Difference Between Collagen and Retinol
Collagen is a type of protein that contains a lot of proline, hydroxyproline and glycine, and is an important part of connective tissues. Retinol is the molecule known as vitamin A, and is a molecule which is very important for vision.
What is Collagen?
Definition:
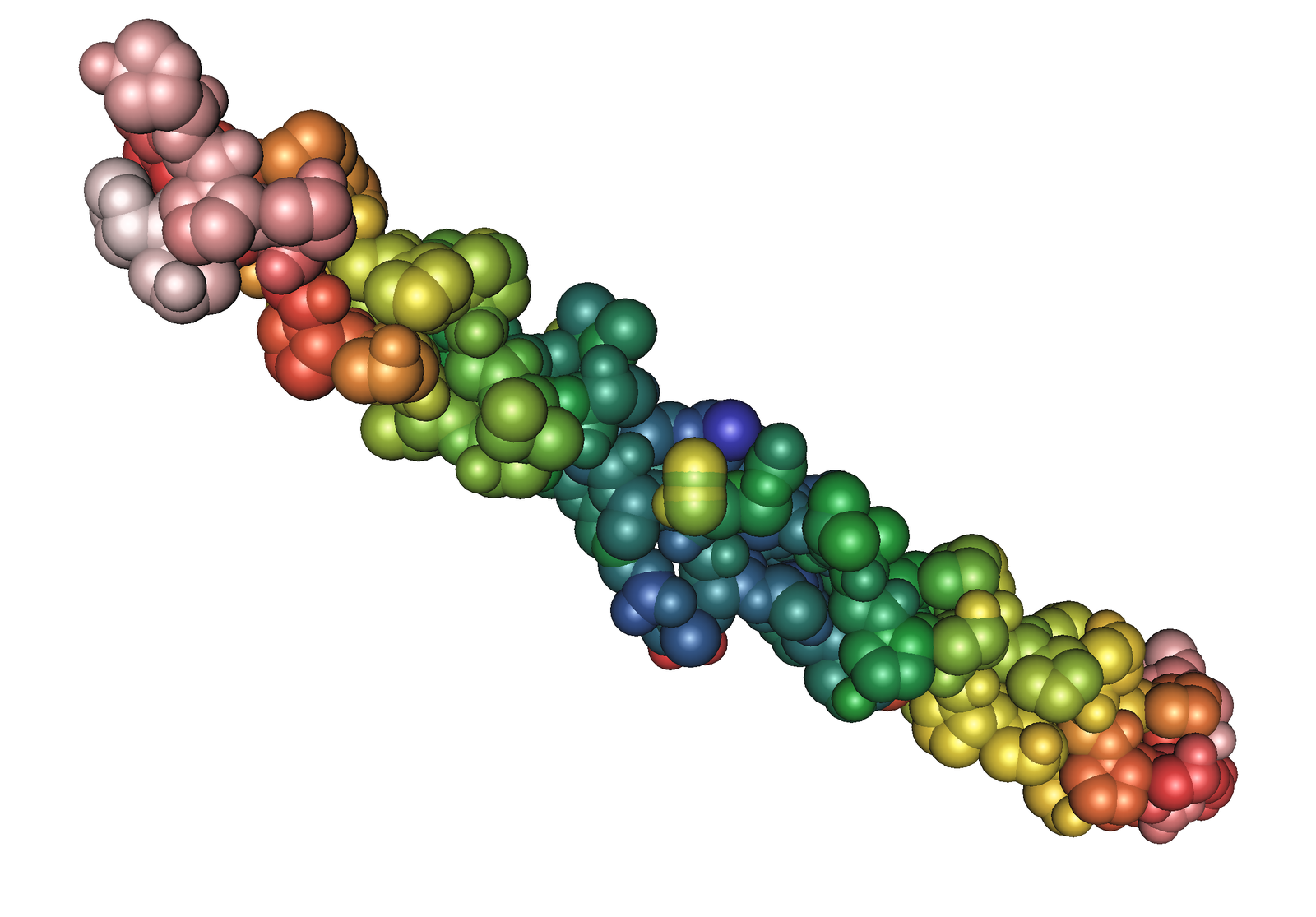
Collagen is comprised of several polypeptides chains that are comprised of glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline components.
Structure:
The collagen consists of three chains of protein subunits which together make up a helical structure containing several covalent bonds. Glycine occurs about every third residue on the chain of polypeptides. Many types of collagen have been discovered throughout the human body forming an important part of many tissues.
Functions:
The collagen fibers of the body are an essential protein making up the matrix of connective tissues such as ligaments and tendons, which occur at the joints of the body. It is also an important part of the skin and is a flexible material which is also tough and does not easily break.
Formation:
Collagen is made by special cells called fibroblasts, and it is made by a combination of proline, lysine, sugars and hydroxyl groups bonded together in a specific way. Enzymes can also make a small amount of collagen outside of cells from procollagen precursor molecules.
