Difference Between Humanoid and Robot
For centuries, imagination has been the sheer driving force behind all technological revolutions and creations. Technology didn’t shape the future just by itself, rather it intertwined with the imaginations and thoughts of those who believed that anything could be possible. If no one would have thought about automation, robots would still be a thing of the distant future. Robots were once a far-off fantasy but now robots are everywhere, performing the jobs of humans more efficiently and with greater accuracy than humans. We have become so accustomed to thinking of robots as part of our future that it’s sometimes hard to process that they were actually conceived over thousands of years ago.
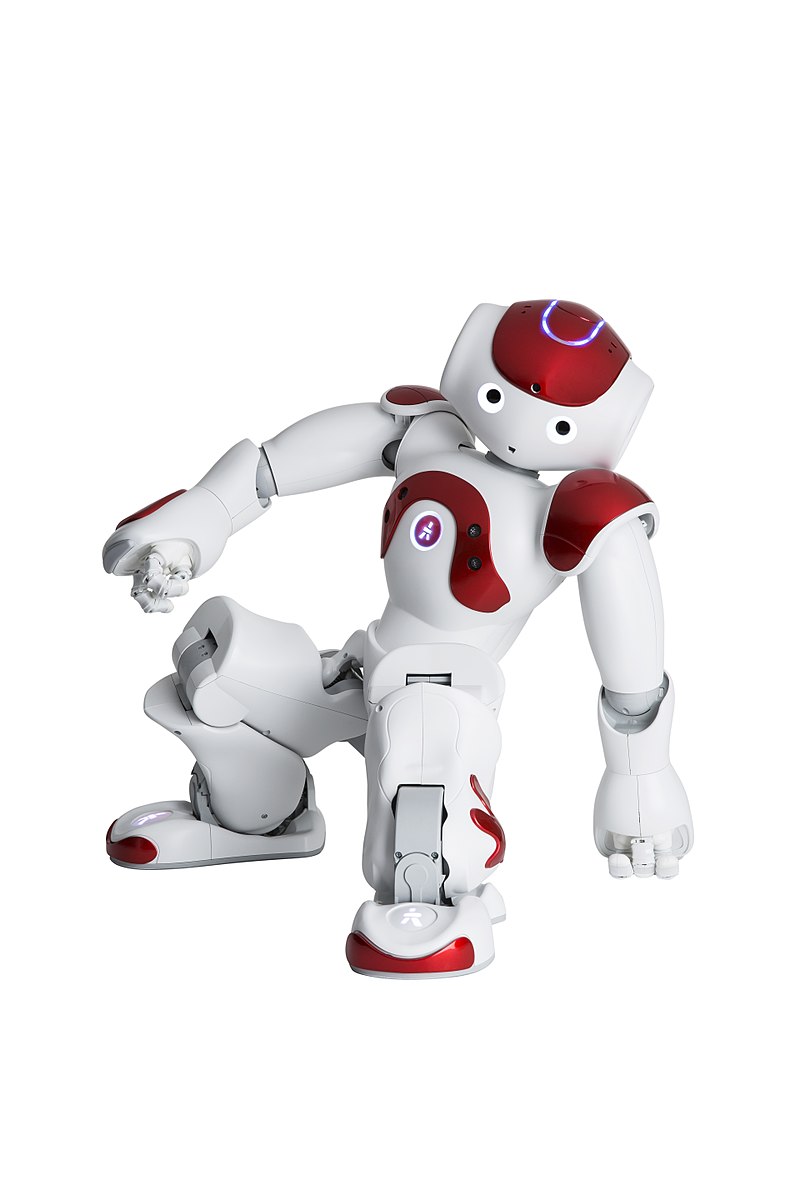
It’s easy to get an impression that robots are changing our lives in so many ways and they always have been for years. We didn’t even realize when robots have become organic, created in a lab from living tissue and cells to look and be just like us, but better and more resilient. Robots have become humanoid robots with a human-like shape. The drive to create smart and intelligent human-like artificial machines has led to the development of humanoids. The advances in robotics engineering have really illuminated the future of humanoid robots. From a largely dominant industrial focus, robotics has fairly expanded into the challenges of unstructured environments. The only confusion comes when robots start to look and act like humans.
What is a Robot?
A robot is a machine capable of executing a complex series of tasks automatically with utmost speed and precision. Robots are automatically operated machines that are designed to replace human effort though they may not resemble humans in appearance or perform tasks like the humans. The definition of a robot is very broad. Like all sophisticated technologies, robots are a result of years of accumulated knowledge about the laws of physics, mathematics and geometry. The very first idea of robots was to create manufacturing machines to replace humans in laborious tasks. Early industrial robots had neither sensing ability nor reasoning ability; they were strictly programmed to execute pre-specified tasks. The industrial robots of today are equipped with computer vision and other sensors and on-board processors that would allow for some autonomy. Robots come in a variety of shapes and sizes.
