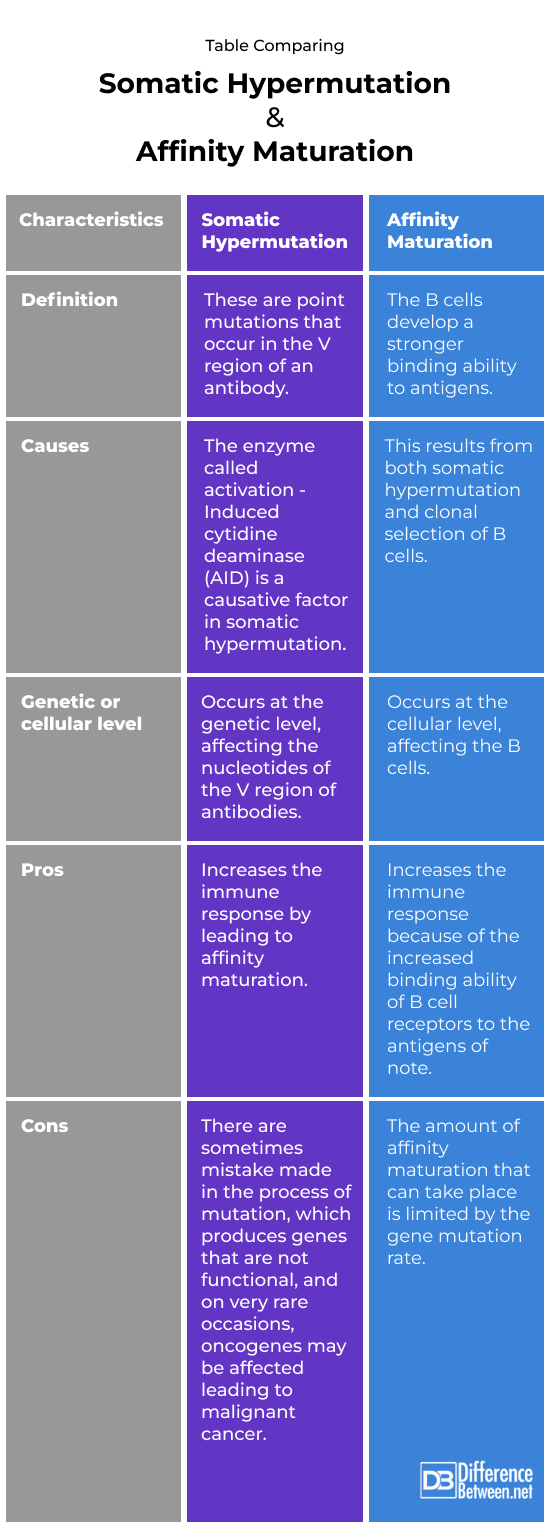
Difference betweenSomatic Hypermutation and Affinity Maturation?
Definition
Somatic mutations are point mutations that occur in the V region of an antibody. Affinity maturation is when B cells develop a stronger binding ability to antigens.
Causes
The cause of somatic hypermutations is the enzyme activation-Induced cytidine deaminase. The cause of affinity maturation is somatic hypermutation and clonal selection.
Genetic or cellular-level
Somatic hypermutation occurs at the genetic level in the form of point mutations. Affinity maturation occurs at the cellular level, with B cells being selected.
Pros
The advantage of somatic hypermutation is that it improves the immune response by leading to affinity maturation. The advantage of affinity maturation is that the immune response is better due to increased affinity to the antigens of concern.
Cons
In the case of somatic hypermutations, mistakes can sometimes be made which can produce nonfunctional genes; it can also affect oncogenes, which can cause cancer. In the case of affinity maturation, there is a limit to the extent of selection, because it depends on the rate of gene mutation.
Table comparing Somatic Hypermutation and Affinity Maturation
Summary of Somatic Hypermutation and Affinity Maturation
- Somatic hypermutation and affinity maturation are both ways that the immune response can be improved.
- Somatic hypermutation is necessary for affinity maturation to occur.
- The greater binding ability of B cells in affinity maturation helps improve the antibody-to-antigen response of the immune system.
FAQ
Is somatic hypermutation the same as affinity maturation?
No somatic hypermutation occurs at the genetic level involving point mutations while affinity maturation is at the cell level, affecting the B cells.
Where does affinity maturation by somatic hypermutation occur?
Affinity maturation by somatic hypermutation takes place in the cells found in the lymphatic tissue, such as the spleen and lymph nodes.
What is the difference between somatic hypermutation and gene rearrangement?
Gene rearrangement refers to the changing location of sequences of genes in lymphocytes of the bone marrow. While gene rearrangement can occur due to mutation (although not point mutation), it also happens during recombination. Somatic hypermutation refers specifically to point mutations at the C and G nucleotides.
How does somatic hypermutation increase affinity?
Somatic hypermutation causes changes that increase the binding ability of antibodies to antigens. This then increases affinity of B cells to specific antigens.
What is the purpose of somatic hypermutation?
The purpose of somatic hypermutation is to assist with antibody-mediated immunity.
What is the purpose of somatic hypermutation B cells?
Somatic hypermutation of B cells increases the ability of antibody sections to bind well with antigens.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Chardès, Victor, et al. "Affinity maturation for an optimal balance between long-term immune coverage and short-term resource constraints." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 119.8 (2022): e2113512119.
[1]Janeway Jr, Charles A., et al. "The generation of diversity in immunoglobulins." Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease. 5th edition. Garland Science, 2001.
[2]Pilzecker, Bas, and Heinz Jacobs. "Mutating for good: DNA damage responses during somatic hypermutation." Frontiers in immunology 10 (2019): 438.
[3]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAEEWbNbnx4-mutation-in-dna-sequence/
[4]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAEoyzZcCHc/
