Difference Between Collagen and Elastin
Collagen is a type of protein that consists of three chains of polypeptides arranged to form a helix. Elastin is a type of protein consisting of various tropoelastin molecules linked together with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic components.
What is Collagen?
Definition:
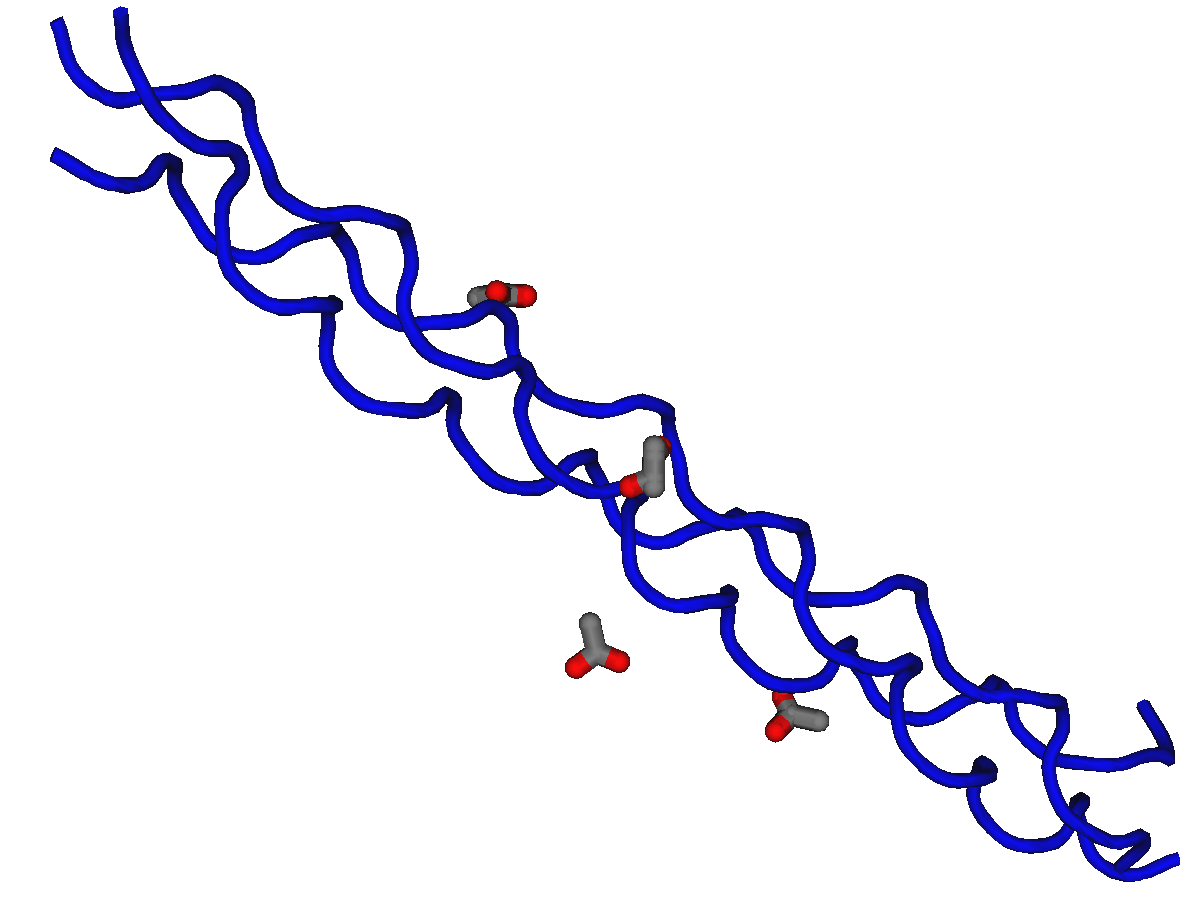
Collagen is a protein that occurs as a triple helix made of three chains of polypeptide proteins containing glycine, hydroxyproline, and proline amino acids.
