Difference Between Egestion and Excretion
What is Egestion?
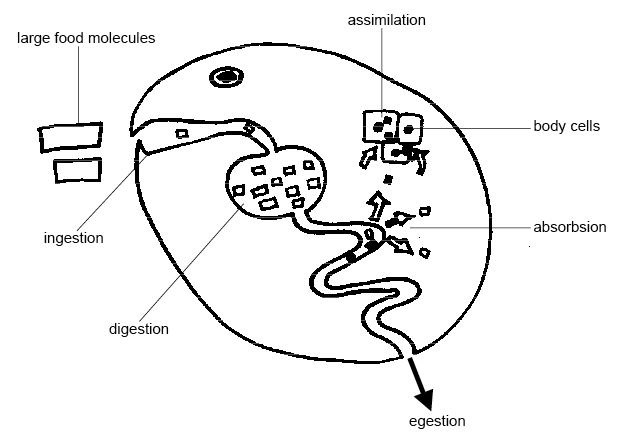
Different groups of animals egest the unutilized food in a different way. In the unicellular organisms, the undigested food is transported to the cell membrane and released outside of the body. Some multicellular animals do not have a specialized digestive system. For example, in the hydra, the food is digested in the stomach sac, and the undigested food is egested through the mouth.
In the higher animals, there is well developed and specialized digestive system. After the digestion and the absorption in the small intestine, the food, that is still not digested and not absorbed heads to the large Intestine. In the large intestine the remaining water, electrolytes, and some vitamins are absorbed. The large intestine does not have a digestive function. Many bacteria live here. They synthesize certain vitamins by breaking down some undigested substances.
Part of the food remains still undigested and unabsorbed. It has to be removed from the body. The unprocessed food remains accumulate in the colon. They are egested periodically from the body through the colon and the anus (or the cloaca). Peristaltic waves push the contents to the anus. The discharged unutilized food particles are semisolid or thick, due to the fact that most of the water is utilized in the animal body.
What is Excretion?
The process of removal of waste products, produced in the cells of animals and plants is called excretion. Through this process, the organisms maintain acid-base balance and control the osmotic pressure. Subject to excretion are substances gone through different metabolic processes inside the cells. Excretory processes in animals are the exhaling step of respiration, sweating, and urination.
The urination is the main excretory process. After entering the cells, the food processed in the digestive tract undergoes complex chemical transformations. In these transformations, waste products are released, especially uric acid. It is harmful to the body and is therefore removed from it via the excretion.
In unicellular animals and Cnidarians, excretion occurs in each cell, without special excretory organs.
The specialized excretive system appears in the flat worms. In animals with no circulatory system, excretion occurs directly from the secretory organs to the environment.
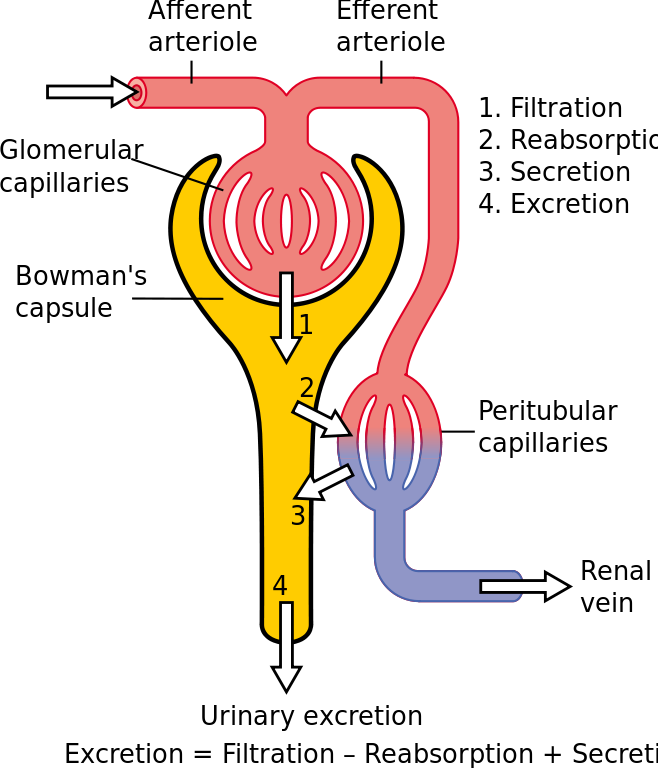
The vertebrates have well developed excretory system and organs. The waste products from the cells fall into the blood and are released through the kidneys when the blood passes through them.
