Difference Between Electric Scooter and Bicycle
As electric vehicles become more powerful, energy efficient and above all, affordable, electric bicycles (e-bike) and electric scooters have become the viable substitutes for conventional transportation methods such as buses, trains, etc. Electric scooters and e-bikes have become increasingly important as they not only reduce noise and pollution, but they also reduce the dependency on oil and also minimize carbon emissions. Because of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, electric bicycles and scooters are gradually shifting from sports and recreational products to everyday commute vehicles. Public transports are often crowded and smelly, and they do not always get you from one point to your exact destination, making stops at key locations. An electric scooter or an e-bike does not suffer from this problem and you have the full control of your trip.
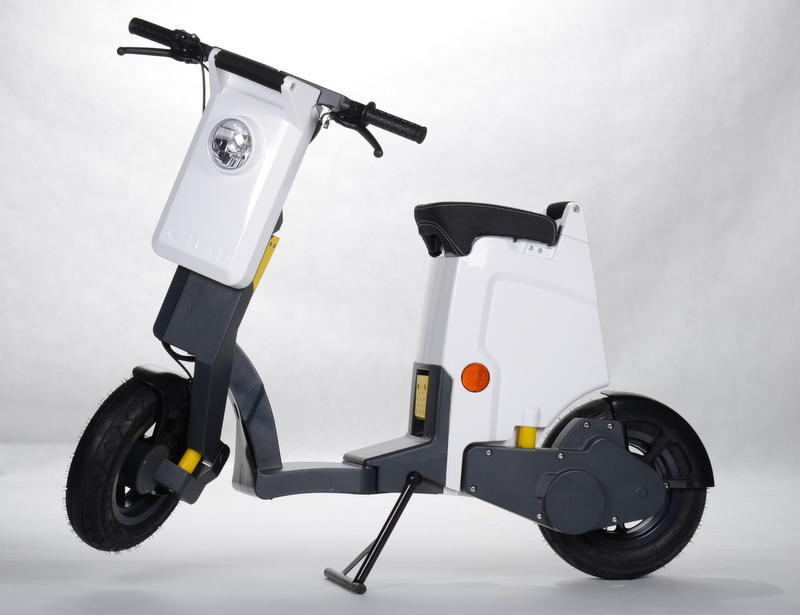

What is Electric Scooter?
Electric scooters, like other EVs, are plug-in electric vehicles with a motor mounted on the frame. They are your everyday two-wheeled scooters with electric motors which power the bike when the cyclist is pedaling. They differ from the traditional unmotorized scooters due to an additional component which is a battery, and the electronics, especially an electric motor. They are meant to provide intermittent mobility support and usually have a wide turning radius. They are extremely compact and lightweight, and pretty much safe to get you from point A to point B without having to worry about the clumsy traffic. Like other electric vehicles, electric scooters are powered by rechargeable Lithium or lead batteries. They are steered with adjustable tillers which are T-shaped steering columns – they are tilted forward or backward and locked at any desired position. Electric scooters come in various types, from small, light scooters to heavy-duty scooters and daily commute scooters.