Structure:
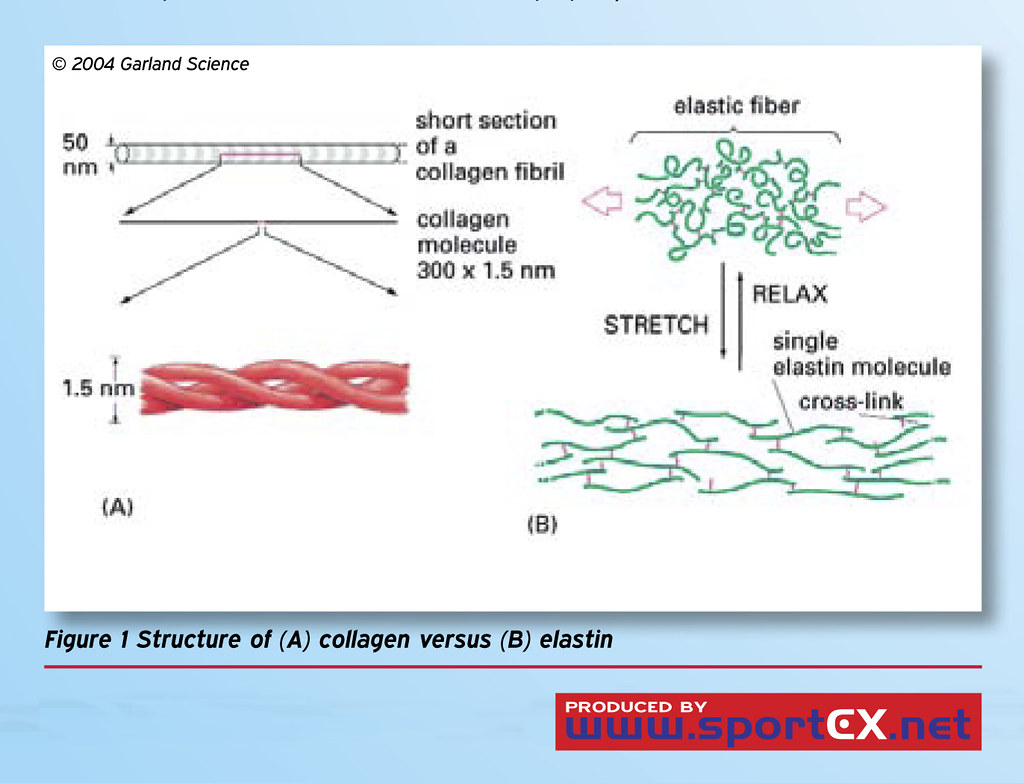
Covalent bonds join the chains of polypeptides of the helix of collagen, and the glycine amino acids occur as every third residue in the molecule. There are three types of collagen found in the human body with type I being the most numerous.
Functions:
This is the main protein found making up much of the connective tissues in humans. It is particularly abundant forming parts of the skin and is found in tendons that connect muscle to muscle. Collagen is also an important part of the ligaments that join bone and muscle together at the joints. Collagen is a strong material that has limited elasticity and flexibility.
Formation:
Fibroblasts are the cells found in connective tissue that actually makes the collagen usually by uniting the amino acids proline and lysine with sugars and other functional groups. A small amount of collagen is also made extracellularly by means of enzymes working on procollagen molecules.
Disorders where there are problems in collagen formation:
The disease Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is when type III collagen is not made by the cells, which then has consequences for connective tissues. People who have EDS are at high risk of joint dislocation and aortic dissections.
What is Elastin?
Definition:
Elastin is a protein molecule that is made of several tropoelastin molecules, which are comprised of hydrophobic and hydrophilic components containing many lysine amino acids, along with glycine and proline molecules.
Structure:
The elastin is made up of many tropoelastin molecules which are linked together and include lysine. There are also alanine, proline and glycine residues, but unlike in collagen the glycine residue does not occur at each third position, and a helix is not formed like in collagen.
Functions:
Elastin is an important tissue that helps make up many connective tissues which helps to give elasticity to such organs as the blood vessels and lungs in the human body. The elastin has great elasticity (1000 times more so than collagen), which enables the lungs to recoil and blood vessels to be able to expand and contract when needed. A further function of elastin is to help regulate cell behavior and to combine with other proteins of the extracellular matrix of connective tissues.
Formation:
Elastin can be formed from chondrocytes in cartilage and fibroblast cells of other connective tissues. The protein elastin is coded for by a single gene within the DNA of humans, and can also be formed by smooth muscle cells and by cells of the endothelium.
Disorders where there are problems in elastin formation:
Problems associated with the gene that codes for elastin results in several different types of disorders including supravalvular aortic stenosis, Williams disorder, and even a tendency for atherosclerosis to develop.
Difference between Collagen and Elastin?
Definition
Collagen is a protein that is made of three polypeptides that are arranged to form a triple helix. Elastin is a protein made of numerous tropoelastin molecules linked together involving hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups interacting.
