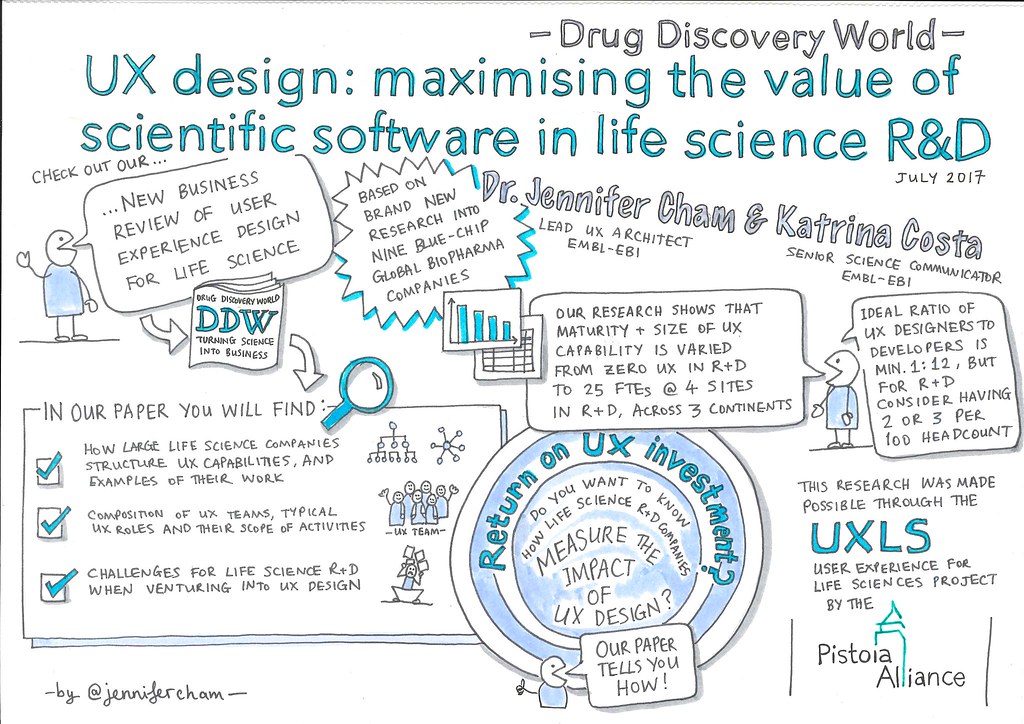
Difference Between UI and UX
The power and sophistication of computing systems and software have grown tremendously over the last couple of years. We have come so far to the point where software is integral to our personal and work life. This creates a nexus of tension around the two very familiar terms: UI (user interface) and UX (user experience). Normally used in pair as UX/UI design, the terms are often used interchangeably or sometimes incorrectly because they work closely together when it comes to product design. Although the terms are not new, they are often confused with each other, especially in the digital product design space. We will help you understand the meaning of the two terms and their differences.

What is User Interface (UI)?
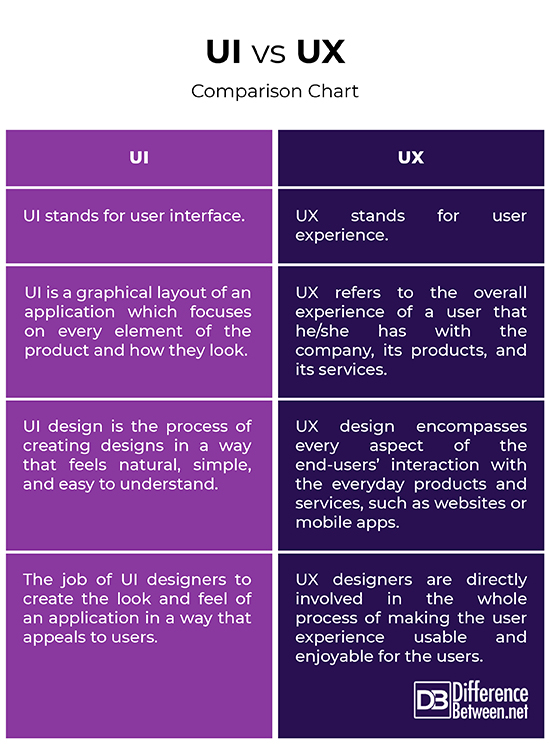
UI, short for user interface, is essentially a conversation between users and a product to perform tasks in order to achieve user’s goals. UI is a fundamental element for human-computer interaction and communication in a device. UI is a graphical layout of an application which focuses on every element of the product and how they look, which includes everything from the buttons users click on to the images they see, the text they read, placeholders, checkboxes, and almost any visual element users interact with. UI is the presentation and interactivity of a product which basically comes down to the look and feel. UI is designed to communicate to people – both in terms of interaction and visual design – in a way that feels natural, simple, and easy to understand. UI determines the look and it’s the job of UI designers to create the look and feel of an application in a way that appeals to users.
