Difference Between Gout and Bursitis
What is Gout?
Definition of Gout:
Gout is the disorder in which monosodium urate crystals are deposited in the joints of the body resulting in painful, red and swollen joints.
Symptoms and Complications:
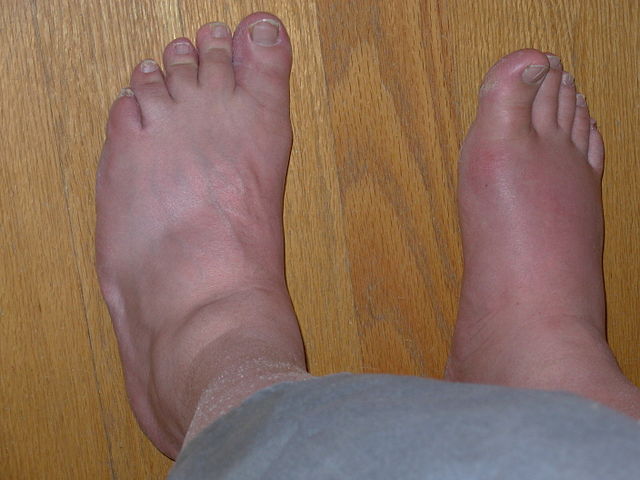
The symptoms typically include pain, swelling and redness at the joints where the urates are deposited. The first symptoms often occur in the toes, at the joints found between the toes and the feet. Painful nodules known as tophi can eventually develop in patients who have gout; these can result in deformities of the joints and even osteoarthritis. Complications of gout include problems such as kidney stones and kidney infections.
Diagnosis of Gout:
The condition can be diagnosed when uric acid crystals are noticed in the fluid taken from the joints. This is the synovial fluid which can be examined under a microscope. Blood tests can also be done to measure how much uric acid and creatinine is present. Ultrasound can be done of the joints and can show urate crystals present. X-rays may be used to eliminate other causes of joint pain and inflammation.
Causes and Risk Factors:
The condition occurs when the amount of urate in the blood plasma is more than 6.8 mg/dL. It is more common in men than women and tends to be caused by both genetic as well as environmental factors. Individuals who have metabolic syndrome are also at increased risk of developing gout. The disorder is more common in men and in those individuals who drink alcohol because this reduces the kidneys’ ability to rid the body of uric acid. The condition can cause a type of chronic or severe arthritis as a result of these crystals of uric acid.
Prevention and Treatment:
You can help to prevent gout by avoiding or reducing the amount of food you eat that contains lots of purines, since it is the breakdown of these that produces uric acid. Foods such as sardines, some meats, and dried beans tend to have lots of purines. The condition can be treated using colchicine and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Medicine can also be used to lower the concentration of uric acid in the blood plasma; for instance, febuxostat and allopurinol can be used to accomplish this and help prevent or reduce the deposition of urates in the joints.
What is Bursitis?
Definition of Bursitis:
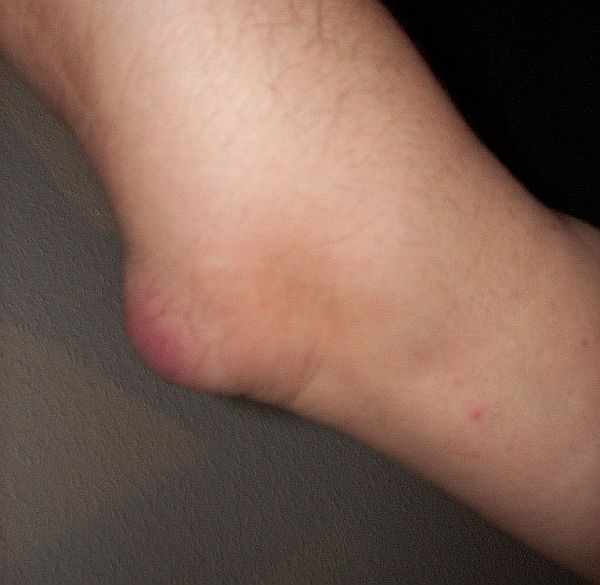
Bursitis is the condition in which the fluid-filled sac at a joint becomes inflamed causing pain and discomfort in the joint during movement. It can be a chronic or an acute problem.
