Difference Between Primary Market and Secondary Market
Primary and secondary market refers to the financial platform where corporations acquire capital, which is essential for their operations.
What is Primary Market?
A primary market is a place where corporations sell shares or units of ownership to that the members of the public to fund operations.
Companies are required to sell shares to the members of the public who are willing to subscribe to such shares so that they can gain capital to expand their existing business or purchase new entity.
The issuer may issue several financial instruments for considerations, which include an offer for sale, right issue, and bonus issue.
What is Secondary Market?
The secondary market is defined as a platform where existing financial instruments, which include shares, debentures, bonds, options, treasury bills, and commercial papers, are traded among sellers and buyers.
The secondary selling and buying of financial instruments are done through auctions in the stock exchange or through over the counter (OTC) platforms.
Difference Between Primary Market and Secondary Market
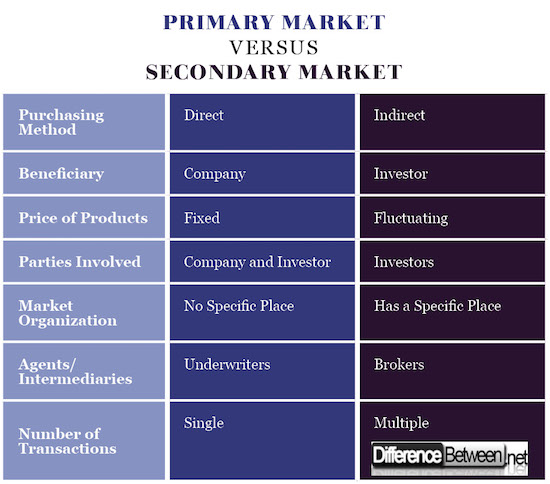
Purchasing Method or Primary and Secondary Market
The primary market for financial instruments is a direct market where companies offer their shares to the members of the public for consideration.
The buyers and sellers interact with one another offering the chance to negotiate for the shares on offer, especially in the auction markets where the highest bidder is assumed to have won the purchasing battle.
The secondary market is an indirect financial platform where prospective buyers purchase shares from others investors. In the secondary market, the original owner of the shares (company) is not involved in the transfer of the units of ownership.
Financing/Beneficiary for Primary and Secondary Market
The main purpose of the primary market is to provide finances to organizations so that they can expand their operations or boost their current activities. Companies offer their shares for a subscription to prospective buyers and investors in return for money, which is essential in funding the events of the company.
On the other hand, secondary market does not offer finances to the company. This is because the shares are traded between prospective investors who have speculative motives. The secondary market involves the exchange of shares from one investor to the other.
The organization is the final beneficiary of the primary market because it will gain all the proceeds, which are acquired after the sale of financial instruments. In the secondary market, the investors are the beneficiary after the transfer of ownership.
Parties Involved in Primary and Secondary Market
The primary market involves direct contact between the company and the investor. The company offers shares to the investor who considers them for purchase concerning the associated profits and the cost of the shares.
The secondary market involves different investors exchanging the financial instruments. The company is not involved because this is an indirect market, which involves investors only.
Price of Financial Instruments for Primary and Secondary Market
In the primary market, the price of the financial instruments is usually fixed. Companies sell their shares in an open market where other members of the public are aware of the prevailing prices. Besides, the price of the shares in an initial public offer is communicated through the print and other media platforms.
However, the participants do not know the price of shares and other products. The price of the financial instruments keeps on fluctuating and is mostly depends on demand and supply aspects. Therefore, the more the products, the lower the prices and the vice versa.
Organization
The primary trade of financial instruments is usually not rooted in any specific place or geographical position. This means that buyers can buy their shares at any place, especially the organizational premises.
The secondary market has physical existence, which means that this form of trade is rooted in a specific place. This explains why there is the existence of the stock exchange offices and halls where investors sell their units of ownership to other investors.
Agents/Intermediaries for Primary and Secondary Market
In the primary markets, underwriters are the intermediaries between the company and the investors who are willing to purchase units of ownership in the company. Some of the common underwriting agencies include banks and insurance companies among others.
Brokers form the intermediaries in the secondary market. Brokers are responsible for assessing the risks and profits associated with a specific financial instrument after which they purchase the promising shares on behalf of the buyer.
Number of Transactions involved in Primary and Secondary Market
In the primary market, a financial instrument is sold once. The enterprise is tasked with the obligation of selling the share to the investor for profit at a fixed rate upon which the investor possesses the full rights to the unit.
The investor is entitled to all the benefits associated with the ownership of the instrument including dividends and resale rights.
On the other hand, a unit of ownership can be sold several times with each transaction involving the exchange of rights and benefits. This is because the secondary market consists of the sale of shares and other financial instruments between investors at a profit.
Difference Between Primary Market and Secondary Market
Summary of Primary and Secondary Market
- The fundamental difference between primary and secondary market is the, in primary market involves the sale of shares by the company to the investor while secondary market consists in selling stock between investors.
- Other notable differences between primary and secondary differences between primary and secondary market include purchasing methods, beneficiaries, number of transactions, intermediaries, market organization, and parties involved among others.
- Difference Between Gross NPA and Net NPA - April 20, 2018
- Difference Between Job Description and Job Specification - April 13, 2018
- Difference Between Yoga and Power Yoga - April 10, 2018
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Gabbi, Giampaolo, and Andrea Sironi. "Which factors affect corporate bonds pricing? Empirical evidence from euro bonds primary market spreads." The European Journal of Finance11.1 (2005): 59-74.
[1]Gajewski, Jean-François, and Carole Gresse. "A survey of the European IPO market." (2006).
[2]Garbade, Kenneth D., and William L. Silber. "Structural organization of secondary markets: Clearing frequency, dealer activity and liquidity risk." The Journal of Finance 34.3 (1979): 577-593.
[3]Image credit: http://www.creative-commons-images.com/clipboard/images/investor.jpg
[4]Image credit: http://maxpixel.freegreatpicture.com/Men-Workplace-Customers-Company-Silhouettes-142329