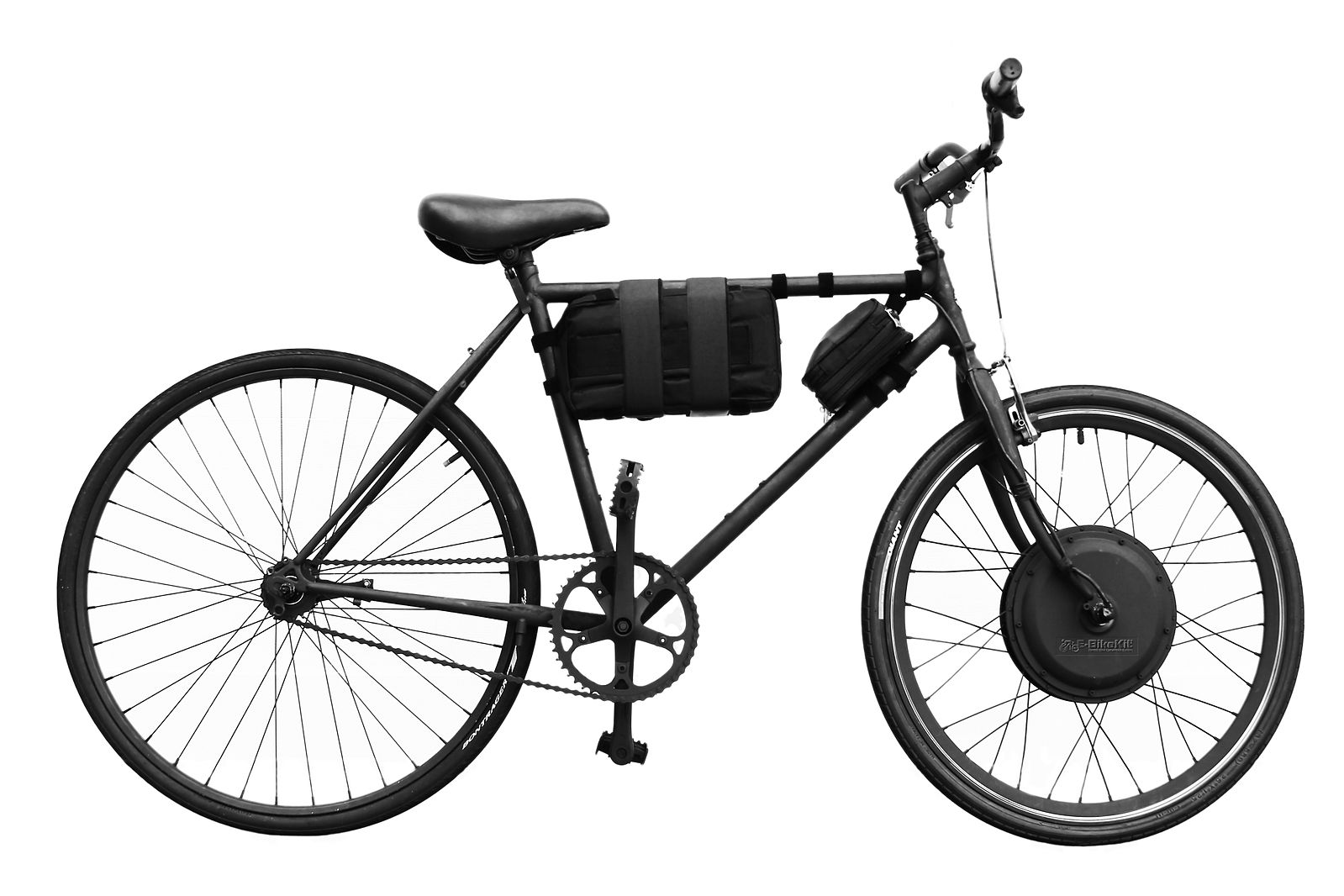

What is Electric Bicycle (e-bike)?
Electric bicycles, or e-bikes, are just like regular bicycles with a pedal and a handlebar, and powered by an electric motor which assist in the vehicle propulsion. E-bikes are an excellent piece of personal transportation equipment for getting around town without worrying about the carbon emissions because the emission rate of e-bikes is significantly low. They have a simple design that closely mimics the looks of a traditional bicycle, but with an addition of an efficient electric motor and a lithium ion battery. Typically, e-bikes refer to all kinds of electrically assisted bicycles that generate enough power and speed to ride safely on the highway similar to a gasoline-powered motorcycle. E-bikes are much like your regular bicycles, at least in terms of rideability but they make for an effortless, emission-free riding experience. They can easily travel up to 50 km/h, much faster than you would cycle.
