Difference Between Soy Lecithin and Sunflower Lecithin

What is Lecithin
Lecithin, also known as alpha-phosphatidylcholine, is an emulsifier or lubricating nutrient that occurs naturally in a wide variety of foods including soybeans and sunflower seeds. It was first isolated in 1845 by the French chemist and pharmacist Théodore Gobley and is used in the food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and paint industries (Nguyen et al.).
Lecithin in the Food industry
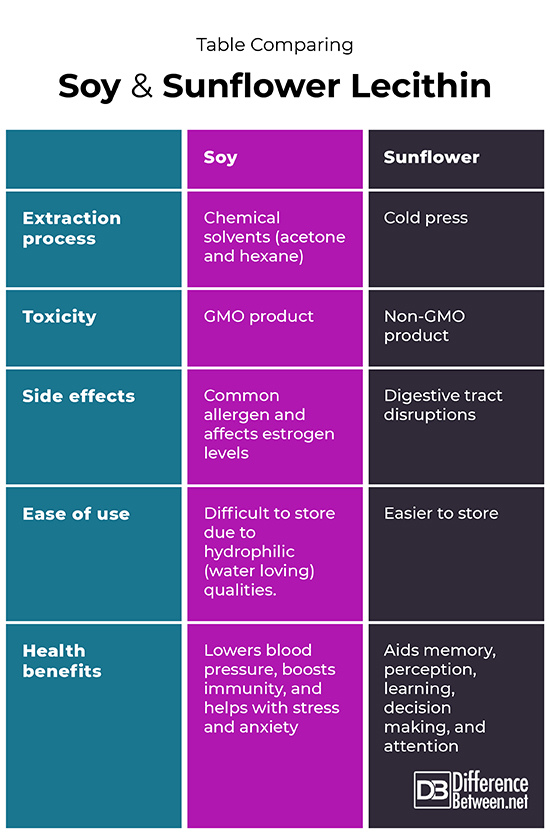
Lecithin is a multifunctional additive and preservative used in the manufacture of chocolate, margarine, mayonnaise, and baked and instant products due to the characteristics of its phospholipids (D.M. Cabezas et al.). Phospholipids enhance the dispersion of water, smooth the texture and quality of products, and can be used as an antioxidant and flavor protector. Bakers prefer sunflower lecithin because it is easier to work with, less of an allergy risk and easier to store than is soy lecithin.
Lecithin in the Pharmaceutical industry
Both soy and sunflower lecithin supplements have been shown to lower cholesterol (J.P. Higgins and Flicker), clear blocked or plugged milk ducts that lead to mastitis in breastfeeding women (Diane Wiessinger et al.) and lessen ulcerative colitis. Clinical studies have also shown that lecithin is beneficial in the treatment of acne and inflammation and improves liver function and cardiovascular health.
Sunflower lecithin contains phospholipids that play a role in improving cognitive functions like memory, perception, learning, decision making, and attention. Soy lecithin can be used to lower blood pressure, boost immunity, and help with stress and anxiety. However, soy lecithin is also a known allergen and exerts estrogenic effects while normal doses of sunflower lecithin may cause stomach aches, diarrhea, and loose stools.
Lecithin in the Cosmetic Industry
Lecithin is used in a large number of cosmetic formulations as a skin conditioner and suspension agent for both rinse-off and leave-on cosmetics because it has been shown not to be toxic or mutagenic and is nonirritating to the human skin (Z. Fiume). Both sunflower and soy lecithin contain antioxidant properties, protecting the cells from oxidative damage, thus delaying aging and keeping the skin free from wrinkles and fine lines.
Lecithin in the Paint Industry
Soy lecithin has several functions in the manufacturing of paint products. It acts as a viscosity reducer, binding and grinding agent, emulsifier, and corrosion inhibitor as well as increases the spreading capacity of the paints.
Side Effects of Lecithin
While lecithin in pharmaceutical and food products can be metabolized by the human body and is well tolerated when ingested, some people may present with allergic reactions after ingesting soy lecithin. Soy lecithin also exerts estrogenic effects in the human body, causing hormonal imbalances, thus predisposing women to infertility, irregular menses, increased risk of breast cancer, and menopausal symptoms. According to the website National Lecithin, the more common side effects of lecithin may include increased salivation, decreased appetite, diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, and abdominal bloating.

