Difference Between Gout and Turf Toe
What is Gout?
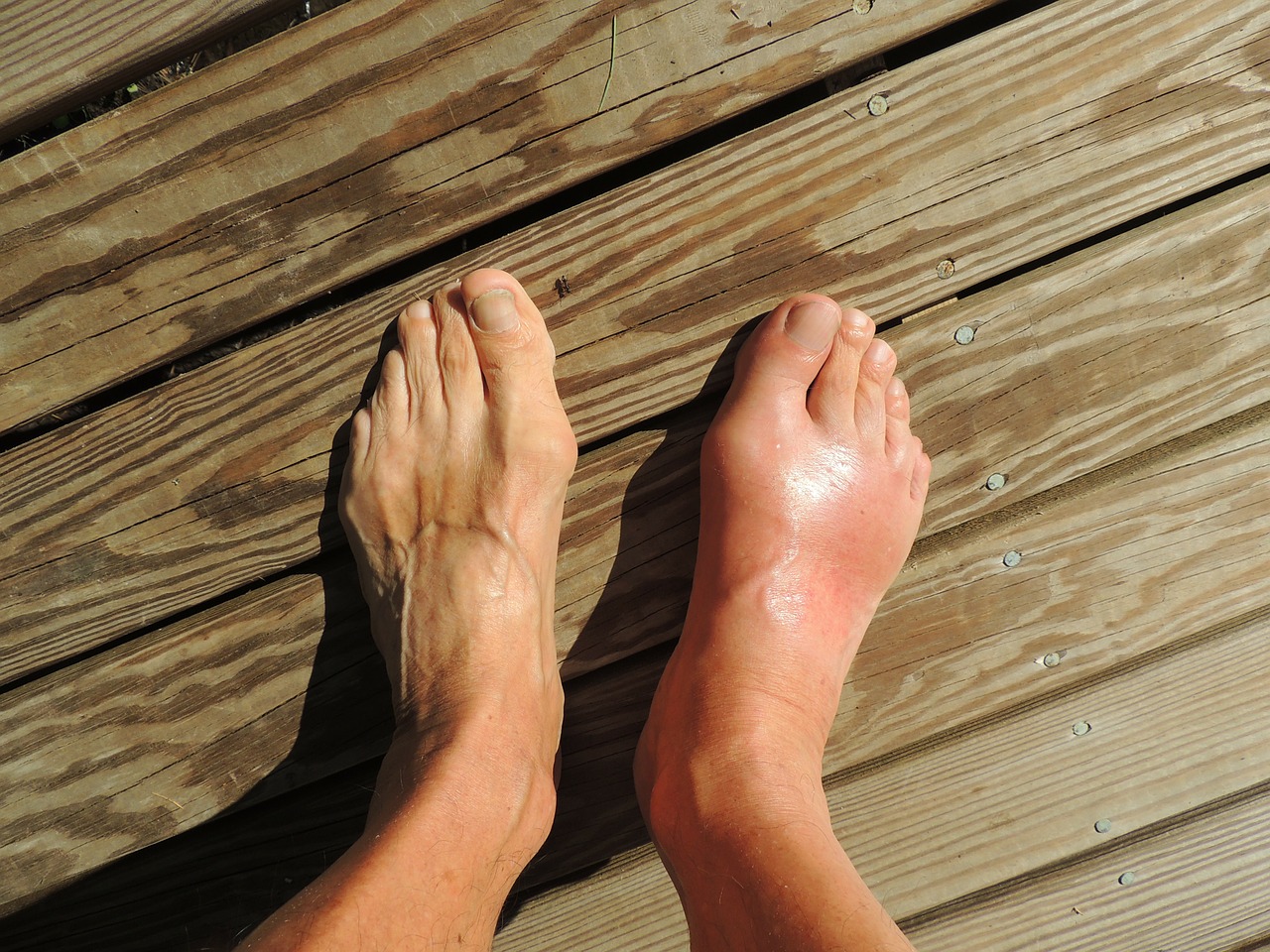
Gout is a metabolic disease characterized by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. Its first symptoms are swelling, severe pain, and redness. Symptoms most often begin at the base of the toe.
Gout affects predominantly men.
The symptoms of gout include:
- Severe, sudden, and long lasting pain in the big toe;
- Increased uric acid levels in the blood;
- Increased protein levels in the blood;
- Difficult movement of the joint;
- Swelling and redness;
- Kidney stones;
- Kidney inflammation;
- High blood pressure (in 30% of the cases).
Gout can be caused by a congenital defect in the purine metabolism or by a decreased renal excretion of the uric acid. Another cause of gout can be an unhealthy lifestyle and excessive consumption of meat and alcohol.
