Difference Between Extended Reality and Augmented Reality
The last two decades have been very generous. Not only have we witnessed a technological revolution like never before, thanks to the inception of the Internet, we have seen a clear transition in how the information technology was used, from desktop computing, then to the web, social media, and finally to mobile computing. Sales of mobile devices have surpasses the sales of conventional desktop computers. As we moved away from desktop computing, it made sense to include the physical world in our computing experience. Given that the real world is not how the computer sees it, a new technology or you can say user interface becomes the need of the hour. This is where “Augmented Reality” (AR) comes to the picture. Along AR, came other familiar but different technological experiences that changed how we interact with the physical world, such as Extended Reality (XR).
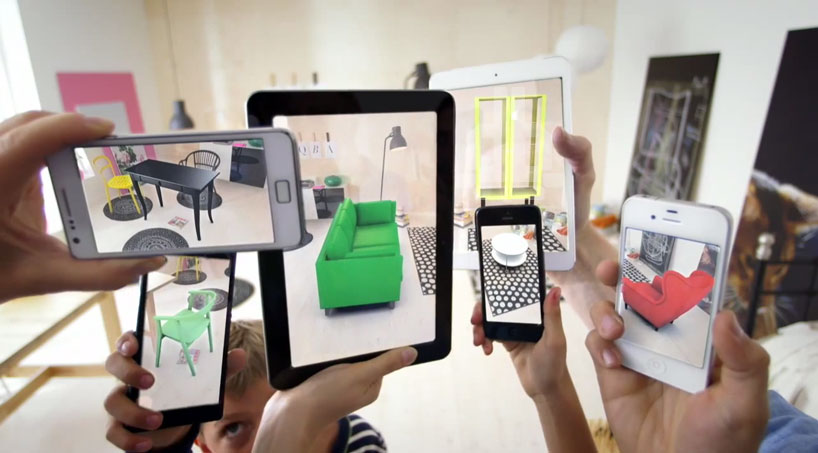

What is Augmented Reality?
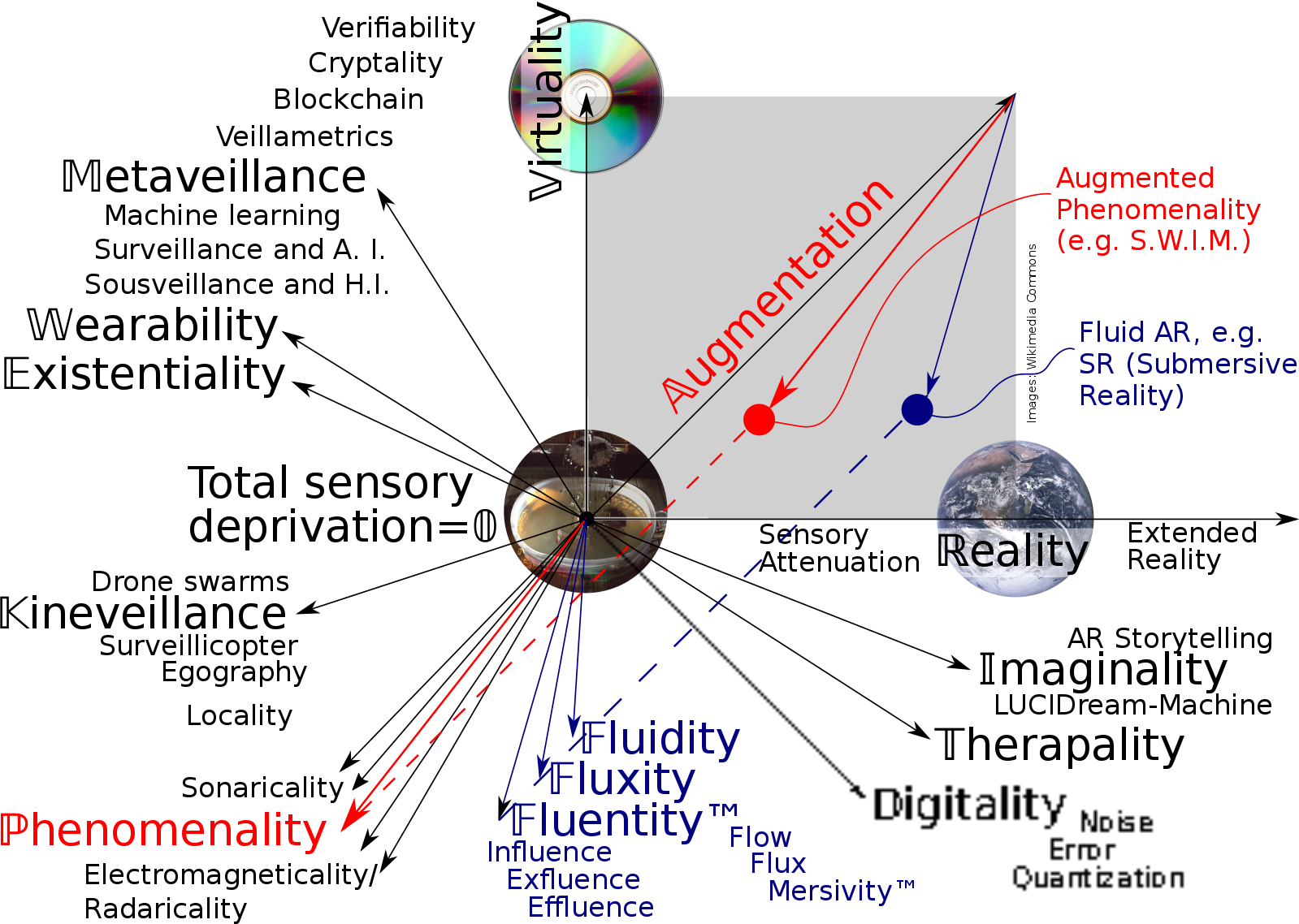
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology or an experience that alters our perception of the physical world around us where the objects in the physical world are replaced by virtual objects with the help of computer-generated inputs. AR, as the name suggests, augments our reality by enhancing parts of our physical world and then replace it with digital content, meaning it allows us to see the real life objects or the environment right in front of us, when they are not exactly there, with a digitally overlaid user interface. AR is the direct link between the physical world and the virtual reality. Probably one of the best examples of AR is the popular game Pokémon Go, which was released in 2016 and quickly became a worldwide sensation. AR simply adds digital information to the world we can interact with in the same manner we interact with the physical world.
