Difference Between Beans and Lentils
Lentils and beans are part of the nutritious legume family famous for their reduced fat content and high content of protein and essential vitamins. These vegetables can be substitutes of meat and other protein-containing foods that have small nutritional values. The distinction between lentils and beans is not obvious to others, and so this article is devoted to highlight the key differences.
What are Lentils?
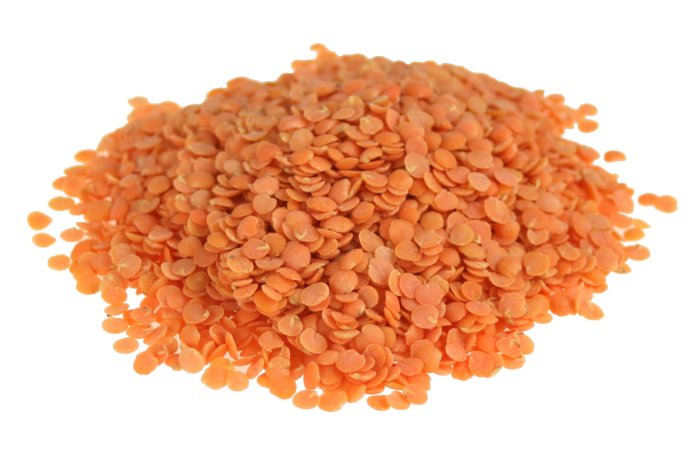
Among other members of the legume family, lentils are small types of vegetables with their shape likened to lens. The Latin name, Lens Culinaris, clearly reflects the shape of lentils. The direct meaning of this Latin name is “cooking lens”.
Lentils are available in a broad variety of types. However, only three are the most popular: green, brown and red lentils. Brown lentils are the least expensive and blend well in soups. Green lentils, on the other hand, are alternatively referred to as French lentils and they are often used for salads. They have the same texture as Beluga lentils, and they become firm when cooked. The last common lentils, the red lentils, are fast to cook and often turn gold and lose shape after being cooked.
Compared with beans, lentils contain more fiber. Typically, half a cup of boiled lentils contains 7.8 grams of fiber whereas half a cup of beans contains 5.2 grams. Also, lentils contain less carbohydrates – carbohydrates (often shortened carbs), convert glucose into energy that the body needs to function and achieve many metabolic functions.
The other advantage of lentils is that they cook quickly and thus need no pre-soaking like beans do. The cook time for lentils differs from type to type. For instance, the red lentils cook for about 20 minutes, brown lentils for 45 to an hour while the green lentils cook for 30 to 45 minutes. It is easy to store lentils after cooking. In stores, lentils can be found dry or prepared in cans. Although lentils may tend to lose color after a prolonged time, they do not lose their nutritional value and their taste.
What are Beans?
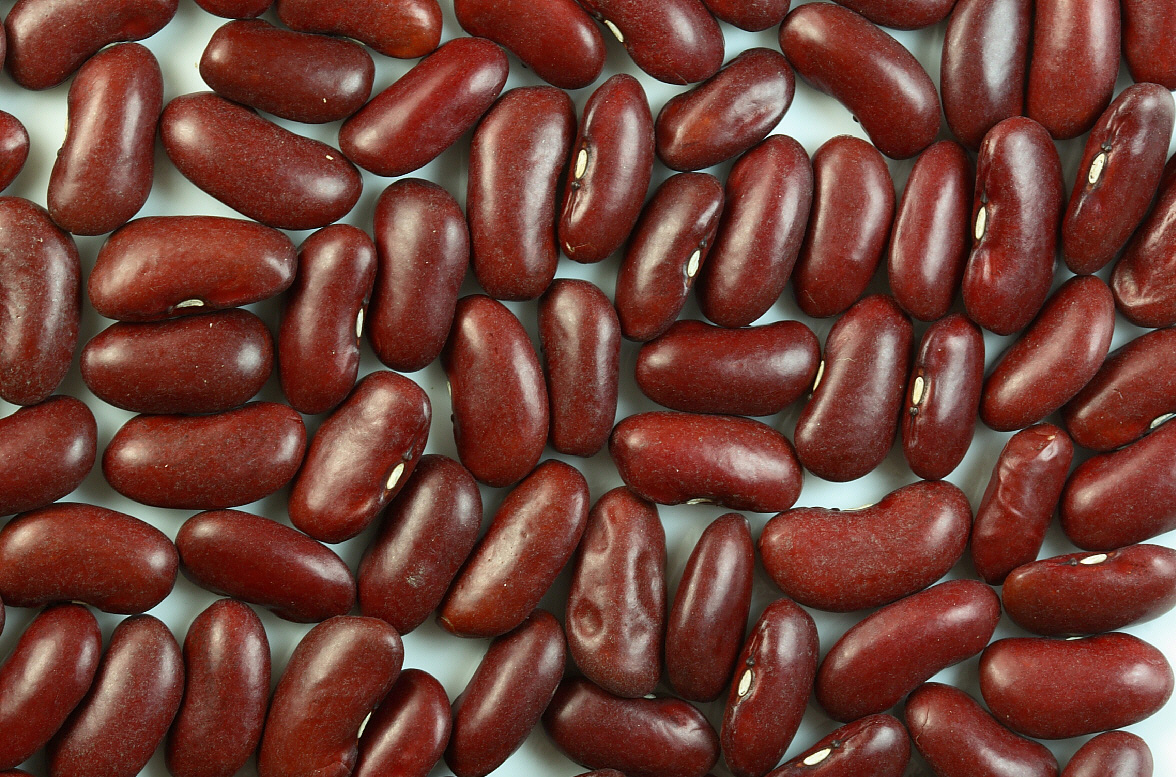
Beans form part of the legume family as they grow in pods. There are many types of beans and they differ in nutritional values and cooking time. Beans are notorious of taking a long time to cook. Ideally, they should be pre-soaked for about eight hours prior to cooking them. And, when cooking beans, a pressure cooker may reduce the cooking time by half. Failure to soak beans may take a long time to cook and thus may consume more power.