Purines are processed into uric acid which should be excreted in the urine. If, for any of the above reasons, part of the uric acid fails to be excreted it accumulates in the form of crystals in the tissues of the joints, the soft parts of the ear, the big toe, the elbow, etc. Crystals cause an inflammatory reaction and impair the function of the joints.
Gout can be diagnosed relatively easy. It is necessary to examine the symptoms and analyze the content of uric acid in the blood. Additional tests like X-ray, ultrasonography, etc. may also be used.
It is necessary to take measures to overcome uric acid levels in order to control the disease. The healthy diet and the limitation of alcohol intake are very important. For treatment of gout are used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, and colchicine.
What is Turf Toe?
Turf toe is a painful injury or rupture of the connective tissue in the area of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe.
It is most common in sports played on artificial terrain, like football, rugby, gymnastics, athletics, and martial arts.
Typically, the sprain of the big toe is associated with sudden acute pain at the time of the trauma. In some cases, the pain subsides and appears again at night or the next morning. The pain may not be strong in normal walking but exacerbate when climbing, jumping, kicking, etc. The pain can be felt in the sides of the big toe, the bottom of the foot or on its upper surface, and in some cases, there may be no specific localization. In case of more serious trauma, local swelling may occur. In more serious cases, the gait is disturbed and the patient starts to limp with the injured leg.
The big toe consists of two bones. The bone at its base is connected to the foot bones by the metatarsophalangeal joint. Often, in sports incidents involving excessive twisting up or down of the big toe (hyperreflexia and hypertension), the ligaments in the area of the metatarsophalangeal joint are impaired, which results in a turf toe.
The most common causes of turf toe are:
- Errors in the rehabilitation of previous sprains;
- Joint instability;
- Unsuitable worm up;
- Unsuitable terrain surface;
- Weakness or muscle fatigue;
- Inappropriate sports shoes (soft or flexible soles).
In most cases, a detailed examination is sufficient to confirm the diagnosis. To exclude additional traumas such as fractures, radiography is usually done. Due to the similarity of the symptoms, gout should be excluded as a cause of the pain in the big toe.
Treatment is conservative and includes temporary thumb immobilization and physiotherapy procedures.
Immediately after the trauma, the principles of first aid for sports injuries apply, including:
- Compress with ice;
- Compression bandage;
- Rest and immobilization;
- Painkillers and anti-inflammatory agents;
After the acute symptoms resolve (24-48 hours), different procedures are applied to allow quicker recovery, as well as to reduce the risk of complications.
Physiotherapy procedures may include:
- Massage;
- Ultrasound therapy;
- Taping and kinesio taping;
- Thermal procedures;
- Exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and balance;
Difference Between Gout and Turf Toe
-
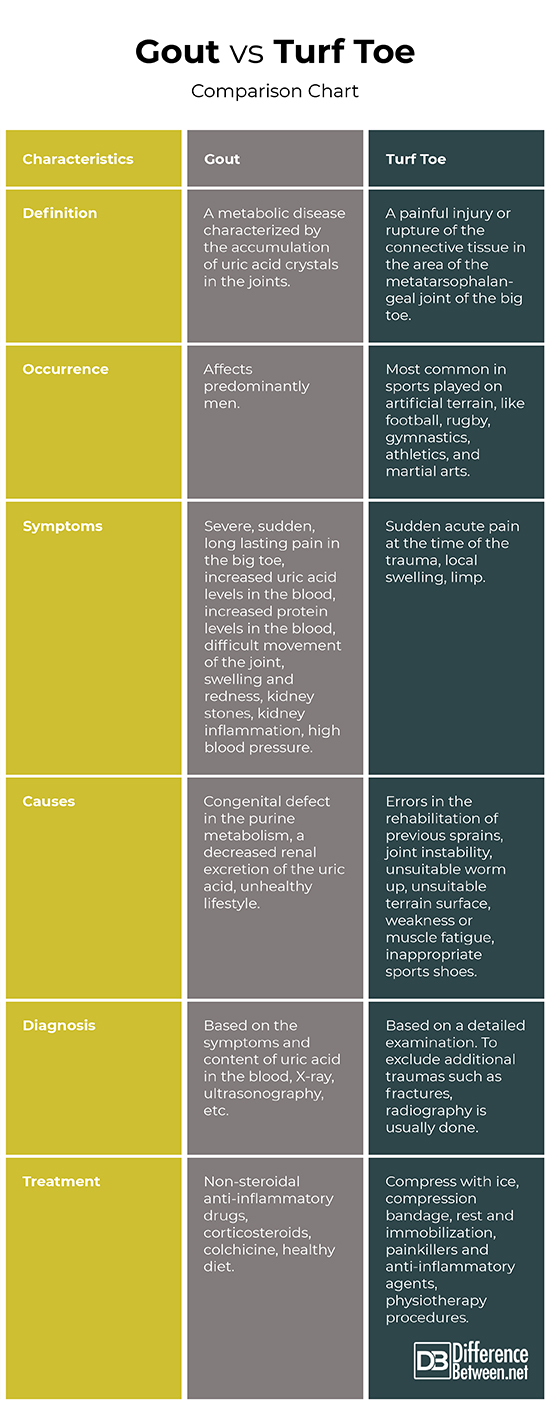
Definition
Gout: Gout is a metabolic disease characterized by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints.