What is Extended Reality?
Extended Reality (XR) is an all encompassing term that combines the experiences of augmented reality, virtual reality and mixed reality, meaning all the technologically-enhanced realities fall under the umbrella term of XR. It is a relatively new technology that blurs the line between the real world and the digital world to create more personalized, immersive visual experiences. XR blends the physical and the virtual worlds together and extends them all the way out to the background and beyond. It has the potential to transform the world around us – the real world –into something personalized, using special headsets, glasses, or anything to enhance your perception. We are at the dawn of a new age where the reality we know is changing in ways you cannot possibly think of.
Is AR an XR?
XR is an all-encompassing term that includes AR, VR and MR technologies. XR can mean AR, VR or MR, but not the other way around. VR places our reality in an entirely simulated world; AR places a digital overlay on what we can see; and MR is like AR but also allows us to interact with objects in the virtual world. XR is when you can’t tell the virtual world apart from the real world. XR is AR, but AR is not XR.
Difference between Extended Reality and Augmented Reality
Technology of Extended Reality and Augmented Reality
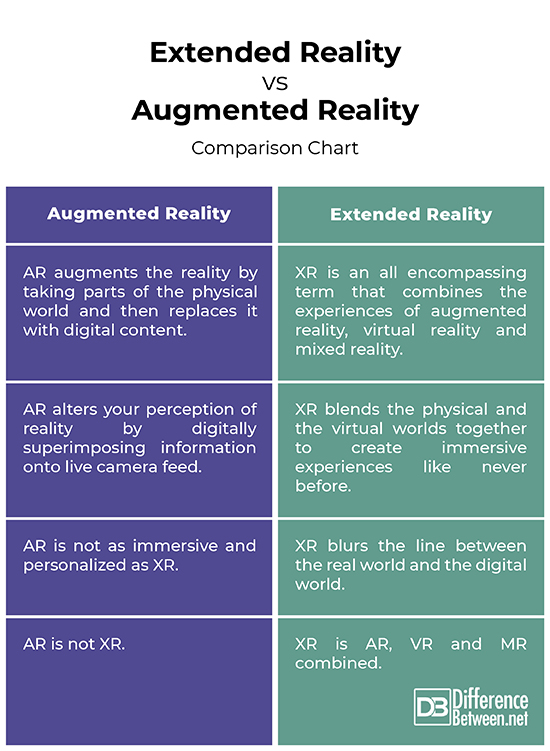
– AR is an interactive experience that places digital elements to your smartphone camera to create an illusion that the digital content you see is part of the real world around you. AR is a technology that alters your perception of reality by digitally superimposing information onto live camera feed. XR, on the other hand, blends the physical and the virtual worlds together and extends them all the way out to the background and beyond. It transforms the world around us into personalized experiences. XR combines the AR, VR and MR technologies.
Experience of Extended Reality and Augmented Reality
– AR provides a direct link between the physical reality and the virtual information about that reality by superimposing digital content onto a real-world environment through a smartphone camera or a headset. It creates an immersive experience by fundamentally alter our relationship with computing. XR creates a super immersive environment that is complimented by photorealistic visuals, making it almost impossible to distinguish between the virtual world and the real world. XR blends the physical and the virtual worlds together to create immersive experiences like never before.
Applications of Extended Reality and Augmented Reality
– The best example of AR is probably the infamous Pokémon Go game. Other innovative examples of the AR in the real world include the Android’s ARCore, Apple’s ARKit, IKEA mobile app, US Army’s Tactical Augmented Reality (TAR), Microsoft Hololens, and more. XR is used by companies from all sectors including gaming, engineering, entertainment, real estate, healthcare, retail, military, and so on. The video game and entertainment industries are the foremost users of XR technology.
Extended Reality vs. Augmented Reality: Comparison Chart
Summary
The AR and XR technologies were once a plaything in tech laboratories and a R&D experiment in large tech companies. But now they have entered the mainstream consciousness. They are proved to be the next pieces of disruptive technology that have the potential the transform the world we know of in ways we cannot possibly think of. AR adds digital information to the world that we can interact with in the same way we interact with the real world. AR augments your experience by altering the environment in ways that are not possible in the real world. XR takes things leap years ahead by combining AR, VR and MR technologies to create a world that is virtually indistinguishable from the real world.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Schmalstieg, Dieter and Tobias Hollerer. Augmented Reality: Principles and Practice. Massachusetts, United States: Addison-Wesley, 2016. Print
[1]Craig, Alan B. Understanding Augmented Reality: Concepts and Applications. London, United Kingdom: Newnes, 2013. Print
[2]Mealy, Paul. Virtual & Augmented Reality For Dummies. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2018. Print
[3]Marr, Bernard. Extended Reality in Practice: 100+ Amazing Ways Virtual, Augmented and Mixed Reality Are Changing Business and Society. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2021. Print
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:MultimediatedReality.svg
[5]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Augmented-reality.jpg