Differences between Sunflower and Soy Lecithin
While both soy and sunflower lecithin are the product of separating the oil from the gum, the key difference is that soy lecithin extraction requires chemicals such as acetone and hexane while sunflower lecithin is extracted naturally by cold pressing. Cold pressing involves dehydrating the sunflowers and thereby separating the gum, oil, and solids.
Soy lecithin is hydrophilic, or water loving, and tends to clump when exposed to air; therefore, sunflower lecithin is considered preferable by bakers because it is easier to work with and store. Sunflower lecithin is also considered the healthier alternative because soy is an allergen and more likely to be a GMO product.
Table comparing soy and sunflower lecithin
Summary
Lecithin is an emulsifier that is used in the food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic and paint industries. Sunflower lecithin appears to be the healthier option because unlike soy lecithin, it is extracted by means of cold pressing rather than with solvents, is less likely to cause allergic reactions, does not stimulate the production of estrogen, and is easier to store.
FAQ
Can sunflower lecithin replace soy lecithin?
As an emulsifier in cooking, sunflower lecithin can replace soy lecithin on a 1:1 ratio. Some would claim sunflower lecithin should replace soy lecithin because it is a non-GMO product, it does not stimulate the production of estrogen, and it is not a known allergen.
Which form of lecithin is best?
Pharmaceutical supplements most often include soy lecithin; however, because soy lecithin stimulates estrogen production, it may cause hormonal imbalances that affect the reproductive system in women. For women, therefore, sunflower lecithin would be best. Chefs and bakers might also choose sunflower lecithin because using soy lecithin excludes those who have allergies to soy products from eating the product, and soy lecithin is more difficult to store because of its hydrophilic or water loving qualities.
What is the difference between sunflower and soy lecithin?
The difference between soy and sunflower lecithin lies in the extraction process used. Sunflower lecithin is healthier because it is extracted by cold press rather than solvents and is a non-GMO product. Soy lecithin powder also clumps more easily, and some people may be allergic to products that use soy lecithin as an emulsifier, thus making sunflower lecithin a better option in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
What does sunflower lecithin do for you?
Sunflower lecithin strengthens the nervous system by protecting the myelin sheath, which helps transmit nerve impulses from the brain and spinal cord to the body. The consumption of sunflower lecithin is thought to improve neurological health and lower the risk of degenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
- Difference Between Ecchymosis and Erythema - August 15, 2022
- Difference Between Autobiographical Memory and Episodic Memory - August 1, 2022
- Difference Between Biological Drive and Social Motive - July 30, 2022
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Cabezas, D.M. et al. "Antioxidant and emulsifying properties of modified sunflower lecithin by fractionation with ethanol-water mixtures." In: Food Industry by Muzzalupo, I. (Ed.). Intech: Croatia, 2013; pp 589–602.
[1]Fiume, Z. "Final report on the safety assessment of Lecithin and Hydrogenated Lecithin." International Journal of Toxicology, vol. 20, Suppl 1, 2001, pp. 21-45. doi: 10.1080/109158101750300937
[2]Higgins, J.P. and Flicker, L. "Lecithin for dementia and cognitive impairment." Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, vol. 3, no. 3, CD001015. doi:10.1002/14651858.
[3]National Lecithin. Sunflower Lecithin vs Soy Lecithin: What's the Difference. July 2021. Available https://nationallecithin.com/2021/07/sunflower-lecithin-vs-soy-lecithin-whats-the-difference/ (Accessed 10 February 2022).
[4]Nguyen M.T. et al. "Mapping the chemical variability of vegetable lecithins." Journal of American Oil Chemists' Society, vol. 91, 2014, 1093–1101.
[5]Wiessinger, Diane et al. "Dealing with Plugs and Blebs, The Womanly Art of Breastfeeding," 2010, La Leche League.
[6]Whitney, Cole. (n.d.) Sunflower Lecithin. Available: https://blog.modernistpantry.com/advice/sunflower-lecithin/ (Accessed 10 February 2022).