Overall molecular structure
Collagen is a protein that is comprised of a helix that is made up of three separate component polypeptides covalently bonded together. Elastin is a protein made of several coiled components but no helix is formed
Most numerous amino acids
Proline, hydroxyproline, and glycine as every third residue make up collagen. Lysine, proline, alanine, and glycine, but glycine is not at every third residue in the case of elastin.
Flexibility
Collagen has only limited flexibility. Elastin is very flexible and in fact, is 1000x more flexible than collagen. Elastin makes up connective tissues, especially in the lungs and blood vessel walls.
Part of which tissues
Collagen makes up much of the ligaments, tendons, and parts of the skin. Elastin is found in connective tissues, particularly of the lungs and blood vessel walls.
Commercial uses
Collagen is often used as part of the surgical repair of tissues. Elastin is commonly used as part of biomaterials to make structures to repair nerves and blood vessels and even for the repair of bones.
Formation
The site of collagen formation is the fibroblast cells. The sites of elastin formation include the smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and chondrocytes.
Disorders
A disorder of collagen is Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS). Disorders of elastin include supravalvular aortic stenosis, Williams disorder, and some cases of atherosclerosis
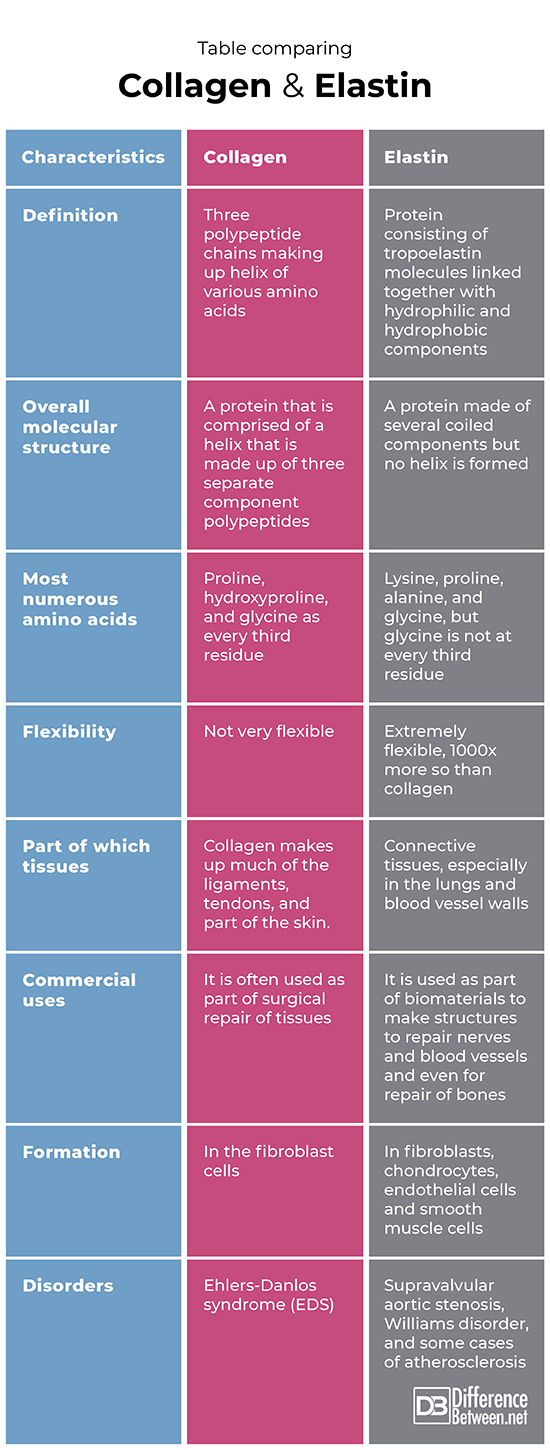
Table comparing Collagen and Elastin
Summary of Collagen Vs. Elastin
- Both collagen and elastin are both protein fibers that are found making up many connective tissues of the human body.
- Collagen contains a glycine residue at every third position while elastin does not, and collagen occurs in the form of a helix.
- Elastin is about 1000 times more flexible than collagen and is very abundant in the lungs.
- Both collagen and elastin can be formed by fibroblast cells of the connective tissue.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Brodsky, Barbara, and Anton V. Persikov. "Molecular structure of the collagen triple helix." Advances in protein chemistry. Vol. 70. Academic Press, 2005. 301-339.
[1]Green, Ellen M., et al. "The structure and micromechanics of elastic tissue." Interface focus 4.2 (2014): 20130058.
[2]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:1bkv_collagen.png
[3]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/8063/8271843643_cf41ede421_b.jpg