Difference Between Keto and Low carb diet
What is Keto diet and Low carb diet?
Both keto and low-carb diet revolve around a low-carb intake which will help adherents in weight loss and improve their health. Both the diets focus on real and whole foods.
What is Keto diet?
The ketogenic diet advocates low carbohydrates, adequate proteins and high fats, initiating a metabolic process known as ketosis. This diet is particularly useful for treating epilepsy in children.
The ketone bodies travel into the brain and supplant glucose (C6H12O6) as a source of energy. High levels of ketone bodies in the blood, a condition called as ketosis, leads to a minimization in the occurrences of epileptic seizures. The basics of a keto diet is:
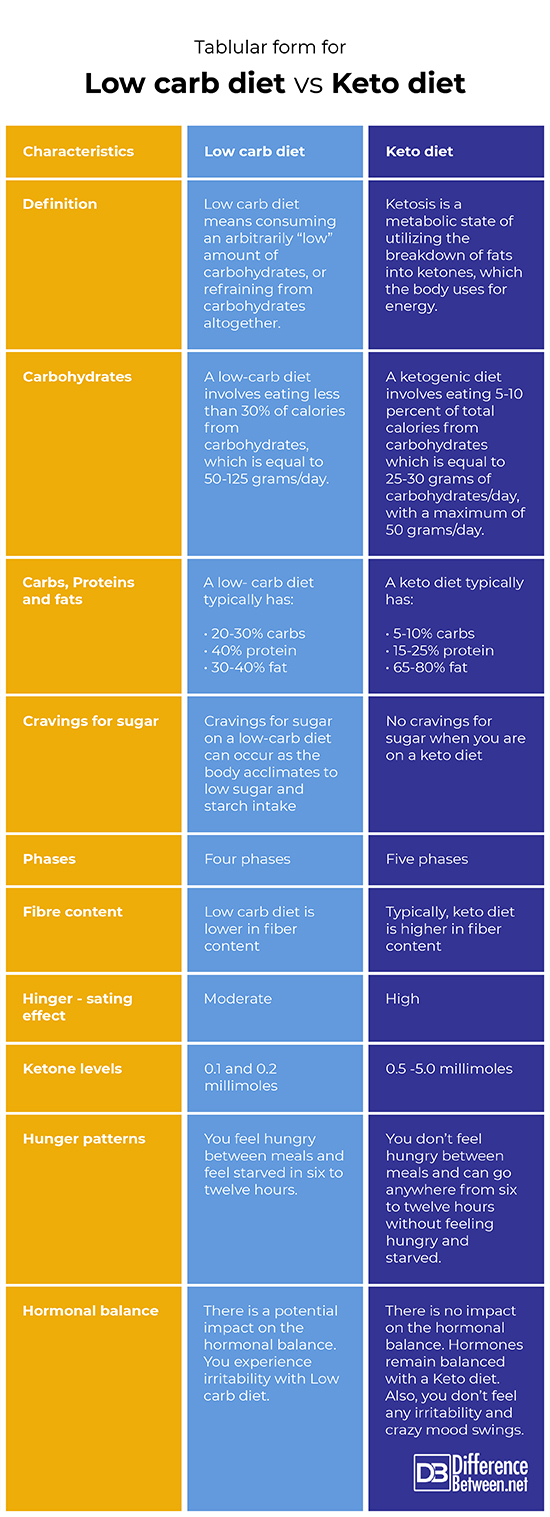
- Get 5%-10% of your calories from carbohydrates
- 15%-25% of adequate protein
- 65%-80% from high fats
Sea-food, avocados, coconut oil, meat and poultry and eggs are foods included in a ketogenic diet.
What is Low carb diet?
Basically, a low carb diet is keto, but the difference lies in the level of carbohydrates. A low carb diet has slightly more carbs – around 75-150 grams a day.
In case of a low-carb diet, weight loss is accompanied by the elevated feeling of ampleness and a propensity towards selection of nutrient-rich diet. A very low-carb diet works slightly better than a low-fat diet for an effective and long-term weight loss.
A low-carb diet limits sweets, pastas, nuts, legumes, seeds and starchy food items. A low-carb diet plan includes food items like certain fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
Difference between Low carb diet and Keto diet
-
Definition
Low carb diet
Low carb diet is defined as high-fat, high -protein diet in which carbohydrates is completely restricted. This type of diet has 4 phases.
- Phase 1 – Induction – Eat under twenty grams of carbs each day for 2 weeks. High-fats, high proteins and low carb transformation (low carb vegetables) is recommended and this way you start your weight loss.
- Phase 2 – Balancing weight Loss (On going weight loss phase) – Eat small amount of fruit and more nuts in your diet. The aim is to determine your body’s carb tolerance without causing you to regain weight or prevent losing weight.
- Phase 3 – Fine- tuning (keep consuming good carbs until weight loss slows down)
- Phase 4 – Maintenance (establish a long-term way of enjoying healthy life).
Keto diet
Keto diet is defined as a high fat, lower carbohydrates and moderate protein diet. There are 5 phases in a keto diet.
Phase 1 – First eight to ten hours of starting a keto diet – Body continues to absorb fuel from previous diet meals.
Phase 2 – One to two days from the day of starting the keto diet – Liver glycogen vanishes after twelve to sixteen hours.
Phase 3 – Three to four days from the day of starting the diet – Gluconeogenesis has started and the protein breakdown will increase.
Phase 4 – Four to seven days from the day of starting the keto diet – Ketosis starts. Brain uses more of ketones. Liver produces more of ketone bodies. Some side effects like keto-flu can be seen.
Phase 5 – After seven days from the day of starting the keto diet – Gluconeogenesis and protein breakdown slows down.
-
Protein intake
Low carb diet
There is no limit on protein intake in Low carb diet.
Keto diet
Keto diet has a limit on protein intake (20-25%)
-
Benefits
Low carb diet
Low carb diet is great for non-endurance athletes and stable energy and blood glucose. You can be more relaxed with your diet if you are following low carb diet unlike keto-diet which requires you to diligently avoid carbs.
Keto diet
Keto diet is great for weight loss, boosting exercise performance, hunger suppression, can burn about 300 more calories a day, gives steady energy throughout the day, decreases inflammation, and works very well for endurance athletes. It also improves body composition and improvement in biomarkers of health can also be seen.
-
Ketone levels
Low carb diet
Blood ketones are between 0.1 and 0.2 millimoles
Keto diet
In a Keto diet, blood ketones rise to 0.5 -5.0 millimoles
-
Ideal for
Low carb diet
Keto diet
-
Primary Objective
Low carb diet
The primary objective of Low carb diet is weight loss
Keto diet
The primary objective of Keto diet is to utilize ketone bodies as main fuel source.
Summary
The points of difference between Low carb diet and Keto diet have been summarized below:
Tablular form for Low carb diet Vs. Keto diet
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Wylie-Rosett, J., Aebersold, K., Conlon, B., Isasi, C. R., & Ostrovsky, N. W. (2013). Health effects of low-carbohydrate diets: where should new research go? Current diabetes reports, 13(2), 271-278.
[1]Iacovides, S., & Meiring, R. M. (2018). The effect of a ketogenic diet versus a high-carbohydrate, low-fat diet on sleep, cognition, thyroid function, and cardiovascular health independent of weight loss: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials, 19(1), 62.
[2]Image credit: https://pxhere.com/en/photo/636320
[3]Image credit: https://pixabay.com/en/food-diet-keto-ketodieta-fitness-3223286/