Disorders where there are problems related to collagen:
There is a disease called Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) in which type III collagen is not formed from the cells, resulting in connective tissue problems that can lead to joint dislocations and even problems with the aorta. Since collagen is an important part of connective tissue, the lack of type III specifically causes problems including an increased risk of aortic dissection.
What is Retinol?
Definition:
Retinol is the main form of vitamin A, which is a nutrient we need to take into the body to help the functioning of the photoreceptor cells of the eyes.
Structure:
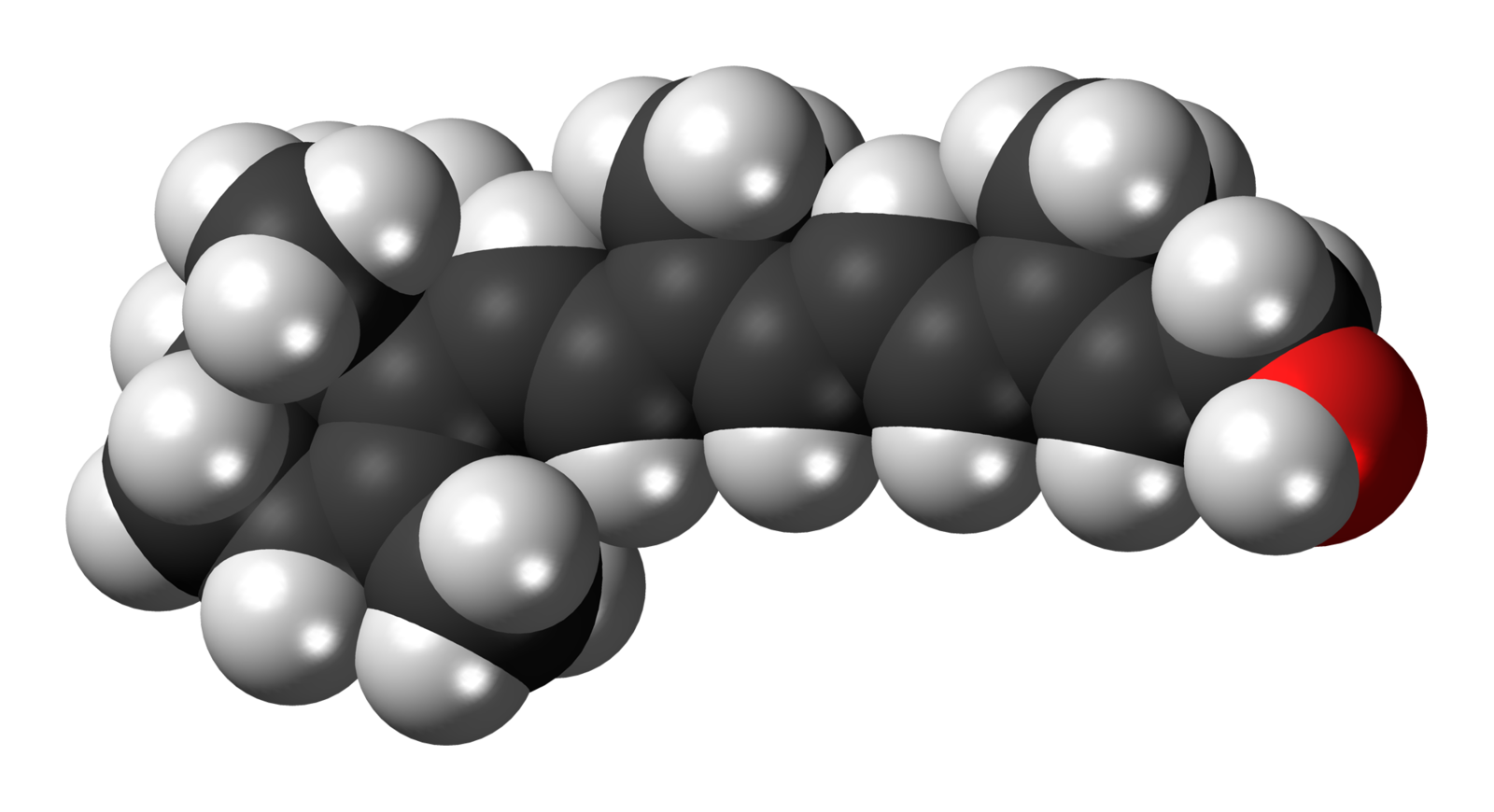
The molecular structure of retinol is that of an alcohol which has the molecular weight of 286, 45 g/mol. The formula for retinol is C20H30 and it is a vitamin that is soluble in fat which means that it can be stored in the liver cells. Retinol is readily broken down by increasing temperatures or by lowering the ph. Retinol melts at about 63oC and boils at 137 oC.
