Difference Between BYOD, CYOD and COPE
BYOD, CYOD and COPE are the fastest growing trends among the corporate sector when it comes to enterprise mobility strategy and they want to make sure they stand firm on their policies. Device management and employee choice have become the cornerstone of IT infrastructure. So, when it comes to enterprise mobility management and solutions, we have three main strategies to go with: BYOD, CYOD and COPE.
What is BYOD?
BYOD, short for Bring Your Own Device, is a rapidly evolving workplace trend that encourages employees to bring their own mobile devices, such as smartphones, laptops or tablets, into their place of work for accessing organization systems and data. It is a common practice that many organizations follow to reduce their corporate costs and thereby increasing productivity. BYOD is just a small part of the much bigger ‘IT consumerization’ movement wherein consumers can bring their own hardware and software into their respective work premises. It gives employees freedom to work on their own devices, choose their own applications and services that best serve their needs. However, employees should adhere to the company’s BYOD policies to protect corporate data because policy must always precede technology.

What is CYOD?
CYOD stands for ‘Choose Your Own Device.’ CYOD is an employee provisioning model similar to BYOD but more like an alternative to BYOD wherein employees are offered to choose from a limited number of company-approved devices as opposed to bringing their personal devices. Basically, a company or organization decides which devices their employees can choose by providing a list of pre-approved mobile devices. The option is quite restrictive compared to BYOD giving organization a level of control. This allows them to limit the disparity of the mobile devices to support yet gives employees some degree of choice. This is more like a mutually beneficial effort that equally benefits both the sides, employees and the organization. The devices are corporate owned, thus provide greater flexibility in imposing restrictions on the device use.
What is COPE?
COPE stands for ‘Corporate-owned personally-enabled.’ COPE is a business model, particularly used among IT organizations, that encourages employees to use corporate-owned mobile devices but at the same time, gives them freedom to make personal phone calls, send texts or install the applications they want. Employees are free to do mostly what they want to do, but the organization still has administrative control over the device. This is a mobility program which is a trade-off between work profile and personal use. The balance weighs more towards the organization side in terms of application management, security and integration, but the employees have some level of control over the personal use of devices as well. COPE recognizes the fact that nobody likes to carry two phones with them – one for personal use and one for work.
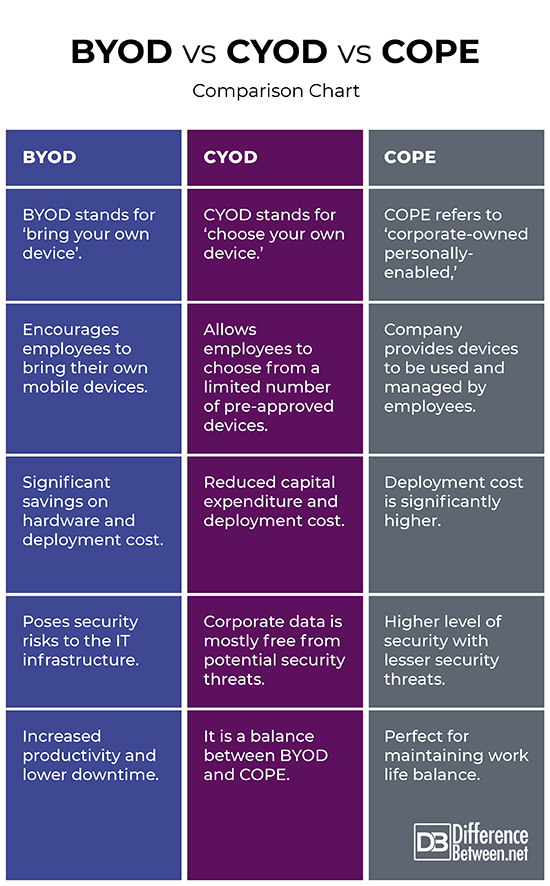
Difference between BYOD, CYOD and COPE
Meaning
– The acronyms themselves are self explanatory. BYOD refers to ‘bring your own device’, CYOD stands for ‘choose your own device,’ and COPE is short for ‘corporate owned personally enabled.’ BYOD is an enterprise trend that encourages employees to bring their personal mobile devices to the workplace; CYOD is like an alternative model to BYOD that allows employees to choose from a limited number of pre-approved devices that they can use on the organizational premises; and finally, COPE is a balance between work and personal use wherein employees are free to do mostly what they want to do, but the organization still has administrative control over the device.
Control
– With the BYOD model, employees are free to work on their personal devices, choose their own applications and services that best serve their needs. They are allowed access to selected corporate resources from their personal mobile devices but within the boundaries of the company’s BYOD policies. The CYOD model is quite restrictive compared to BYOD when it comes to freedom for employees, giving organization a greater level of control over which devices are allowed on the network. COPE, on the other hand, is a business model wherein the company or entity buys and provides computing resources and devices to be provided to employees.
Cost
– BYOD is probably the most cost-effective employee provisioning model that helps save companies a great deal of money along with significant savings on hardware expenditure and deployment cost. CYOD also reduces capital expenditure and hardware deployment cost significantly, but studies also suggest organizations spend up to 10 times more on hardware and software deployment than what they spend on device procurement. With COPE, the organization is full responsible for monitoring and maintenance of devices being issued, which contribute to higher upfront and deployment costs.
Security
– BYOD provides more freedom to employees, but with freedom comes vulnerabilities. BYOD definitely increases productivity, but at the same time, also brings in a number of security risks because security is a little difficult to enforce on personal devices. With CYOD, employees operate within the company compliance security policies. CYOD also ensures that the most up-to-date versions of the operating system and applications are supported, and with security solutions in the hands of the company, the corporate data is mostly free from potential security threats. COPE provides greater control and authority of devices and how you use them, which means higher level of security with lesser vulnerabilities.
BYOD vs. CYOD vs. COPE: Comparison Chart
Summary
All of them have their fair share of pros and cons, and which one is better for your organization depends mainly on the size of your organization. With COPE, the mobile devices are the responsibility of the organization, so strict monitoring and device management and security policies must be in place, and devices must always be kept up to date . COPE is a workaround of fully corporate-owned devices that allows you to make calls, send texts or do whatever you want to do, but at the end of the day, the organization has the complete administrative control over the device. BYOD and CYOD are quite similar employee provisioning models that provide some level of flexibility and control over your devices, but at the same time, pose some security risks to the IT infrastructure.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Vossen, Gottfried et al. The Web at Graduation and Beyond: Business Impacts and Developments. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2017. Print
[1]Au, Man Ho and Raymond Choo. Mobile Security and Privacy: Advances, Challenges and Future Research Directions. Massachusetts, United States: Syngress Publishing, 2016. Print
[2]Clarke, Glan E. et al. CompTIA A+ Certification All-in-One For Dummies. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2019. Print
[3]Image credit: https://data-revolution.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/dr-integarate-sources.png
[4]Image credit: http://www.ams.io/wp-content/uploads/2016/01/mobile-security-enterprise.jpg
[5]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:BES10_diagram.png
