Difference Between Spam and Phishing Mail
In today’s Internet age where information travels around the world in seconds, cyber threats are imminent and organizations are constantly struggling to keep their information safe and secure from these threats. The volume and sophistication of such attacks has rendered existing security protocols and measures only partially effective leaving the victims totally vulnerable and these attacks are only increasing. However, these so-called threats are not new; in fact, in the last couple of years the number and sophistication of these attacks have increased dramatically. The most common threats include phishing and spamming, each of which presents serious threats to the integrity of IT operations. Spam is the electronic equivalent of junk mail that arrives in your email inbox from non-trusted sources in bulk which is very annoying. Phishing is the most common cyber attack frequently done through emails that direct users to fraudulent websites which seem legitimate in order to collect their sensitive credentials.
What is a Spam Mail?
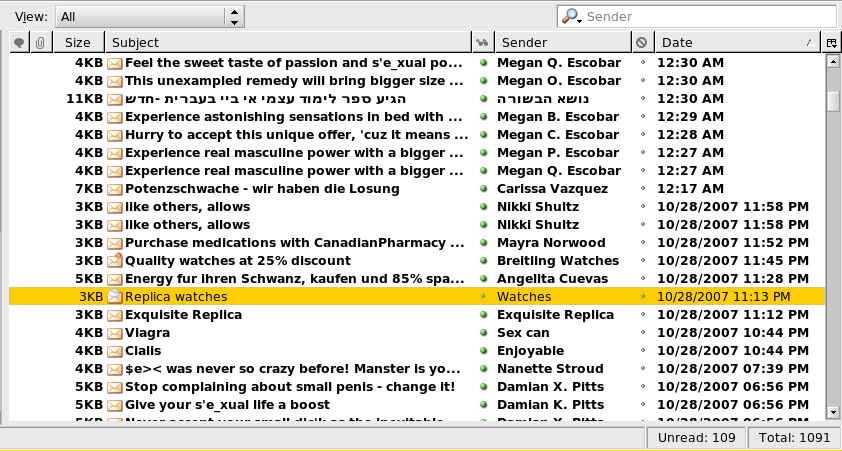
A spam email (or email spam) is an electronic equivalent of junk email which refers to ‘unsolicited bulk email’. This means emails with irrelevant content or some advertising material are sent in bulk as part of a larger collection of messages to millions of users with the sole purpose of playing with their emotions. Junk emails are sent without explicit consent from the recipient for commercial purposes in mass quantities by spammers and cyber criminals with the intention of making money from the recipients who actually respond to the mails whether willingly or accidentally. Spammers can make a lot of money if only a fraction of people respond to the mails and buy the advertised product or subscribe to any service. Spam emails are sometimes sent to a mailing list to spread malware and compromise their content. So it is always advised to be aware of fraudulent emails or spam emails.
What is a Phishing Mail?
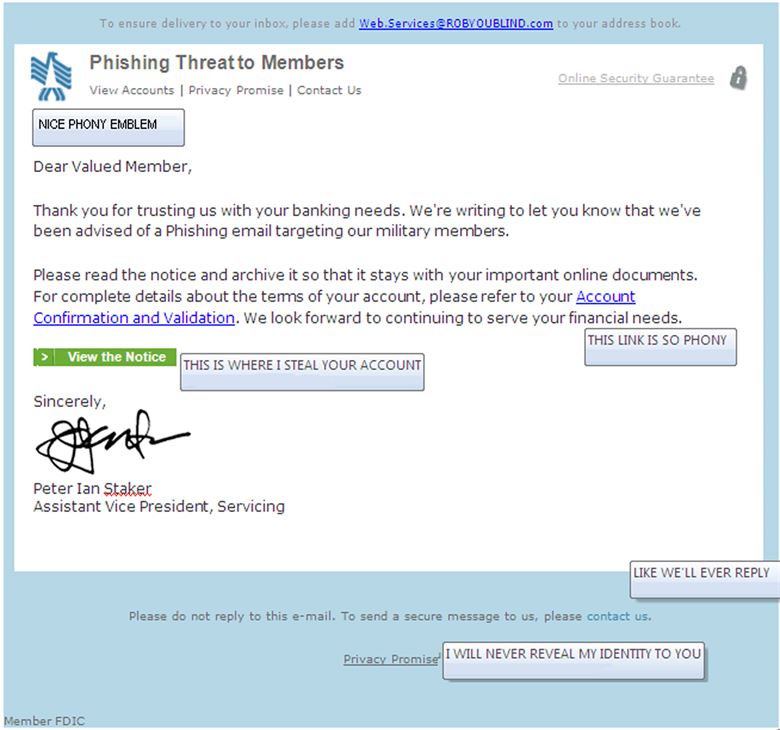
Phishing is an act of fraudulently retrieve users’ sensitive or confidential credentials by mimicking electronic communications claiming to be from a trustworthy source or some reputed organization in an automated fashion. It is a cyber attack where the cybercriminals send an email that appears legitimate asking for users’ credentials or seeking “Urgent action required”. It is a form of social engineering attack to obtain sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, social security numbers, and credit card numbers. The goal is to trick the users into believing that the message is legitimate and comes from a legitimate source in an attempt to obtain sensitive information for nefarious purposes or to ask for some sort of donation to questionable causes. Spear phishing is targeted at specific individuals like a baited hook to obtain confidential information.