Beans contain more carbohydrates than lentils. Half a cup of beans contain about 27 grams of carbs. But this content of carbs differs from one type of beans to the other. But beans are short of fiber when compared with lentils.
The good part with beans is that they have low content of fat, which makes them a suitable addition to a dietary plan. They provide reduced sodium and calories while benefitting the body with essential fatty acids. While beans in general have low fat, soybeans do not but they (soybeans) contain a rich content of omega-3 fatty acids. Combining beans with oats and other grains provide more amino acids to make a complete diet for vegetarians.
Beans can be a great addition to a dietary plan of diabetic patients as they do not cause a rise in blood sugar levels. A cup of cooked beans provide 15 grams of fiber which is beneficiary to the body.
Beans are versatile and so they can be added in many dishes. Add them to curries, soups or salads or make them a standard diet that replaces meat products completely as they (beans) have sufficient proteins while meat, despite having a rich content of proteins, has fat and cholesterol which are not good for a dietary plan.
Generally, beans take longer to cook than lentils. But, properly-soaked beans can take up to 45 minutes to fully become done. Of course this time depends on the type of the beans; the large the type of bean the longer the time it takes to cook.
Key Differences Between Lentils and Beans
Definition
Beans are part of the legume family. They are large, oval or kidney shaped, and they come in a plethora of varieties characterized by both the appearance and the nutritional values. Lentils are the smallest members of the legume family. They also come in varieties but only three are popular: green, brown and red.
Nutritional Benefits
Both lentils and beans have more nutritional benefits. They contain proteins and essential vitamins as well as low content of fat. Beans have more carbohydrates and less fiber than lentils. Soybeans, a class of beans, contains fat but provides a rich content of omega-3 fatty acids.
Description
Lentils are generally small and lens shaped as reflected by the Latin name. They come in different colors. Beans, on the other hand, are oval-shaped or kidney-shaped.
Cooking Time or Method
To cook lentils, you need not pre-soak them as they are normally easy to cook in less time. Pour them in a pot and pour water. Do not pour too much water and do not put salt while boiling lentils as it may make them hard. The cooking time differs between the types of lentils. Beans cook for a long time if not pre-soaked. Soak beans for about 8 hours before cooking to lessen the cooking time. Moreover, a pressure cooker can cut the cooking time by half.
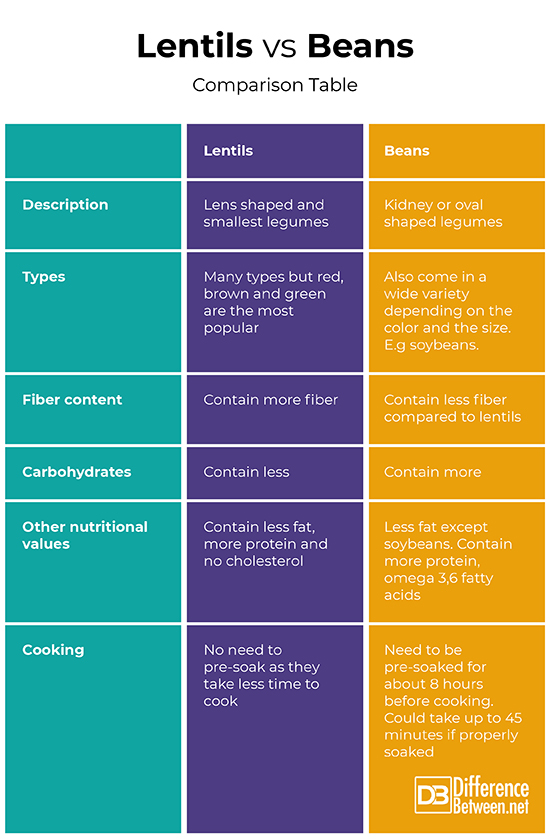
Lentils Vs. Beans: Comparison Table
Summary of Lentils Vs. Beans
- Lentils are lens shaped and smallest legumes
- Beans are oval or kidney shaped
- Both beans and lentils come in different types
- Common lentils are green, brown and red
- Lentils contain more fiber and less carbohydrates. Fiber suppresses the absorption of carbohydrates
- Beans contain more carbohydrates and less fiber
- Beans contain less fat except soybeans
- Beans and lentils contain no cholesterol and thus can replace meat as they equally have a rich content of proteins and essential vitamins fatty acids, and more
- Lentils take less time to cook whereas beans take more time. However, the cooking time for beans can be reduced by soaking them
- Difference Between CBD and Indica - April 22, 2019
- Difference Between Unilateral Contract and Bilateral Contract - February 8, 2019
- Difference Between Polki and Kundan - December 15, 2018
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Patricia Ross, Trish Ross (2003). Easy Beans: Fast and Delicious Bean, Pea and Lentil Recipes. Big Bean Publishing
[1]Martin Dort (2016). Beans! Peas and Lentils. h.f.ullmann
[2]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kidney_beans.jpg
[3]Image credit: http://www.picserver.org/pictures/lentils01-md.jpg