Difference Between Brown Rice and Quinoa
What is Brown Rice & Quinoa?
Both brown rice and quinoa are gold star grains. Both are forms of natural grains which do not need lot of dressing. Both are fairly high in calories and good for health. Both are gluten-free and a good source of fibers and minerals. Both are beneficial in supporting a healthy digestion.
Both of these grains serve as brain-boosting foods and are an amazing way get some carbohydrates in a meal with a lot of fiber content. Also, both grains are low on the Glycaemic Index.
What is Brown Rice?
Brown rice is a whole grain rice form which has a covering or hull that is inedible. Brown rice possesses more of proteins, fiber, selenium, potassium, choline, phosphorus, and magnesium in comparison to white rice. Brown rice is also responsible for improving the good gut bacteria of the microbiome. Brown rice only has a hard-protective membrane removed called – the hull, leaving the nutrient-packed germ and bran. As a result, brown rice keeps all the nutrients packed such as minerals, vitamins, and antioxidants.
Brown rice is rich in magnesium which is important for healthy bones and teeth and also helps in regulating blood pressure and blood glucose levels. Brown rice is also a rich source of manganese that strengthens collagen production that is very important for maintaining skin health. More nutrients are bioavailable when one eats sprouted brown rice. Brown rice contains phenols and flavonoids, that help in protecting the body from oxidative stress.
What is Quinoa?
Quinoa is a flowering herbaceous plant in the amaranth family and has edible seeds. Quinoa is not a grass and offers dietary fiber, protein, minerals and vitamins. It does not contain gluten-free after harvesting quinoa, the seeds of quinoa are processed in order to remove the bitter tasting outer coating on the seed. Quinoa is very high in proteins and possesses all essential amino-acids and contains low Glycaemic Index, which is good for blood sugar control. Quinoa has high beneficial nutrient content and is responsible for improving metabolic health.
Difference between Brown rice verses Quinoa
-
Primary characteristics
Brown rice
Brown rice is eaten after the husky covering is removed. Since bran and germ are not removed in brown rice, it retains fiber content and has more nutritional value because of the vital nutrients present in it.
Quinoa
Quinoa, is basically the seed of the goosefoot plant. Since it is prepared and eaten just like a grain, many people use it as a substitute for rice in their diets. Because of its versality, it is perfect to have quinoa for dinner, lunch, or even breakfast.
-
Taste
Brown rice
Brown rice when cooked is darker in comparison to white rice. It has a chewier and a nuttier taste and since germ and bran is not removed from the main grain, it could take a longer time to eat and digest.
Quinoa
Quinoa is chewy in comparison to brown rice, but its texture is softer and quinoa has a neutral flavour.
-
Benefits
Brown rice
- It’s easy to digest.
- Brown rice is high in fiber content and helps to reduce BP.
- It may promote weight loss
- It helps control blood sugar
Quinoa
- It’s a complete protein that is rich in minerals.
- It is gluten free and helps protect your gastrointestinal tract
-
Calories
Brown rice
Brown rice consists of 218 calories
Quinoa
Quinoa consists of 222 calories.
-
Selenium content
Brown rice
Brown rice is much higher in Selenium (27%) which the body utilizes to make antioxidants
Quinoa
Quinoa contains 7% of Selenium
-
Carbohydrates
Brown rice
Brown rice weighs in with forty-five grams.
Quinoa
Quinoa contains thirty-nine grams of carbs in a cup.
-
Amino Acids
Brown rice
Brown rice is not a complete protein. It contains only few of the amino acids.
Quinoa
Quinoa is a complete protein. That means it contains all 9 important amino acids. This makes quinoa a great option for vegans, vegetarians and anyone who do not want to rely on meat consumption for maintain a balanced diet. In order to fuel your body with wholesome amino acids, quinoa is a better choice.
-
Lysine content
Brown rice
A cup of cooked brown rice contains only 0.2 gram of lysine content.
Quinoa
A cup of cooked quinoa contains around 0.5 gram of lysine. It is a perfect choice for vegetarians, as consuming quinoa gets them enough amino acids, including lysine.
-
Digestibility
Brown rice
Brown rice is digestible in comparison to quinoa. Its digestibility can be further improved by soaking and sprouting.
Quinoa
Quinoa consists of a natural bitter compound that deters birds from eating the plant’s seed coating in nature. This substance which serves as a seed coating is known as saponin, and it interferes with digestion. Saponin is toxic in nature. In order to remove this toxic coating and for making quinoa taste better and digestible, it should be soaked and rinsed in water before cooking.
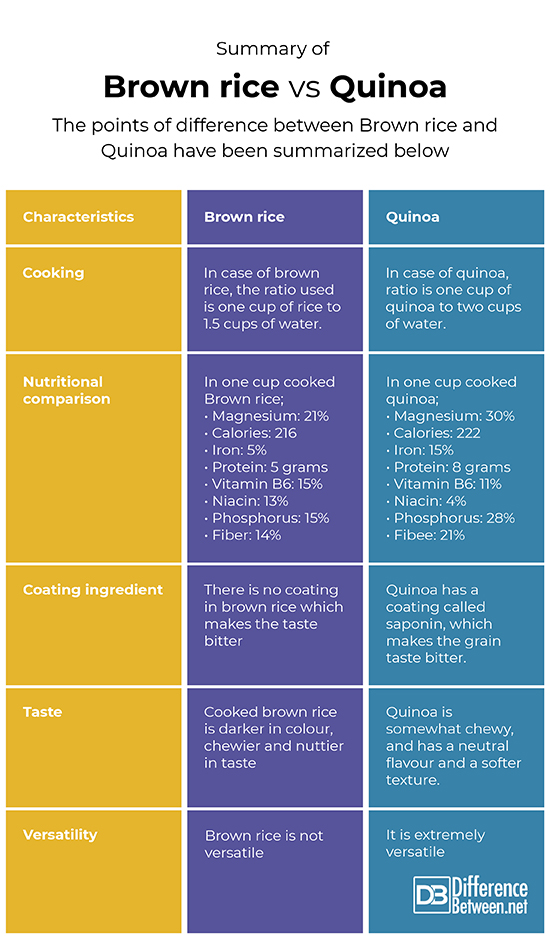
Summary of Brown rice verses Quinoa
The points of difference between Brown rice and Quinoa have been summarized below:
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Ignacio, C. C., & Juliano, B. O. (1968). Physicochemical properties of brown rice from Oryza species and hybrids. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 16(1), 125-127.
[1]Jancurová, M., Minarovicová, L., & Dandar, A. (2009). Quinoa–a review. Czech Journal of Food Sciences, 27(2), 71-79.
[2]Mohan, V., Spiegelman, D., Sudha, V., Gayathri, R., Hong, B., Praseena, K., ... & Ramachandran, S. (2014). Effect of brown rice, white rice, and brown rice with legumes on blood glucose and insulin responses in overweight Asian Indians: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes technology & therapeutics, 16(5), 317-325.
[3]Navruz-Varli, S., & Sanlier, N. (2016). Nutritional and health benefits of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Journal of Cereal Science, 69, 371-376.
[4]Image credit: https://pixabay.com/en/quinoa-grain-seed-food-healthy-405538/
[5]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Brown_rice_2.jpg



I Read almost 5 other articles but yours is the MOST expansive amd informative .. Big Thanks Doctor