Difference Between Sea Salt and Rock Salt
Sea salt and rock salt are some of the salt varieties used as food flavors despite the significant number of differences between the two varieties.
What is Sea Salt?
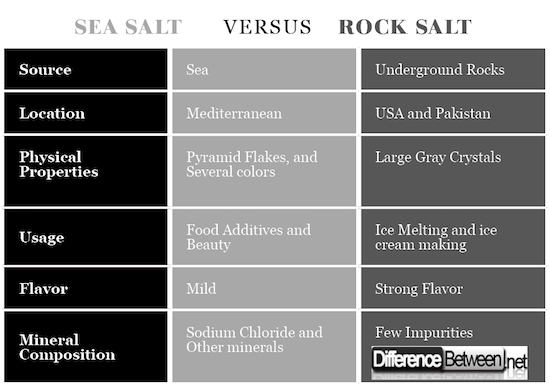
Sea salt is formed by evaporation of sea water where it contains sodium chloride at higher percentage despite having other minerals components. Some of the trace minerals found in sea salt include iodine, magnesium, and Sulphur among others.
Sea salt mostly referred as kosher by the Jewish communities, contains 98% sodium chloride and is usually considered to be less salty than the mainly used table salt. Several researchers have highlighted that sea salt is healthier than table salt due to its flavors.
What is Rock Salt?
Rock salt is the industrial name used for Halite. This is the salt that is commonly used as table salt after it has been sourced from a refined version of rock salt and usually added to food to add the salty taste. Rock salt is mined from underground rock formations.
It has sodium chloride as the most abundant component in its formation, but it also contains other minerals is very small quantities that are difficult to detect. It has crystal particles that make it hard to dissolve in water or food.
Difference Between Sea Salt and Rock Salt
1) Source
Sea Salt : Sea salt is usually sourced from the sea water which explains its name. Solid salty particles are formed after seawater evaporates. These solid particles are later picked through a specialized method and refined after which they are refined and packaged ready for transportation to consumers who buy them in wholesale and retail.
Rock Salt: Rock salt is sourced from undergrounds rocks which form under the earth surface. It is assumed that the sea water must evaporate long time ago to leave salt particles covered under the sand to create rock salt which is mined like other minerals and refined for consumption.
2) Location
Sea Salt : Sea salt is mined in abundant in the Mediterranean Sea and later exported to other parts of the world. Although this type of slat can be found on other seas, especially the coastal region of the Indian Ocean, large quantities of the commodity are located in the floors of the Mediterranean Sea.
Rock Salt: Rock salt is not as abundant as the sea salt which can be found on many large water bodies around the world. However, significant depositories of rock salt can be located in United States of America and Pakistan which is the most significant natural rock salt mine in the world.
3) Physical Properties
Sea Salt : Sea salt has to define physical characteristics that make it easy to detect once it is exposed to the eyes of an individual. Usually, this type of salt is in crystalline form which can be fine or coarse. However, sea salt appears in the form of sheer and pyramid flakes.
Additionally, sea salt has its color ranging from white, pink, black, and gray depending on the place of origin and the type of impurities present.
Rock Salt: On the other hand, rock salt is characterized by large and chunky crystals which are not uniform in nature. Moreover, rock salt exhibits a gray color which is highly attributed to a large number of impurities.
4) Usage
Sea salt is mostly used as food additives for preservation and flavoring purposes. It is also used in spa treatments and other factors associated with a beauty which include pedicure among others. You will also find sea salt mostly used for meat and seafood preservation.
Rock Salt: Rock salt is mostly used in places where large amounts of salt are required, especially in ice cream making and melting of ice from roads after a snowfall because it lowers the melting point of ice. It is important to highlight that rock salt is not preferred to use salt directly on food.
5) Flavor
Sea Salt : The other distinguishing factor between sea salt and rock salt is that sea salt has a subdued flavor which makes it be highly used like regular table salt in dishes. The subdued flavor of the sea salt is described as mild by many salt proponents.
Rock Salt: On the other hand, rock salt has a stronger flavor which makes it the most appropriate preservative for meat and seafood. The flavor makes it possible to use rock salt to accent the taste of food, primarily when used in small quantities.
6) Mineral
Sea Salt : Mineral composition is a significant factor that distinguishes between the two salt varieties. Sea salt is known to contain other minerals apart from sodium chloride. Some of the minerals that are likely to be found in sea salt include magnesium and Sulphur among others.
The presence of trace elements and other minerals explains the reasons why sea salt has a mild flavor. Nonetheless, sea salt contains 98% sodium chloride.
Rock Salt: On the other hand, rock salt does not contain many foreign elements and has a significantly higher composition of sodium chloride compound as compared to the sea salt. However, some impurities present in rock salt makes it exhibit the gray color.
Difference Between Sea Salt and Rock Salt
Summary of Sea Salt vs. Rock Salt
- Sea salt is a variety of salt that is collected on the floors of the sea after sea water evaporates while rock salt is a variety of salt that is mined below the earth surface where it exists in forms of rocks.
- Sea salt has a significantly large number of other elements which include magnesium and Sulphur while it’s most substantial composition is sodium chloride. This is not the same for rock salt which contains some impurities which dictate its color.
- Large deposits of sea salt can be found in the Indian Ocean and other oceans around the world while the United States and Pakistan have large deposits of rock salt.
- Other differences between sea salt and rock salt include the physical properties, flavor, and usage among others.
- Difference Between Gross NPA and Net NPA - April 20, 2018
- Difference Between Job Description and Job Specification - April 13, 2018
- Difference Between Yoga and Power Yoga - April 10, 2018
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Keene, William C., et al. "Sea‐salt corrections and interpretation of constituent ratios in marine precipitation." Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 91.D6 (1986): 6647-6658.
[1]Tolbert, S. H., and A. P. Alivisatos. "Size dependence of a first order solid-solid phase transition: the wurtzite to rock salt transformation in CdSe nanocrystals." Science 265.5170 (1994): 373-376.
[2]Tsang, Chin-Fu, Frederic Bernier, and Christophe Davies. "Geohydromechanical processes in the Excavation Damaged Zone in crystalline rock, rock salt, and indurated and plastic clays—in the context of radioactive waste disposal." International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences42.1 (2005): 109-125.
[3]Image credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/jsjgeology/33275221442
[4]Image credit: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sea_salt#/media/File:Salt_Farmers_-_Pak_Thale-edit1.jpg