Difference between Spam and Phishing Mail
Meaning
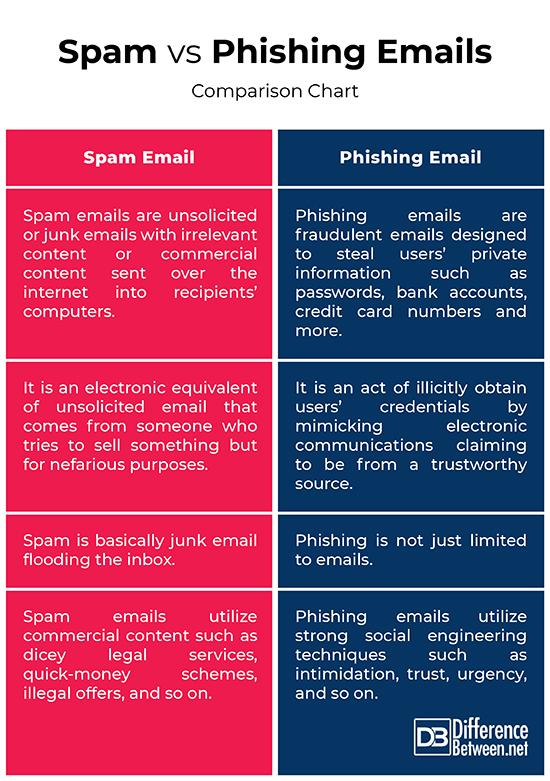
– Spam emails are an electronic equivalent of unsolicited emails (or junk emails) which are sent in bulk as part of a larger collection of messages to millions of users with the intention of making money from the recipients who actually respond to the mails. Spam emails are sent without explicit consent from the recipient for commercial purposes in mass quantities. Phishing emails, on the other hand, are fraudulent emails designed to steal users’ private information such as passwords, bank accounts, and credit card numbers which appear legitimate or seem to have come from a trusted source or reputed organization.
Goal
– Spam emails are a form of commercial advertising designed to flood the email inbox of users with the sole objective of selling some product to as many recipients as possible. Spammers can make a lot of money if only a fraction of people respond to the mails and buy the advertised product or subscribe to any service. Phishing is a form of social engineering attack often carried out via emails with the intention of obtaining sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, bank account numbers, social security numbers, credit card numbers and more.
Characteristics
– Spam emails are unsolicited or junk emails with irrelevant content or commercial content or bulk newsgroup postings sent over the internet to a mailing list, for the purpose of advertising or spreading malware into recipients’ computers. Commercial content may include dicey legal services, unrealistic quick-money schemes, illegal offers, or counterfeit commercial products, mostly pharmaceutical products. Phishing emails, on the other hand, are malicious emails seeking some action utilizing strong social engineering techniques such as intimidation, “urgent action required” message, trust, and so on with the sole objective of obtaining personal information for illicit uses.
Spam vs. Phishing Emails: Comparison Chart
Summary
Spam emails are unsolicited or junk emails with irrelevant content or commercial content sent over the internet into recipients’ computers to make them to buy the advertised product or subscribe to their services but for nefarious purposes. Spammers can actually make a lot of money if only a fraction of people respond to the mails. Phishing emails, on the other hand, are fraudulent emails designed to steal users’ private information such as passwords, bank accounts, and credit card numbers which appear legitimate or seem to have come from a trustworthy source or private organization.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Jakobsson, Markus and Steven Myers. Phishing and Countermeasures: Understanding the Increasing Problem of Electronic Identity Theft. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2006. Print
[1]James, Lance. Phishing Exposed. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2005. Print
[2]Lininger, Rachael and Russell Dean Vines. Phishing: Cutting the Identity Theft Line. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2005. Print
[3]Image credit: https://media.defense.gov/2010/Mar/30/2000380364/780/780/0/100330-F-0000M-001.JPG
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Screenshot-spam.png