Difference B etween Traditional and Modern Biotech
Although several discoveries have been made in biology and technology over the years which ultimately led to its development, the term biotechnology is believed to be first coined by a Hungarian agricultural engineer Karl Ereky in 1919. He built a slaughterhouse and a farm for thousands of pigs, and produced over 100,000 pigs in a year. According to him, biotechnology was the process of upgrading the raw materials biologically into socially useful products. For that, he is regarded by some as the founding father of biotechnology.
Today, biotechnology is defined by different organizations in several different ways. In the recent years, the scope of biotechnology has expanded. Biotechnology is the use of living organisms and systems to manufacture useful products or to perform an industrial task. Biotechnology encompasses both traditional biotechnology and modern biotechnology. But without the traditional biotech, there won’t be modern biotech. The diversity of microorganisms and development of genetics expanded the potential of traditional biotech, and ultimately led to the development of modern biotechnology.
What is Traditional Biotechnology?
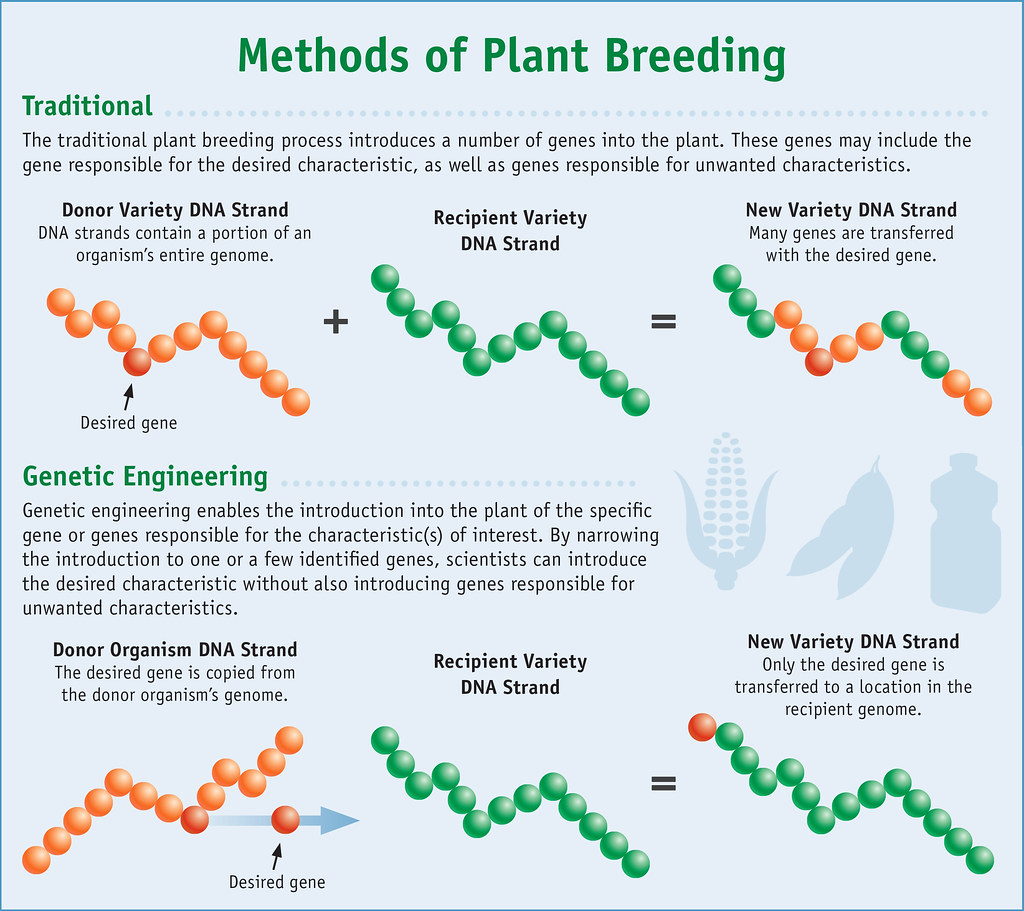
Traditional biotechnology refers to the traditional techniques of using living organisms to yield new products or modify foods or other useful products for human use. Without the traditional biotech, there won’t be modern biotechnology. The early examples of biotechnology include breeding animals and crops to make cheese/yoghurt, bread, beer and wine. Some traditional techniques such as selective breeding, hybridization and mutagenesis, are used in current applications of biotechnology. Other technologies include fermentation, selective breeding, food processing, tissue culture and more. The diversity of microorganisms and development of genetics expanded the potential of traditional biotechnology, and ultimately led to the development of modern biotechnology.
What is Modern Biotechnology?
