Difference Between Internet of Things and Cloud Computing
We live in a world swarming with data – it is the backbone of the digital age. In this data-centric world, it’s important to manage inflow, storage and exploration of massive piles of data and volume of information coming from multiple sources. These data, in their current form, do not have any meaning unless they are being collected and mined for information. The question is not how much data you have, but what you can do with it. This calls for good design principles that can leverage the different tools to extract insights from the big data so that to uncover potential business value. Internet of Things and Cloud computing are two closely affiliated technologies that have become the backbone of this data-centric world. So, what is IoT? And what is Cloud computing? Let’s take a look.
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a vast network of physical objects, devices, buildings, vehicles, and other ‘things’ which could be embedded with sensors, electronics and software that allow them to collect and interchange data. IoT is a system of interconnected things that have unique identifiers and which are capable of exchanging data over a network with little or no human interaction. The Internet is the most important and disruptive technology ever invented. The internet is part of our lives now. But, the Internet is not just about connective people; it’s about connecting things – the things that have the ability to share their experiences with other things.
When you take things and give them the ability to sense, touch, control, and communicate, they become the Internet of Things. Smartphone is one of the best examples of the Internet of Things – it knows if you’re moving the phone, it knows how much light is in the room, it detects if you are holding it close to your ears, and well, it knows a lot of things. And it also has the ability to facilitate communication over a wireless network. Other examples of IoT include connected appliances, fitness trackers, smartwatch, air quality sensors, smart assistants, smart home security systems, etc.
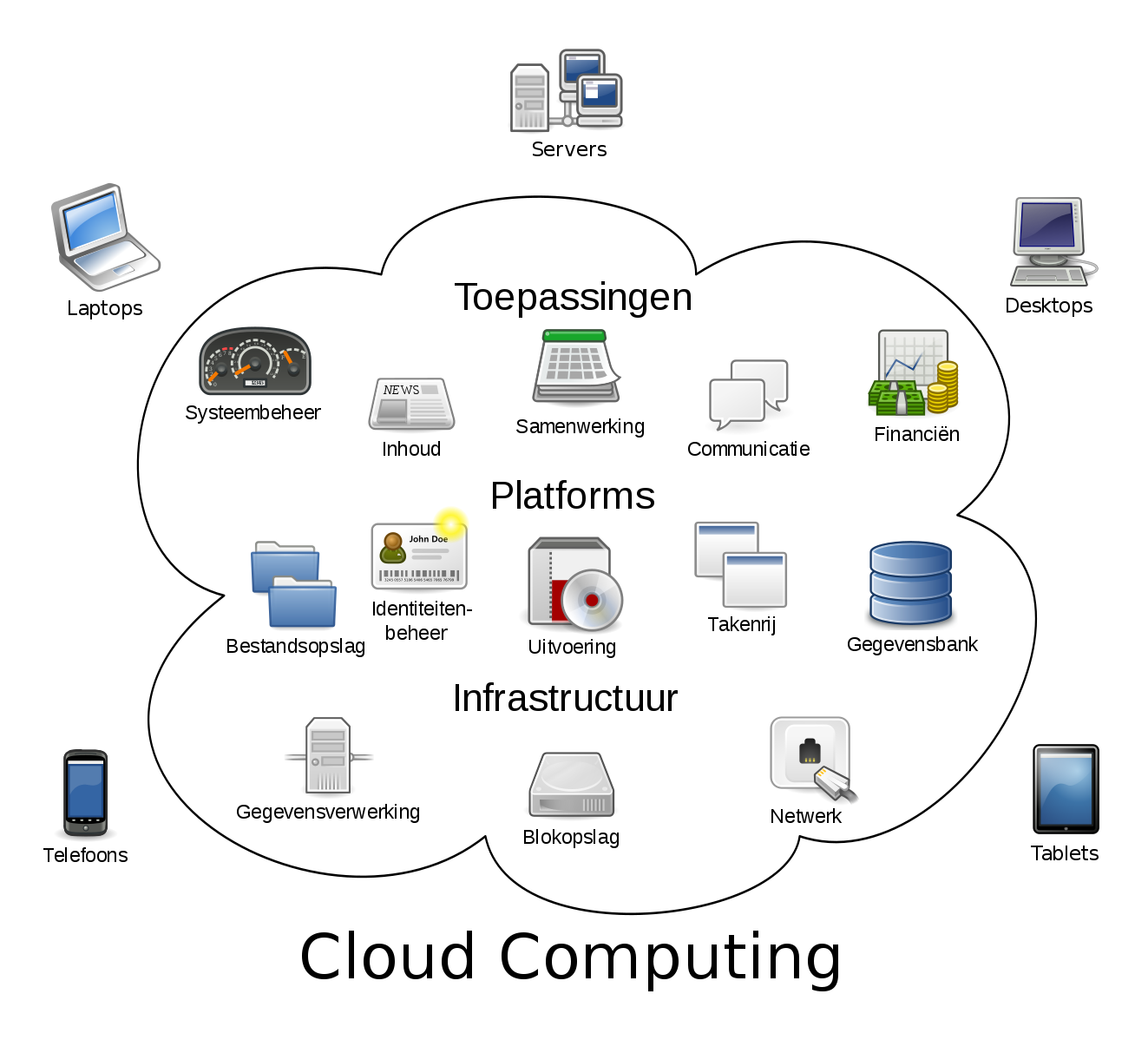
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of computing resources – including servers, databases, storage, software, networking, and other IT resources – via the internet based on a pay-as-you-go model. On-demand means that a user can request and receive access to a service offering, without the need of an administrator or a support staff. Cloud computing allows access to large amounts of computing power virtually, by aggregating resources and offering a single system view. The terms cloud computing has been coined as an umbrella term to describe a plethora of on-demand computing services initially offered by commercial providers, such as Amazon, Google, and Microsoft. It describes a model on which a computing infrastructure is viewed as a ‘cloud’ from which individuals and businesses access computing resources and applications from virtually anywhere they want on-demand.
