Difference Between Erosion and Deposition
What is Erosion and Deposition?
Erosion and Deposition are the processes that change the way the surface of the earth looks over time. Both are continuous geological processes that are natural and result in relief features seen over the surface of the earth. Erosion is when the movement starts; deposition is when it stops.
What is Erosion?
Erosion is the process of eroding or being eroded by external agents like wind, water, or other natural agents. This process can dissolve rock, weakening it or turning it into tiny fragments. The process of erosion moves bits of rock or soil from one place to another. Factors affecting erosion process include: climate (The frequency, intensity, and duration of rainfall and the size of the area on which the rain falls are fundamental factors in determining the amount of runoff), vegetative cover, Soil characteristics (Particle Size Distribution and Texture; Permeability (structure); and Fibrous organic matter content (structure)) topography (shape, length, inclination and aspect of a slope), tectonics, development.
The erosion process could be downward, deepening the valley, and headward, extending the valley into the hillside, making steep banks and head cuts.
Erosion by ice – Glaciers erode the surface of the Earth in two ways: Plucking and Abrasion
Erosion by water – Sediment, picked up by flowing water, is moved along in one of four ways: Traction, Saltation, Suspension and Solution.
Erosion in the sea – Erosion by the sea occurs by process called longshore drift and drift caused by tidal currents Turbidity currents also transport sediment for hundreds of miles – from the continental shelves out into the deep ocean.
Erosion by gravity – Soil creep, mudflows, landslips and Rockfalls
What is Deposition?
Deposition is the process in which weathered and knocked rock pieces, sediments, particles and soil are carried by process of erosion to a new place and deposited there. This process transports previously eroded sediments, which, at the loss of enough kinetic energy in the fluid, is deposited, building up layers of sediment.
Deposition of sediments by wind, water & ice
Continental – River and Deltas, Glaciers and Hot deserts
Marine – Shoreline and Nearshore environments, Offshore and deep-water environments
Sediments Produced by Living Organisms
Limestone, coal, Oil and gas
Sediments produced by Evaporation
Oolitic limestone
Gypsum
Rock salt
Factors Affecting Deposition – deposition usually occurs when the velocity of the transporting agent (wind or water) decreases. This results in the settlement of the particles.
1. Size – generally the larger the sediment size, the faster the settling rate.
2. Shape – generally the more spherical the sediment shape, the faster the settling time.
3. Density – generally the denser the sediment particle, the faster it will settle.
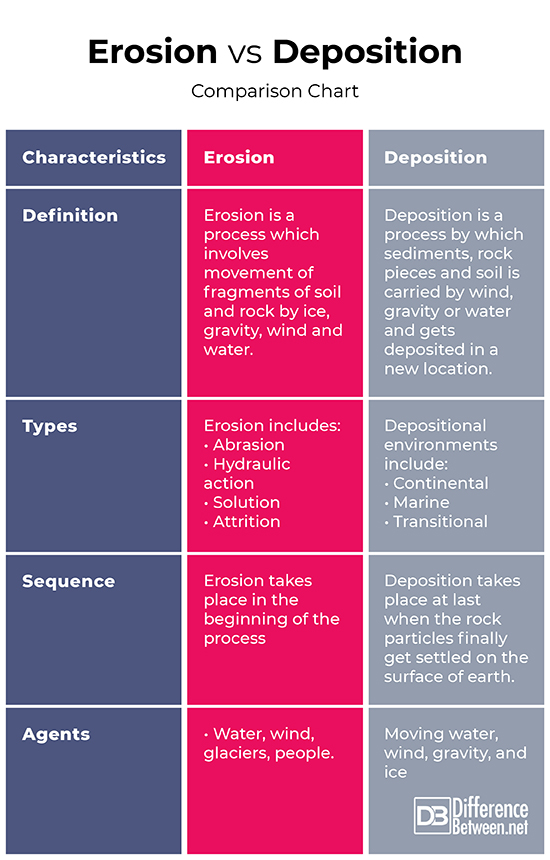
Difference between Erosion and Deposition
1. Definition
Erosion
Erosion is defined as wearing away of rock along the coastline.
Deposition
Deposition is a process in which sediments, knocked rock pieces, and soil are carried by wind, gravity and water and deposited in a new location to a landform or land mass.
2. Types
Erosion
The 4 main types of erosion are
- Abrasion – When pebbles grind along the river bank and bed in a sand-papering effect.
- Hydraulic action – This is the sheer power of the water as it smashes against the river banks. Air becomes trapped in the cracks of the river bank and bed, and causes the rock to break apart.
- Solution – happens when sea water dissolves certain rock types.
- Attrition – takes place when sea carries the rocks and these rocks knock against each other. As a result, they break apart to become more rounded and smaller.
