Difference Between Cache and Cookies
Cache and cookies are two different types of temporary storage kept on the client’s machine to improve the user experience of browsing the Internet. Cache dramatically reduces the average time it takes for the browser to access the Web content by storing most of the content you come across on the Web locally. Caching is the most effective and the simplest mechanism to improve the browser’s response time because the browser can simply load the content from the local cache. Cookies make your online browsing experience easier by saving browsing information such as browsing session and user choices including personal information to make your browsing experience smooth and easier.
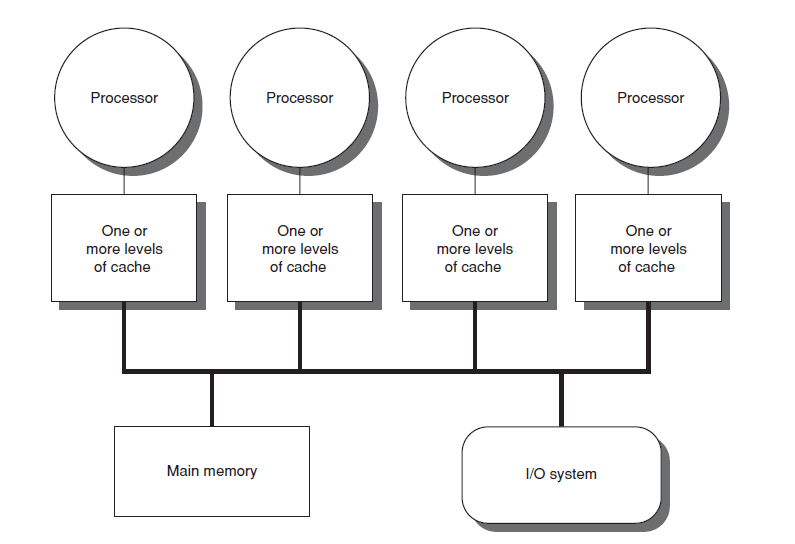
What is Cache?
A computer system, in general, is composed of three basic components: a central processing unit (CPU) which does all the heavy lifting; the memory which stores instructions and data; and an Input/output system, which moves information in and out of the system. A process repeatedly retrieves an instruction from memory to the CPU, fetches any operands that it specifies, and performs an operation, and possibly writes a result to that same memory. All the information that a processor needs over time is stored in the main memory. However, memories get slower as they get larger. Main memory is typically much slower than the CPU. To rectify this, most computers today include caches. Caches significantly reduce the average time it takes for the CPU to access the desired information. Caching plays an important role in modern computer memory and disk systems. When it comes to the World Wide Web, caching is a well-known strategy for temporarily storing frequently-accessed static content.
What is Cookies?
Cookies are created automatically every time you visit a website. Like virtual door keys, cookies are a small chunk of data generated by a web server and stored as a text file in memory or on disk. A cookie (typically an HTTP cookie) provides a way for websites to store information on a client device for later retrieval. In many respects, cookies are the solution for the problems caused by HTTP’s stateless, which maintains no record of the pages you visit at a website. Cookies are typically used to represent or reference private information, and they should not be shared between users. Cookies make your online browsing experience easier by saving browsing information. Cookies enable the server to keep track of your browsing activity and compile a list of your purchases. Some cookies are stored in memory and are deleted when the browser is closed. These are called session cookies.
Difference between Cache and Cookies
Meaning
– A web cache (or HTTP cache) is a core design protocol of the HTTP protocol used to store on-line page resources during a browser for the long run to improve the performance of the web-based system. Web caching is a well-known strategy for temporarily storing frequently-accessed static content. A cookie (or HTTP cookie), on the other hand, is a small chunk of data generated by a web server and stored as a text file in memory or on disk. Cookies provide a way for websites to store information on a client device for later retrieval.
Storage
– Web caching caches popular objects at location close to the clients to avoid Web service bottleneck, reduce traffic over the Internet, and improve scalability of the Web system. When you visit a web page, all the elements are downloaded and stored locally in the browser cache so that if you visit the page again, the locally stored elements do not have to be downloaded again. Website preferences and other information can be stored in cookies. While some cookies are stored in memory and are deleted as soon as the browser is closed, there are cookies that remain on a device until they expire or are deleted.
Use
– The browser cache stores most of the content you come across on the Web locally to help improve the browser’s response time when visiting the website again. Browsers pull HTML documents, images and other web page elements to the local device and it stores that content in temporary files as browser cache or Web cache. Cookies, on the other hand, can track your movement about your activity around a website and they make your online browsing experience easier by saving browsing information as well as an information you’ve volunteered, such as your name and interests.
Cache vs. Cookies: Comparison Chart
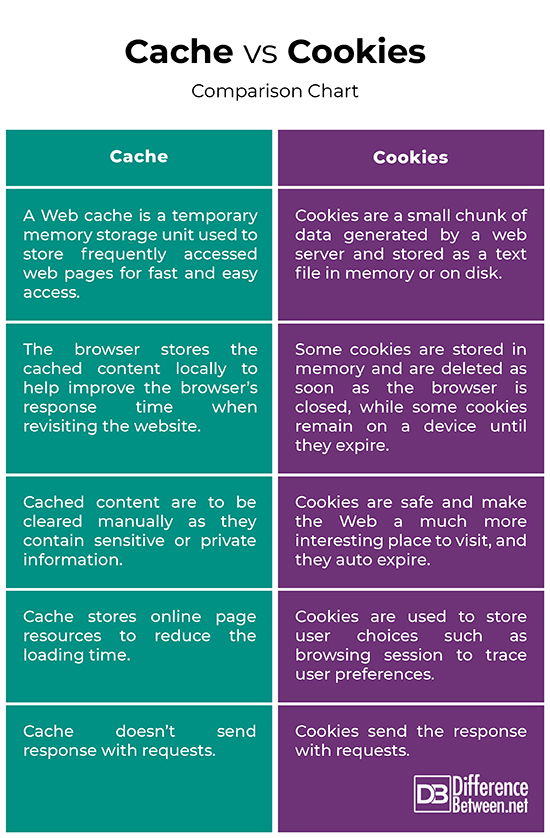
Summary of Cache vs. Cookies
Caching plays an important role in modern computer memory and disk systems, and when it comes to the World Wide Web, caching is a well-known strategy for temporarily storing frequently-accessed static content help improve the browser’s response time when revisiting a website. Web cookies, on the other hand, provide a way for websites to store information on a client device for later retrieval and make the Web a much more interesting place to visit. Cache stores online page resources while cookies store user choices such as browsing session to trace user preferences. Cookies are created automatically every time you visit a website.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Jacob, Bruce, et al. Memory Systems: Cache, DRAM, Disk. Burlington, Massachusetts: Morgan Kaufmann, 2010. Print
[1]Przybylski, Steven A. Cache and Memory Hierarchy Design: A Performance Directed Approach. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2014. Print
[2]Yu, Wen and Haibo He. Advances in Neural Networks Isnn 2009: 6th International Symposium on Neural Networks, Isnn 2009 Wuhan, China, May 26-29, 2009 Proceedings. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2009. Print
[3]Parsons, June J. New Perspectives on Computer Concepts 2018: Comprehensive. Boston, Massachusetts: Cengage, 2017. Print
[4]Image credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/refletsdevert/5463547866/
[5]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cache_Organization.png