Which one is better IoT or Cloud computing?
The Cloud computing collects the data from the IoT sensors and compute it accordingly. Over the past few years, the integration of IoT and cloud computing have contributed to the implementation of several application scenarios such as smart transportation, cities and communities, homes, environment, and healthcare. Both the technologies serve to increase efficiency in our everyday tasks. Although, both are very different paradigms, they are not contradictory technologies; in fact, they complement each other.
Difference between Internet of Things and Cloud Computing
Meaning of Internet of Things and Cloud Computing
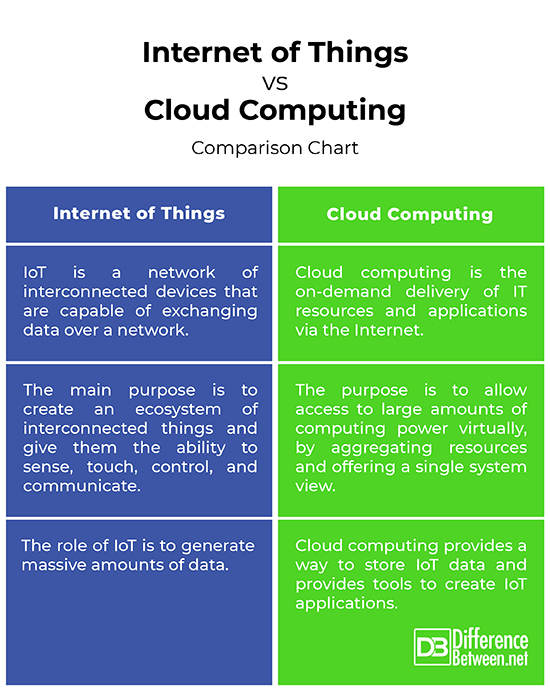
– IoT is a system of interconnected things that have unique identifiers and which are capable of exchanging data over a network with little or no human interaction. IoT is a network of interconnected devices, machines, vehicles, and other ‘things’ which could be embedded with sensors, electronics and software that allow them to collect and interchange data. Cloud computing allows individuals and businesses access to on-demand computing resources and applications from virtually anywhere they want.
Purpose of Internet of Things and Cloud Computing
– The main purpose of IoT is to create an ecosystem of interconnected things and give them the ability to sense, touch, control, and communicate with other things. The idea is to connect everything and everyone, and help us live and work smarter. IoT provides businesses real-time insights into everything from everyday operations to performance of machines and logistics and supply chain. Cloud computing, on the other hand, helps us make the most out of all the data generated by the IoT, giving us the flexibility of connecting to our business from anywhere, anytime we want.
Applications of Internet of Things and Cloud Computing
– The most important and common applications of IoT are smartwatches, fitness trackers, smartphones, smart home appliances, smart cities, automated transportation, smart surveillance, virtual assistants, driverless cars, thermostats, implants, lights, and more. The real world examples of cloud computing include antivirus applications, online data storage, data analysis, email applications, digital video software, online meeting applications, etc.
Internet of Things vs. Cloud Computing: Comparison Chart
Summary
While both IoT and Cloud computing are two different technologies that aim to make our everyday lives easier, they are not contradictory technologies; in fact, they complement each other. Both work in collaboration to increase efficiency in our everyday tasks. The basic concept of IoT is connectivity wherein physical objects or things are linked to the web – from fitness trackers to smart cars and smart home appliances. The idea is to connect everything to the internet and control them from the internet. Cloud computing helps manage the IoT infrastructure.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Tomar, Pradeep and Gurjit Kaur. Examining Cloud Computing Technologies Through the Internet of Things. Pennsylvania, United States: IGI Global, 2017. Print
[1]Singh, Surjit and Rajeev M. Sharma. Handbook of Research on the IoT, Cloud Computing, and Wireless Network Optimization. Pennsylvania, United States: IGI Global, 2019. Print
[2]Rountree, Derrick and Ileana Castrillo. The Basics of Cloud Computing: Understanding the Fundamentals of Cloud Computing in Theory and Practice. London, United Kingdom: Newnes, 2013. Print
[3]Buyya, Rajkumar, et al. Cloud Computing: Principles and Paradigms. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2010. Print
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cloud_computing_nl.svg
[5]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/4355/36802620122_fe3ca90fca_c.jpg