Functions:
Vitamin A is important since it is essential for good eyesight. This is because vitamin A, retinol, is transformed into the molecule retinal which plays a role in the functioning of the photoreceptor cells of the eye. These are the cells that are responsible for receiving light energy in the eye, and thus are important in vision. Vitamin A deficiency can be a problem causing issues with your eyesight, but excess amounts of vitamin A can also be dangerous since this is a fat-soluble vitamin that accumulates in the liver cells.
Formation:
The formation of retinol is achieved using the precursor molecule provitamin A, which is often taken in with food or by taking vitamin supplements. Carotenoid pigments found in the fruits and vegetables are also converted into retinol by the action of the enzyme β-carotene 15, 15′-dioxygenase.
Disorders where there are problems related to retinol:
Taking in excessive quantities of vitamin A can be harmful and even deadly while taking in too little vitamin A can cause night blindness and has been associated with an increase in infant mortality in developing countries.
Difference between Collagen and Retinol?
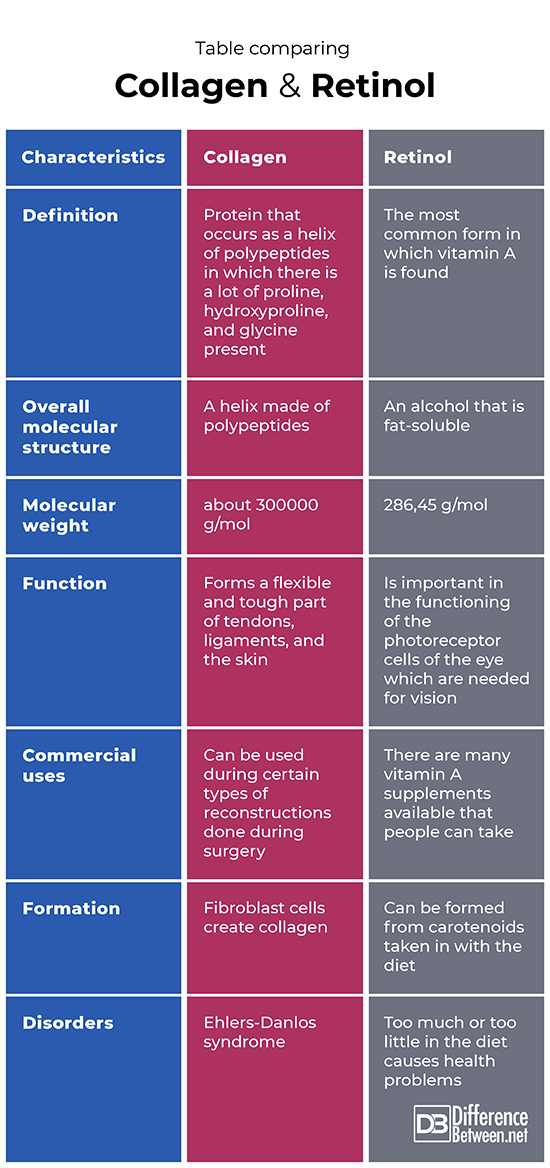
Definition
Collagen is a protein helix made of polypeptides that have a lot of hydroxyproline, glycine and proline present. Retinol is the most common form in which vitamin A is found in the human body.
Overall molecular structure
The molecular structure of collagen is that of a helical shape comprised of polypeptide chains linked together by covalent bonds. The molecular structure of retinol is that of an alcohol.
Molecular weight
The molecular weight of collagen is about 300000 g/mol. The molecular weight of retinol is about 286, 45 g/mol.
Function
Collagen forms a flexible and tough part of tissues such as tendons, ligaments, and the skin. Retinol is essential for the correct functioning of the photoreceptor cells of the eye which are needed for vision.
Commercial uses
Collagen is used in some types of reconstructive surgeries. Retinol is available as supplements that people can take if their diet is lacking in vitamin A.
Formation
Fibroblast cells found in connective tissue are responsible for producing the collagen. Vitamin A, retinol, can be formed from carotenoids that are taken in in the diet.
Disorders
A disorder related to collagen is Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. A person can have disorders if they take in too much or too little retinol.
Table Comparing Collagen and Retinol
Summary of Collagen Vs. Retinol
- Collagen and retinol are both important substances found in the human body.
- Collagen is a fibrous protein that is an essential component of connective tissues.
- Retinol is the most abundant form in which vitamin A is found in the body.
- Collagen is secreted by cells called fibroblasts.
- Vitamin A is made from carotenoid pigments taken in through the diet, and from various provitamin A precursor molecules.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Retinol_3D_spacefill.png
[1]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:1bkv_collagen_02.png
[2]Brodsky, Barbara, and Anton V. Persikov. "Molecular structure of the collagen triple helix." Advances in protein chemistry. Vol. 70. Academic Press, 2005. 301-339.
[3]O'Byrne, Sheila M., and William S. Blaner. "Retinol and retinyl esters: Biochemistry and physiology Thematic Review Series: Fat-soluble vitamins: vitamin A." Journal of lipid research 54.7 (2013): 1731-1743.