The kidneys remove the salts, urea, and excess water from the blood and excrete them with the urine. From the kidney, the urine is collected by the ureter and is transported to the urinary bladder. There the urine is stored until urination when it is released into the environment through the urethra.
In plants, the excretion consists in the release of carbon dioxide and oxygen via the stomata. The carbon dioxide is produced as a result of the respiration and the oxygen – as a result of the photosynthesis.
Plants also accumulate waste products in the cells of the leaves (as crystals). They are removed from the plant’s body when the leaves fall.
Difference Between Egestion and Excretion
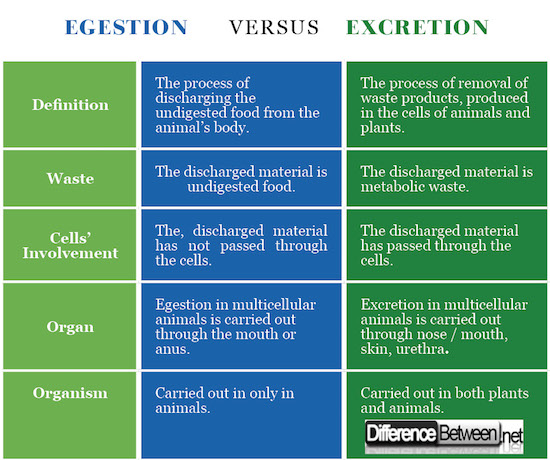
Definition of Egestion and Excretion
Egestion: The process of discharging of the undigested food from the animal’s body is called egestion.
Excretion: The process of removal of the waste products, produced in the cells of animals and plants is called excretion.
Discharged Material from Egestion and Excretion
Egestion: The material, discharged in the process of egestion is undigested food.
Excretion: The material, discharged in the process of excretion is metabolic waste.
Cells’ Involvement
Egestion: The material, discharged in the process of egestion has not passed through the cells.
Excretion: The material, discharged in the process of excretion has passed through the cells.
Organs
Egestion: Egestion in multicellular animals is carried out through the mouth or anus.
Excretion: Excretion in multicellular animals is carried out through nose / mouth, skin, urethra.
Organisms
Egestion: Egestion is carried out only in animals.
Excretion: Excretion is carried out in both plants and animals.
Egestion vs. Excretion : Comparison Chart
Summary of Egestion and Excretion:
- The process of discharging of the undigested food from the animal’s body is called egestion.
- The process of removal of the waste products, produced in the cells of animals and plants is called excretion.
- In egestion the discharged material is undigested food, while in excretion it is metabolic waste.
- The material, discharged in the process of egestion has not passed through the cells. The material, discharged in the process of excretion has passed through the cells.
- Egestion in multicellular animals is carried out through the mouth or anus, while the excretion is carried out through nose / mouth, skin, urethra.
- Egestion is carried out only in animals, while excretion is carried out in both plants and animals.
- Difference Between Gallstones and Cholecystitis - September 5, 2021
- Difference Between Constipation and Cramping - August 4, 2021
- Difference Between Whole Genome Sequencing and Microarray - May 6, 2021
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Richard H., G. Wyse, M. Anderson. Animal physiology. Sunderland: Sinauer Associates. 2008. Print.
[1]Rastogi S. Essentials of Animal Physiology. New Delhi: New Age International. 2007. Print.
[2]Arumugam N. and A. Mariakuttikan. Animal physiology. Nagercoil: Sara S Publications. 2011. Print.
[3]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7d/Physiology_of_Nephron.svg/658px-Physiology_of_Nephron.svg.png
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Anatomy_and_physiology_of_animals_From_ingestion_to_egestion.jpg#/media/File:Anatomy_and_physiology_of_animals_From_ingestion_to_egestion.jpg

Got what I wanted. Thanks