Difference Between Kimchi and Sauerkraut
Almost everybody knows how delicious and aromatic fermented foods are. Fermentation not only keeps the natural taste, aromas and color of veggies intact, but also preserves their essential nutrients. The idea of preserving foods in glass jars in not new. In fact, fermentation has been among the hottest kitchen trends for years. And there are many health benefits of eating fermented veggies. Two of the most popular fermented foods are kimchi and sauerkraut, both of which are made by pickling fresh cabbage leaves (and other veggies). Although seem strikingly similar, sauerkraut and kimchi come from different origins.

Kimchi
Kimchi is one of the people’s favorite fermented foods that is made from many different veggies like napa cabbage, daikon radish (also known as Japanese radish and Chinese radish), green onion and sometimes, carrots. Kimchi is basically a traditional Korean side dish made from fermented vegetables. From kimchi fried rice to kimchi fries, kimchi omelets, there are all sorts of ways this thing can be used. Kimchi is made from fermented veggies using a process called lactic acid fermentation. The origin of kimchi dates back to thousands of years. Although the production techniques and the flavors of kimchi have evolved over time, the basic principle remains the same. It is basically cabbage fermented with additional seasonings such as ginger, garlic, and Korean chilly spices.

Sauerkraut
Sauerkraut is the German word for fermented, salted, shredded cabbage. The same fermentation process that is used to make kimchi is used for making sauerkraut. Although the dish is mostly associated with German culture, it originally came from China and was later picked up in central European countries. Sauerkraut is the art of fermenting and pickling veggies that dates back to thousands of years. It’s quite easy to make and requires only salt, cabbage and time. Sometimes, other ingredients are also added, like apples, juniper berries or caraway seeds. Sauerkraut was the most important vegetable in the Roman Empire and was thought to have medicinal values. It has health benefits that are hard to refute.
Difference between Kimchi and Sauerkraut
Origin
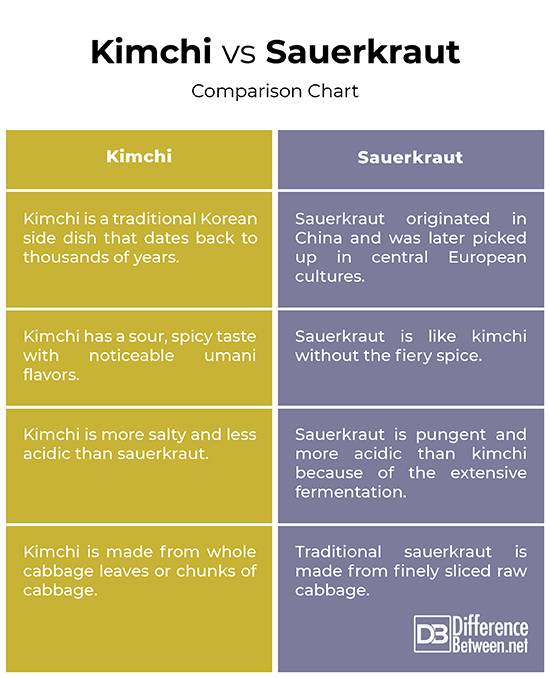
– Well, the common perception is that sauerkraut belongs to the German culture because it is a combination of German words ‘sauer’ which means sour and ‘kraut’ which means cabbage. But it wasn’t really invented by the Germans. In fact, sauerkraut believed to have originated nearly 2,000 years ago in ancient China. Chinese laborers who worked on the Great Wall of China were actually fed fermented vegetables. Kimchi, on the other hand, is a Korean side dish that dates back to thousands of years. It started as a tradition to store and preserve vegetables during the winters when many Koreans dies of starvation.
Ingredients
– Well, both kimchi and sauerkraut are popular fermented foods made by pickling fresh cabbage leaves and other veggies with lactic acid bacteria. Although they look very similar, there are subtle differences between the two. Kimchi is made from many different veggies like napa cabbage, daikon radish, green onion and sometimes, carrots. Additional seasonings are also added, such as ginger, garlic, spring onions, chili peppers, etc. Sauerkraut, on the other hand, is traditionally made from finely sliced raw cabbage and salt.
Flavor
– One of the main differences between the two is flavor/taste. Kimchi has a sour, spicy taste with noticeable umani. It is crunchy and ranges from sweet and sour to spicy depending on a number of factors like what are the ingredients used and how long it has been fermenting. It is rich and complex in taste, and this is the reason it’s popular worldwide. Sauerkraut, on the other hand, is like kimchi without the fiery spice. Traditional sauerkraut is pungent and acidic and has a much more tart flavor profile because of the extensive fermentation time.
Kimchi vs. Sauerkraut: Comparison Chart
Summary
Sauerkraut is made from finely sliced raw cabbage and salt, which makes it a great substitute for the Korean kimchi. Well, they both look similar but the main difference between the two is that sauerkraut is lightly seasoned whereas kimchi uses additional seasonings such as ginger, garlic, spring onions, chili peppers, etc. Coming to taste, kimchi is saltier, crunchier, and less acidic than its German counterpart. Sometimes, other ingredients are also added in sauerkraut, like apples, juniper berries or caraway seeds. Also, sauerkraut ferments for longer than kimchi.
Which is healthier kimchi or sauerkraut?
Both are healthy fermented foods made from cabbage but with slightly different ingredients. Kimchi contains more probiotic content than sauerkraut, hence it has more probiotic benefits. Kimchi also made from many different vegetables with different seasonings or spices.
Are kimchi and sauerkraut the same thing?
Kimchi is Korean and sauerkraut is basically Chinese. Besides their flavor and appearance, both are popular fermented foods made by pickling fresh cabbage leaves.
Why does kimchi have more probiotics than sauerkraut?
Kimchi is fermented using lactic acid fermentation which uses the same lactobacilli bacteria that is found in yoghurt and other fermented dairy products.
Can you substitute sauerkraut for kimchi?
Sauerkraut is a fermented cabbage dish and condiment, which makes it a good kimchi substitute. But kimchi offers more health benefits and has rich taste because it contains more ingredients than sauerkraut.
Is kimchi supposed to be eaten hot or cold?
You can eat kimchi straight out of the fridge. It is best eaten when cold, but usually at room temperature.
What is kimchi called in English?
Kimchi basically refers to fermented vegetables, particularly cabbage, and contains salt and other seasoned vegetables, like napa cabbage, daikon radish, green onion and sometimes, carrots.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Fermentation for Beginners: The Step-by-Step Guide to Fermentation and Probiotic Foods. California, United States: Drakes Press, 2013. Print
[1]Hutkins, Robert W. Microbiology and Technology of Fermented Foods. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2008. Print
[2]Farnworth, Edward R. Handbook of Fermented Functional Foods. Florida, United States: CRC Press, 2003. Print