Difference between Electric Scooter and Bicycle
Portability
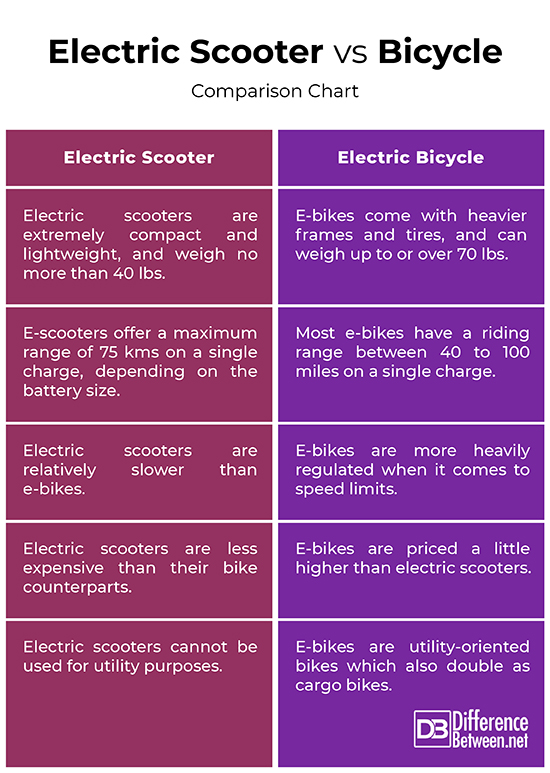
– In terms of portability, electric scooters are extremely compact and lightweight; in fact, an average electric scooter is significantly lighter than its e-bike counterpart. A typically e-scooter weighs no more than 40 lbs and anything that is below the 50 mark is considered light in the electric bikes segment. Electric bikes, on the other hand, are electrically assisted bicycles with a pedal and a handlebar, and a heavier frame and tires, which only add up to the weight. Plus, some e-scooters can be folded to fit into a suitcase and the batteries are small enough to carried on a plane.
Speed
– Electric bikes are typically categorized into Class 1, Class 2 and Class 3. While both e-bikes and e-scooters come with pedal-assist feature, which gives you a boost on tough terrains via pedaling, e-bikes can be a bit faster than e-scooters for the obvious reasons. But, in some countries, e-bikes are heavily regulated which limit their speed in the range of 28 to 32 km/h. In New York, e-bikes are restricted to a 25 km/h speed limit. Some high-powered e-bikes can stretch up to 45 km/h or more. Electric scooters are relatively slower than e-bikes.
Exercise
– Electric bikes not only serve your daily commute needs but also double as a great workout equipment. They offer superb assistance in getting you from one point to another and the throttles ones can be used as mopeds, which are a great option to take you out on a serious workout routine. Even studies suggest those who ride e-bikes tend to get regular and more exercise than those who ride regular bikes. And you can always turn up the pedal assist feature if you are tired after a long ride.
Range
– Most e-bikes have a riding range between 40 to 100 miles on a single charge but that depends on a variety of factors such as rider weight, battery capacity, average speed, etc. With high-powered e-bikes, you can easily expect the battery to last easily up to 100 miles before it needs to be juiced up. You can stretch even more if you turn up the economical settings. Electric scooters, on the other hand, do not have that much riding range and can offer a maximum range of 75 kms on a single charge, depending on the battery size.
Electric Scooter vs. Bicycle: Comparison Chart
Summary
So, anyone who can afford an electric scooter can also afford an e-bike, and if you can afford both, then you can get the best of both the worlds. Individuals with a lower physical condition as well as people who commute daily to work, are more likely to go for e-bikes because they not only cover long distances and they do not have any adverse effects on the environment. Plus, e-bikes double as a great fitness equipment and in addition, enhance the carrying capacity of the bike, thanks to heavy-duty, utility-oriented bikes. E-bikes not only help overcome the physical limitations of the rider but also allow them to commute to longer distances effortlessly.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Larminie, James and John Lowry. Electric Vehicle Technology Explained. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2012. Print
[1]Braddom, Randall L. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2010. Print
[2]Rérat, Patrick. Cycling to Work: An Analysis of the Practice of Utility Cycling. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2021. Print
[3]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Electric_Bicycle.jpg
[4]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/6/6d/GiGi_Electric_Scooter.jpg

how can you change from one unit to another in an article? you compared ebikes range at 100miles to 75kms for escooters. Thats not a comparison!