Deposition
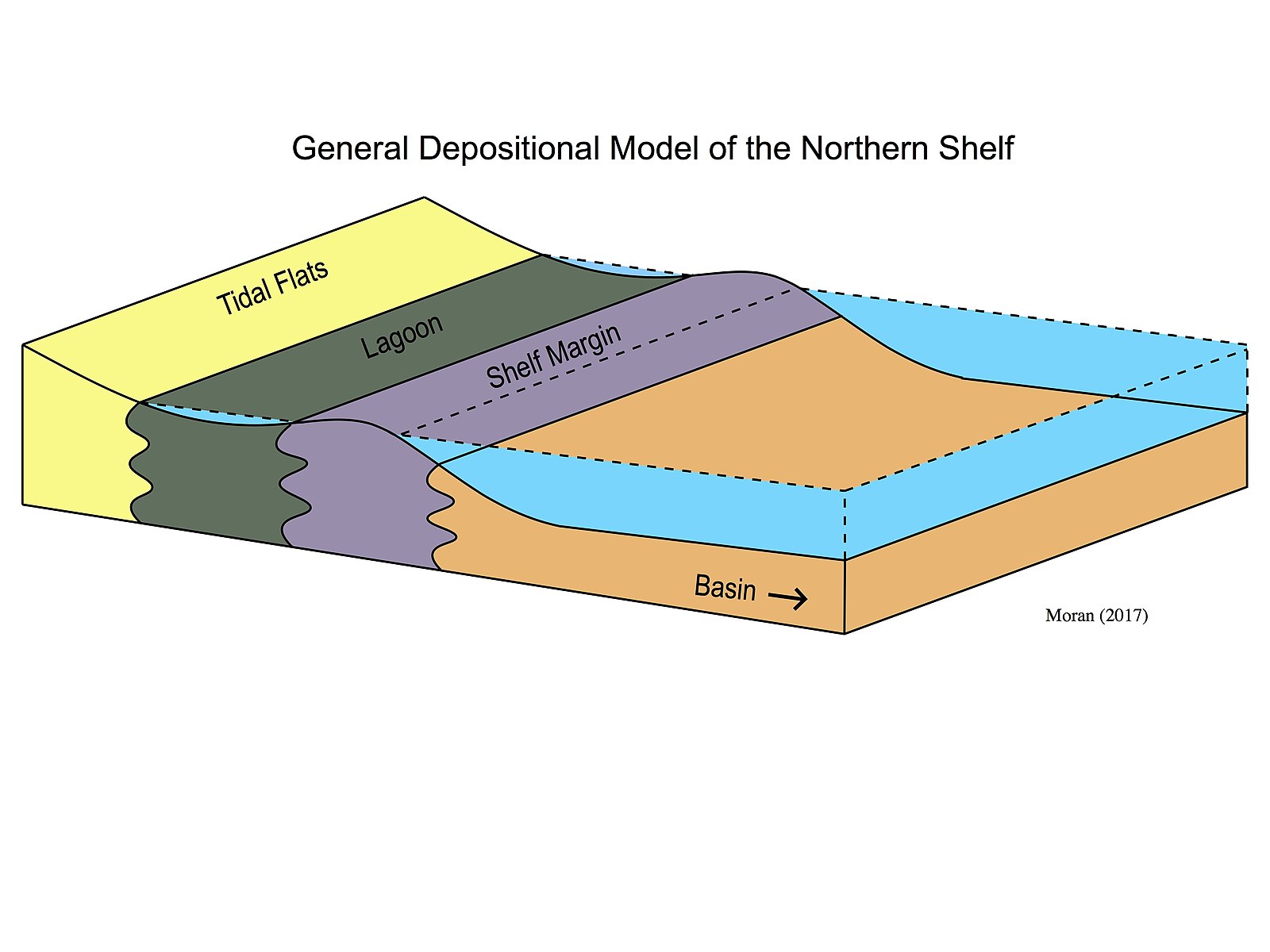
Depositional environments include:
- Continental
- Alluvial
- Fluvial
- Glacial Eolian
- Lacustrine
- Paludal
- Marine
- Carbonate shelf
- Shallow marine clastic
- Continental slope
- Deep marine
- Transitional
- Deltaic
- Estuarine
- Lagoonal
- Beach
3. Effect
Erosion
Erosion process happens on the surface of the earth and it does not impact or cause any effect on the Earth’s mantle and core.
- Pollution and Poor Water Quality
- Deforestation and Flooding
- Soil Degradation
- Mudslides and Structural Problems
Deposition
- Rivers and streams fill with melting snow in the springtime
- Water vapor changes directly to ice without first becoming a liquid
- Sediment deposition destroys fish spawning beds
- Reduces the useful storage volume in reservoirs, clogs streams
- Carry toxic chemicals
4. Occurrence
Erosion
Erosion occurs when:
- There is a loss of plant cover, which increases the amount of soil lost to wind and water erosion
- Delta is formed at the mouth of the river
- Plant roots crack a parking lot
- Ice freezes and cracks rocks. They break into smaller pieces
Deposition
Deposition occurs when:
- Water carrying the sediment slows down
- The glacier carrying the sediment melts
- The wind carries the sediment dies down
- Beach gets washed away by a hurricane
- Sand dunes are blown away by a wind
- Rocks are broken down into soil
5. Creation of Landforms
Erosion
Landforms created by erosion – Headlands, bays and cliffs
Deposition
Landforms created by deposition – Spits, salt marshes and beaches.
Summary
The points of difference between Erosion and Deposition have been summarized as below:
Erosion Vs. Deposition: Comparison Chart
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Deposition_Model.jpg
[1]Image credit: https://www.nps.gov/subjects/erosion/images/ARCH_Flooding-in-lower-Park-Avenue.jpg?maxwidth=1200&autorotate=false
[2]Lane, S. N., Westaway, R. M., & Murray Hicks, D. (2003). Estimation of erosion and deposition volumes in a large, gravel‐bed, braided river using synoptic remote sensing. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms: The Journal of the British Geomorphological Research Group, 28(3), 249-271.
[3]Kikuyama, S., Suzuki, T., Sasaki, J., Achiari, H., Soendjoyo, S. A., Higa, H., & Wiyono, A. (2017). A study on coastal erosion and deposition processes in subang, Indonesia. Asian and Pacific Coasts, 503-514.
[4]Partheniades, E. (1965). Erosion and deposition of cohesive soils. Journal of the Hydraulics Division, 91(1), 105-139.