Difference Between Computer Vision and Image Processing
The terms computer vision and image processing are often used interchangeably in many contexts as they both involve computations on images. But they are not the same thing. Let’s take a look at what they are and how they are different.

What is Computer Vision?
Computer Vision is the field of AI that gives computers and machines the ability to see, understand and interpret the visual world around us via machine learning techniques. It applies machine learning techniques to recognize patterns and deduce meaningful information from digital images, videos or other visual inputs. We are surrounded by all kinds of visually similar objects that we see and interact with every day. Although they look and feel the same, there are subtle details that make them stand out. The idea of computer vision is to recognize and interpret images the same way humans do, distinguishing them, classify them, and sort them based on their characteristic traits, such as size, color, and so forth. It seeks to replicate the complexity of the human vision system while giving the computers the power to make sense of the digital world.
What is Image Processing?
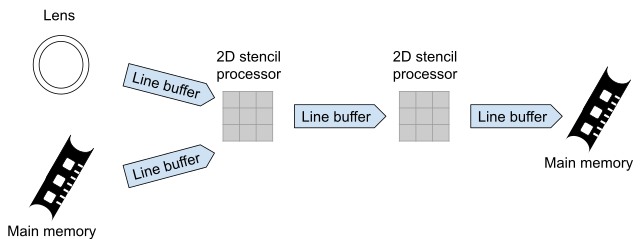
The field of digital image processing refers to both digital and optical image processing by means of a digital computer. A digital image consists of a finite number of elements, each of which has a particular location and value. These so called elements are called visual elements, picture elements, and pixels. A computer sees an image as a two-dimensional signal made of rows and columns of pixels. Images play a significant role in human perception. However, unlike humans, computers or machines transform an image into digital form and perform some process on it to get some meaningful information out of it. The idea is to process and enhance the image according to a specific task. Processing may involve noise reduction, brightness and contrast enhancement, and so on.
Difference between Computer Vision and Image Processing
Meaning
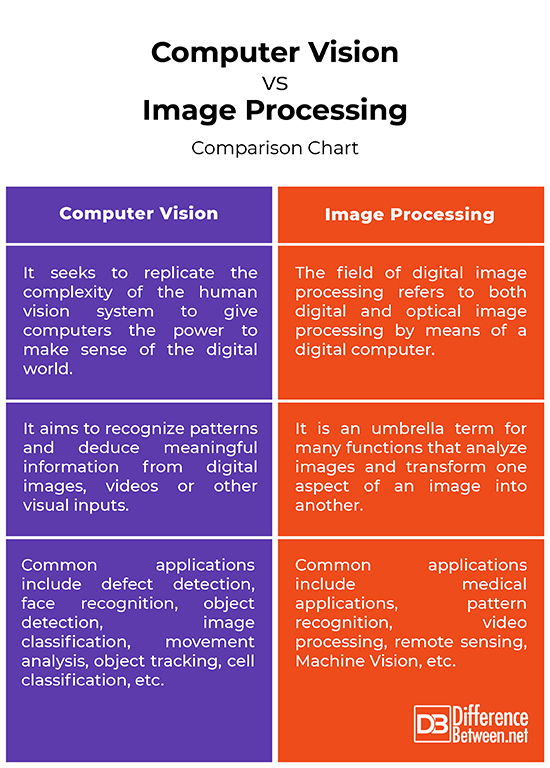
– Computer Vision is a field of artificial intelligence that seeks to replicate the complexity of the human vision system while giving the computers the power to make sense of the digital world. It enables computers to recognize, interpret and process images in the same way we do. Image processing, on the other hand, is the manipulation of images in order to extract meaningful information out of them. Image processing is the science of extracting information from images.
Concept
– Image processing, as the name suggests, focuses on processing images, which basically means the input and output are both images. It is an umbrella term for many functions that analyze images and transform one aspect of an image into another. Computer vision, on the other hand, focuses on gain a better understanding of the visual world by giving machines the ability to recognize patterns and deduce meaningful information from digital images, videos or other visual inputs.
Applications
– Some of the early and most common applications of image processing are image enhancement, filtering, sharpening and restoration. Most social media apps and image and video editing apps we use these days provide filters to enhance images. Other modern day applications include medical applications, pattern recognition, video processing, remote sensing, Machine Vision, etc. Some real world applications of computer vision are defect detection, face recognition, object detection, image classification, movement analysis, object tracking, cell classification, and more.
Computer Vision vs. Image Processing: Comparison Chart
Summary
Image processing algorithms transform images in many ways, such as sharpening, smoothing, filtering, enhancing, restoration, blurring and so on. Computer vision, on the other hand, focuses on making sense of what the machines see. A computer vision system inputs an image and outputs images based on some specific task, such as object labels and coordinates. Both of them work together in many cases; in fact, many computer vision systems rely on image processing algorithms. Image processing involves processing of raw input images and enhancing them, or preparing them to do some specific tasks.
What are the steps in image processing?
Image acquisition is the very first step in image processing, followed by analyzing and manipulation, image enhancement and restoration, image transformation, image segmentation, color image processing, image compression, morphological processing, and object detection and recognition.
What is the first step in image processing?
The first step in image processing is digital image acquisition using sensors in optical or thermal wavelengths. It involves giving image a digital form.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Shapiro, Linda. Computer Vision and Image Processing. Massachusetts, United States: Academic Press, 1992. Print
[1]Gonzalez Rafael C. Digital Image Processing. Noida, India: Pearson Education India, 2009. Print
[2]Petrou, Maria M. P. and Costas Petrou. Image Processing: The Fundamentals. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2010. Print
[3]Acharya, Tinku and Ajoy K. Ray. Image Processing: Principles and Applications. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2005. Print
[4]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/3/3b/Computer_vision_sample_in_Sim%C3%B3n_Bolivar_Avenue%2C_Quito.jpg
[5]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d8/Image_processing_pipeline.svg/640px-Image_processing_pipeline.svg.png