Turf Toe: Turf toe is a painful injury or rupture of the connective tissue in the area of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe.
-
Occurrence
Gout: Gout affects predominantly men.
Turf Toe: Turf toe is most common in sports played on artificial terrain, like football, rugby, gymnastics, athletics, and martial arts.
-
Symptoms
Gout: The symptoms of gout include severe, sudden, and long lasting pain in the big toe, increased uric acid levels in the blood, increased protein levels in the blood, difficult movement of the joint, swelling and redness, kidney stones, kidney inflammation, high blood pressure.
Turf Toe: The symptoms of turf toe include sudden acute pain at the time of the trauma, local swelling, limp.
-
Causes
Gout: Gout can be caused by a congenital defect in the purine metabolism, by a decreased renal excretion of the uric acid or by an unhealthy lifestyle.
Turf Toe: The most common causes of turf toe are errors in the rehabilitation of previous sprains, joint instability, unsuitable worm up, unsuitable terrain surface, weakness or muscle fatigue, inappropriate sports shoes (soft or flexible soles).
-
Diagnosis
Gout: Gout can be diagnosed based on the symptoms and content of uric acid in the blood. Additional tests like X-ray, ultrasonography, etc. may also be used.
Turf Toe: In most cases, a detailed examination is sufficient to confirm the diagnosis. To exclude additional traumas such as fractures, radiography is usually done.
-
Treatment
Gout: For treatment of gout are used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, and colchicine. The healthy diet and the limitation of alcohol intake are very important.
Turf Toe: Immediately after the trauma, the principles of first aid for sports injuries apply, including compress with ice, compression bandage, rest and immobilization, painkillers and anti-inflammatory agents. After the acute symptoms resolve physiotherapy procedures may be applied, including massage, ultrasound therapy, taping and kinesio taping, thermal procedures, exercises.
Gout Vs. Turf Toe: Comparison Chart
Summary of Gout Vs. Turf Toe:
- Gout is a metabolic disease characterized by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints.
- Turf toe is a painful injury or rupture of the connective tissue in the area of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe.
- Gout affects predominantly men. Turf toe is common in sports played on artificial terrain, like football, rugby, gymnastics, athletics, and martial arts.
- The symptoms of gout include severe, sudden, and long lasting pain in the big toe, increased uric acid levels in the blood, increased protein levels in the blood, difficult movement of the joint, swelling and redness, kidney stones, kidney inflammation, high blood pressure. The symptoms of turf toe include sudden acute pain at the time of the trauma, local swelling, limp.
- Gout can be caused by a congenital defect in the purine metabolism, by a decreased renal excretion of the uric acid or by an unhealthy lifestyle. The most common causes of turf toe are errors in the rehabilitation of previous sprains, joint instability, unsuitable worm up, unsuitable terrain surface, weakness or muscle fatigue, inappropriate sports shoes.
- Gout can be diagnosed based on the symptoms and content of uric acid in the blood. Additional tests like X-ray, ultrasonography, etc. may also be used. In most cases, a detailed examination is sufficient to diagnose a turf toe. To exclude additional traumas such as fractures, radiography is usually done.
- For treatment of gout are used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, colchicine, and healthy diet. For treatment of turf toe are applied the principles of first aid for sports injuries and physiotherapy procedures.
- Difference Between Gallstones and Cholecystitis - September 5, 2021
- Difference Between Constipation and Cramping - August 4, 2021
- Difference Between Whole Genome Sequencing and Microarray - May 6, 2021
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Doral, M., R. Tandoğan, G. Mann, R. Verdonk (Eds.). Sports Injuries. Prevention, Diagnosis, Treatment and Rehabilitation. Basel: Springer International Publishing. 2012. Print.
[1]Konshin, V. Beating Gout: A Sufferer's Guide to Living Pain Free. New York: Ayerware Publishing. 2009. Print.
[2]Schlesinger, N., P. Lipsky. Gout. 1st Edition. Amsterdam: Elsevier. 2018. Print.
[3]Image credit: https://www.pexels.com/photo/94071/
[4]Image credit: https://pixabay.com/en/feet-gout-pain-foot-human-anomaly-174216/