What is User Experience (UX)?
User experience, abbreviated as UX, is the overall experience of a user that he/she has with the company, its products, and its services. A good or bad user experience is determined by how easy or difficult a product or service is to interact with, in terms of the interface elements. Many people believe than UX just means user experience, but UX is the process of the user experience design. This involves the entire process of the acquiring the product, including designing, branding, usability and function. UX is mainly a cycle of four fundamental activities – Analyze, Design, Implement, and Evaluate. Analysis translates to understanding user work and needs; design means creating conceptual design and determining interaction behavior, and look and feel; implementation translates to prototyping; and evaluation translates to ways to see if the design is up to the mark in accordance with user needs. And it’s the job of UX designers to advocate for the users’ needs with the design solutions.
Difference between UI and UX
Meaning
– UI, stands for ‘user interface’, refers to the graphical layout of an application which consist of buttons, images, text, graphics, placeholders, checkboxes, or just any visual element users interact with. UI is the presentation and interactivity of a product with a focus on looks or style. UX, on the other hand, stands for ‘user experience’ and is the overall experience of a user that he/she has with the company, its products, and its services. UX is how a user feels when interacting with a system, which could be a mobile app, a web app, or desktop software.
Design
– UI design is the presentation and interactivity of a product, the look and feel of the product. UI design is the process of creating designs in a way that feels natural, simple, and easy to understand. It is a fundamental element for human-computer interaction and communication designed to communicate to people, both in terms of interaction and visual design. UX design, on the other hand, encompasses every aspect of the end-users’ interaction with the everyday products and services, such as websites, mobile apps, web apps, etc. It involves the entire process of the acquiring and implementing the product, from designing to branding, usability, and function.
Job
– UI determines the look and it’s the job of UI designers to create the look and feel of an application in a way that appeals to users. UI designers work on the visual elements of an application in a way that is attractive and convenient for users. The job of UX designers is to advocate for the users’ needs with the design solutions. UX designers are directly involved in the whole process of making the user experience usable and enjoyable for the users. They design how the interface works and makes sure the navigation is intuitive and a great experience for the users.
UI vs. UX: Comparison Chart
Summary
While UX focuses on the overall experience of the product and how to make the experience usable and enjoyable for the users, UI is focused on the look and feel, such as text, fonts, images, buttons, colors, layout, graphics, and spaces. UI is the vehicle for UX, which is the user connection to an application, which needs to be as simple and as clear as possible for the users. UX is focused on the overall experience of the product and not just on its look and style. UX covers a lot of different areas, such as designing, branding, usability, accessibility, and function.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Anderson, Jonathan et al. Effective UI: The Art of Building Great User Experience in Software. Sebastopol, California: O'Reilly Media, 2010. Print
[1]McKay, Everett N. UI is Communication: How to Design Intuitive, User Centered Interfaces by Focusing on Effective Communication. Burlington, Massachusetts: Morgan Kaufmann, 2013. Print
[2]Canziba, Elvis. Hands-On UX Design for Developers. Birmingham, United Kingdom: Packt, 2018. Print
[3]Hartson, Rex and Pardha S. Pyla. The UX Book: Process and Guidelines for Ensuring a Quality User Experience. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2012. Print
[4]Image credit: https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2017/04/20/13/02/technology-2245662_1280.jpg
[5]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/4292/36041293135_a47c674834_b.jpg