Modern biotechnology involves the use of GE techniques, such as recombinant DNA, functional and structural genomics, DNA diagnostic probes, and other methods for genetic modification. The development of recombinant DNA technology has marked the beginning of so-called modern biotechnology. Modern biotech has contributed significantly to enhancing our knowledge of biological systems. Modern biotechnology techniques are currently being used in many areas such as food, agriculture, forestry, healthcare, environment, minerals, and industrial processes to develop new products and processes. One of the most extensive applications of modern biotech is in agriculture. Recombinant DNA techniques and mutagenesis are used to develop plants with novel traits. Biotech diagnostics have been used to detect a wide variety of diseases and genetic conditions.
Difference between Traditional and Modern Biotech
Definition
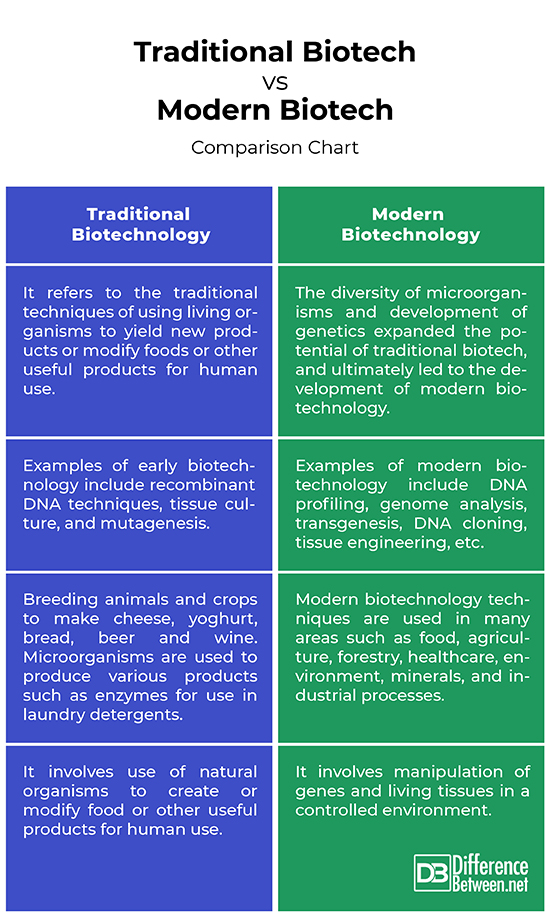
– Traditional biotech, as the name suggests, refers to the traditional methods of using living organisms to yield new products or modify foods or other useful products for human use. Traditional biotech is based on active techniques which have great efficiency and accuracy. The modern biotechnology shares the same foundation, but it refers to biotechnological techniques for the manipulation of genetic material, cells and living tissues in a controlled environment. Modern biotech involves making products from whole organisms or parts of organisms.
Method
– Traditional biotechnology may include the products of tissue culture, micro-propagation, or various strategies used to eliminate disease, while modern biotechnology incorporates a specific focus on industrial usage of rDNA, cell fusion and novel bioprocessing techniques. Recombinant DNA technology is the foundation of modern biotechnology. Modern biotech uses GE techniques, such as DNA diagnostic probes, recombinant DNA, functional and structural genomics for genetic modification. Traditional biotechnology is based on active techniques which have great efficiency and accuracy, and are cheaper.
Applications
– Traditional biotechnology remains the technology of choice for the most important agronomic traits. Early examples include breeding animals and crops to make cheese, yoghurt, bread, beer and wine. Microorganisms are also used to produce various products such as enzymes for use in laundry detergents. Modern biotechnology is applied in medicine and healthcare in therapeutics, mainly for the discovery, development and production of novel drugs, and in diagnostics, for protein and nucleic acids based tests. Biotechnology applications in the environment focus primarily on using living organisms to treat waste and prevent pollution.
Traditional Biotech vs. Modern Biotech: Comparison Chart
Summary of Traditional Biotech vs. Modern Biotech
In a nutshell, biotechnology encompasses both traditional biotechnology and modern biotechnology. But without the traditional biotech, there won’t be modern biotech. Traditional biotech involves use of natural organisms to create or modify food or other useful products for human use, while modern biotech involves manipulation of genes and living tissues in a controlled environment to generate new tissue. Modern biotechnology is applied in medicine and healthcare in therapeutics, mainly for the discovery, development and production of novel drugs, and in preventives for the development recombinant vaccines.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Mathuriya, Abhilasha S. Industrial Biotechnology. New Delhi, India: Ane Books, 2010. Print
[1]McKelvey, Maureen D., et al. The Economic Dynamics of Modern Biotechnology. Cheltenham, United Kingdom: Edward Elgar Publishing, 2004. Print
[2]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/7287/8737954801_4f038c0d3c_b.jpg
[3]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/3681/11717751704_dd29fbff47_b.jpg