What is a Humanoid?
A humanoid is a robot with a human-like appearance that allows interaction with tools or environments made for humans. Humanoid robots are complex machines capable of performing a variety of tasks within different environments. The external appearance of a humanoid robot is based on that of the human body, including the way it moves closely resembles human movement. Humanoids provide a platform to study the construction of systems that behave and interact like humans. In addition, it provides a physical visual of how humans interact, think and react with the surroundings. Humanoid robots can work in the environment for humans such as dwelling, factory, office, disaster zones, etc. In addition, humanoids are designed to use tools and manipulate objects designed for humans.
Difference between Humanoid and Robot
Definition of Humanoid and Robot
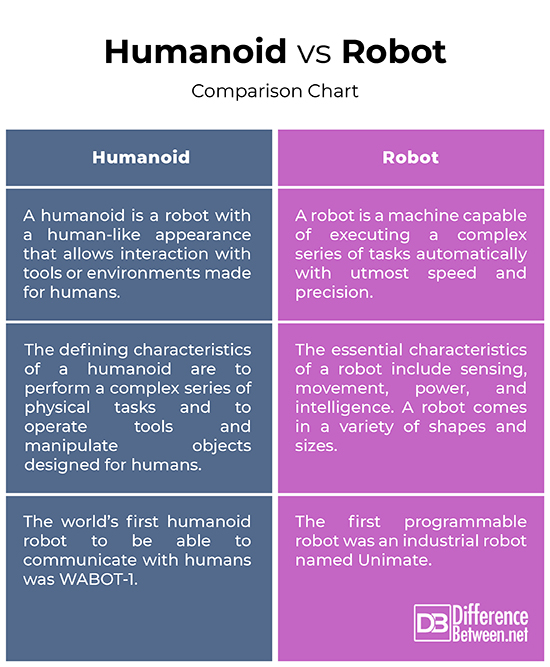
– A robot is a machine capable of executing a complex series of tasks automatically with utmost speed and precision. A robot is any computer-programmed machine designed to perform actions normally intended for humans, either automatically or by remote control, though they may not resemble humans in appearance or perform tasks like the humans. Coming to humanoids; there is no commonly accepted definition of the term humanoid. Nevertheless, the external appearance of a humanoid robot is based on that of the human body, including the way it moves closely resembles human movement.
Characteristics
– A robot is an automatically operated machine that comes in a variety of shapes and sizes. A robot can be distinguished by a few essential characteristics including the ability to sense its surroundings and to be able to move around its environment, and the most important of all, human intelligence which requires some kind of programming. The defining features of humanoid robots can be derived based on their ability to operate autonomously in various environments; to perform a complex series of physical tasks designed for humans; to operate tools and manipulate objects designed for humans; and to interact with humans without endangering them.
Applications of Humanoid and Robot
– Industrial robots aid in common industrial applications such as welding, lifting, cutting, sorting, painting, etc. More advanced robots are used almost everywhere, from intelligent home system to space shuttles, from surveillance drone robots to space exploration, and from farming applications to inspecting disaster prone areas. Robots are also used in the field of medicine for surgical assistance and to transport dangerous substances. Humanoids are basically robots that are designed to mimic human behavior. A broad range of applications from daily household works to complex medical surgery, deep ocean exploration, and other dangerous tasks are performed by humanoid robots.
Humanoid vs. Robot: Comparison Chart
Summary of Humanoid vs. Robot
Robots have no officially accepted definition; they represent very different structures and abilities and are used in a wide range of applications from daily household works to complex medical surgery, deep ocean exploration, and other potentially dangerous tasks. Humanoids are no different than robots; in fact, they are robots that mimic the external appearance and behavior of humans, including the way they move, react, behave and respond. A humanoid is a robot with a human-like appearance that allows interaction with tools or environments made for humans.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:NAO_Robot_.jpg
[1]Image credit: https://pixnio.com/objects/electronics-devices/humanoid-robot-device-robot-machine-technology-modern-indoor
[2]Nocks, Lisa. The Robot: The Life Story of a Technology. Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Publishing Group, 2007. Print
[3]Nenchev, Dragomir N., et al. Humanoid Robots: Modeling and Control. Oxford, United Kingdom: Butterworth-Heinemann, 2018. Print
[4]Kajita, Shuuji, et al. Introduction to Humanoid Robotics. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2014. Print