Difference Between LCHF and Keto
The LCHF diet is Low Carbohydrate and High Fat in which a person eats fewer carbohydrates and more fats. The keto diet is where ketogenesis is triggered by eating minimal carbohydrates and proteins and more fats.
What is LCHF?
Definition:
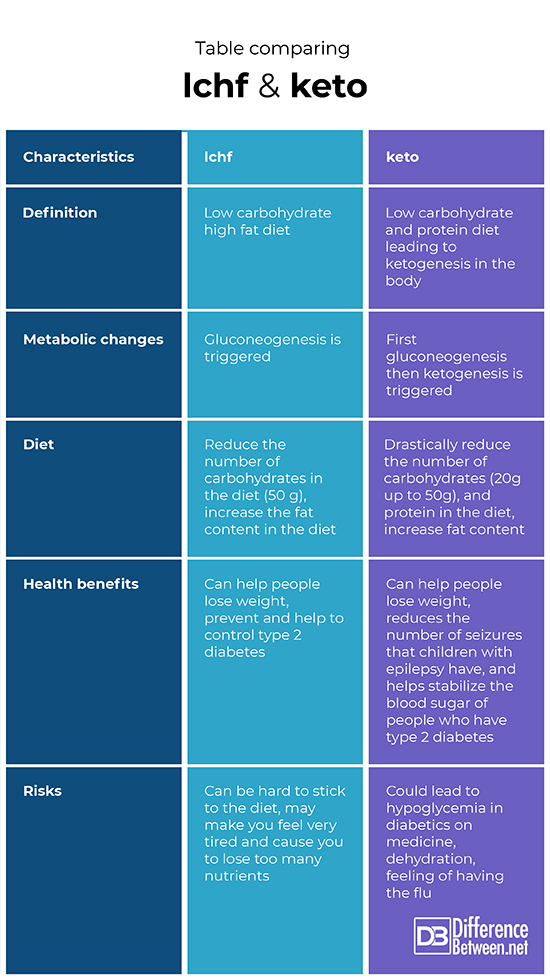
LCHF is the low carbohydrate high fat diet which encourages a person to decrease carbohydrate intake while increasing fat intake. The drop in carbohydrates causes the body to start gluconeogenesis in which glucose is produced endogenously.
The Diet of LCHF:
The suggestion for LCHF is to eat very little amounts of carbohydrates such as starches, cereals and other grain-based foods such as bread, pasta, and anything that is corn-based. Carbohydrates are limited to about 50g per day. Dried fruit should be avoided as should any processed foods and drinks that have a lot of sugar. Margarine and substances containing a lot of Omega-6 fatty acids should be avoided. These fatty acids occur in oils like sunflower and safflower. You can eat vegetables, meats, dairy products, and fish. Natural olive oil can be used for cooking.
Health Benefits in LCHF:
The Low Carb High Fat diet can help people to lose weight and more importantly can help people who have type 2 diabetes. It may help prevent type 2 diabetes because the presence of carbohydrates in the digestive system triggers the release of insulin, so taking in fewer carbohydrates means that less insulin will be secreted by the pancreas. Type 2 diabetics often have insulin resistance which means that the cells are unable to take up the glucose from the bloodstream leading to blood sugar levels that are too high causing damage to organs, so eating less sugar is helpful.
Risks with Low Carb High Fat Diet:
The diet may be hard to maintain and it can cause you to lose too many minerals and vitamins if you are not careful. You may end up feeling very tired and have little energy with this diet, at least at first.
What is Keto Diet?
Definition of Keto Diet:
Keto is the ketogenic diet in which a state of ketogenesis is triggered in the body due to the types and amounts of different foods that are eaten. Ketogenesis is stimulated when blood glucose levels drop to very low levels. The idea is that the body is stimulated to break down fats rather than sugars and proteins. What normally happens is that the liver catabolizes carbohydrates down into monomers of glucose, but under the keto diet the liver instead catabolizes fats to form ketone bodies.
The Diet of Keto:
Carbohydrates and proteins are drastically reduced in terms of quantity that is consumed, while the amounts of fats are actually increased. Carbohydrates are usually limited to between 20 to 50 g per day. Any food item which is very processed or contains sugars, such as grains and cereals, are removed from the diet. This means that fruits and starches like potato are also not eaten as they also have a lot of sugar present.
Health Benefits in Keto Diet:
Research has indicated that the keto diet is very useful for decreasing the number of seizures that epileptic children have. It also seems to help with type 2 diabetes in assisting with the stabilization of blood glucose levels.
Risks in Keto Diet:
Although the keto diet can help lower blood sugar it could lead to hypoglycemia if a person is already taking a blood sugar lowering medicine. When first starting the diet a person may become dehydrated from the initial water loss, it also may leave a person with symptoms similar to influenza, including feelings of fatigue along with headaches. Your body may become too depleted of minerals and vitamins and you may have a loss of bone density. The other issue is that you may risk heart disease if you take in excess saturated fat.
Difference Between LCHF and Keto?
Definition of LCHF Vs. Keto
The lchf diet is where a person eats very few carbohydrates and more fats. The keto diet is where a person eats very little carbohydrates and proteins, but more fat, such that ketogenesis is triggered.
Metabolic Changes in LCHF Vs. Keto
What happens with the lchf diet is that it stimulates gluconeogenesis to occur. By comparison, the keto diet at first triggers gluconeogenesis but then a state of ketogenesis is triggered.
Diet
The lchf diet requires that you reduce the number of carbohydrates you consume and increase the fats in your diet. You can still eat protein. In the keto diet you greatly decrease the number of carbohydrates and proteins that you consume and increase the fats in your diet.
Health Benefits
The benefit of the lchf diet is that it can assist people in losing weight and can help with type 2 diabetes. The benefit of the keto diet can help with weight loss and can help with type 2 diabetes. The keto diet has also been shown to help children who have epileptic seizures.
Risks in LCHF Vs. Keto
There are some risks to the lchf diet in that it can cause a person to become dehydrated, very fatigued and may lead to a loss of nutrients. The risks with the keto diet are that you may feel like you have the flu, can make you dehydrated and can be risky for diabetics who are on medicine as it can cause hypoglycemia.
Table Comparing LCHF and Keto
Summary of LCHF Vs. Keto
- Lchf and keto are both diets in which the concentration of carbohydrates is reduced and the concentration of fats is increased.
- The keto diet involves eating even fewer carbohydrates and also limiting protein content.
- There are health benefits to the diets and also some risks.
- It is therefore important to check with your doctor before starting either of these diets.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Brouns, Fred. "Overweight and diabetes prevention: is a low-carbohydrate–high-fat diet recommendable?" European journal of nutrition (2018): 1-12.
[1]Kobayashi, Yasuhiro, et al. "Significant suppression of myocardial 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake using 24-h carbohydrate restriction and a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet." Journal of cardiology 62.5 (2013): 314-319.
[2]Yancy, William S., et al. "A low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet versus a low-fat diet to treat obesity and hyperlipidemia: A randomized, controlled trial." Annals of internal medicine 140.10 (2004): 769-777.
[3]Image credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/goblinbox/5495182882
[4]Image credit: https://pixabay.com/en/food-diet-keto-ketodieta-fitness-3223286/