Symptoms and Complications:
Symptoms include stiffness, tenderness, and pain with movement or if you apply pressure, as well as swollen joints where the bursae are affected. The joints most often affected are those where there is a lot of movement, for instance, the elbows and knees, but toes can be affected as well. Septic bursitis is a complication that can occur in which the bursa becomes infected. This is more common in people such as carpenters and plumbers due to their occupation.
Diagnosis:
The condition can be diagnosed by looking at bursal fluid extracted from the joints. The use of X-rays and MRI can help to eliminate other possible causes of pain in the joints.
Causes and Risk Factors:
The cause of bursitis is often repeated use of a joint, so if you are throwing a ball often or kneeling on the floor a lot. This means that people who play sport or have certain occupations in which joints are repeatedly in motion are most at risk of developing this condition. If you have diabetes, arthritis or gout you will also be at increased risk of getting bursitis.
Prevention and Treatment:
The disorder can be treated using anti-inflammatory medications and also corticosteroid injections and splints. You can help prevent the condition of bursitis by warming up properly before playing sport, by using pads to kneel on and lifting objects with care. Keeping a healthy weight will also be advisable and can help prevent illnesses like diabetes type 2 which can lead to an increased risk of bursitis.
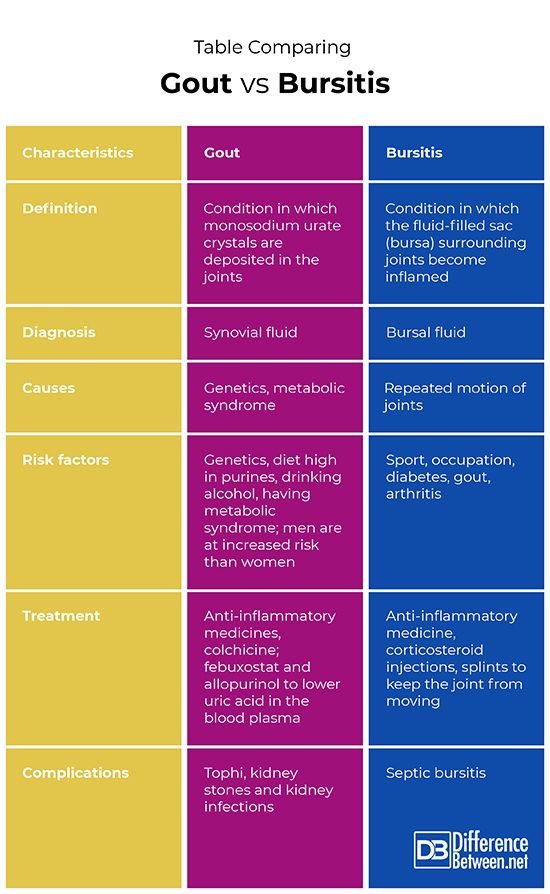
Difference between Gout and Bursitis
Definition
Gout is the condition in which monosodium urate crystals are deposited in the joints causing pain, swelling and redness. Bursitis is the condition in which the fluid-filled sac, known as the bursa, surrounding a joint, becomes inflamed.
Diagnosis
Gout can be diagnosed by examining the synovial fluid for the presence of the urate crystals. X-ray can help eliminate other causes of gout. Bursitis can be diagnosed by looking at bursal fluid and also by eliminating other causes by using MRI or X-ray.
Causes
The condition of gout can be caused by genetic factors as well as environmental factors such as having metabolic syndrome and eating food that is high in purines. The condition of bursitis is caused by repetitive motion of joints, and is thus common in people who play a lot of sport and in certain occupations.
Risk Factors
Gout is partly caused by genetics, so having a family history puts you at increased risk. Also having metabolic syndrome, drinking alcohol, being male, and eating many foods high in purines increase the risk of developing gout. Bursitis is more likely in people who play a sport in which there is repetitive motion of a joint, as well as people who have certain occupations. Arthritis, diabetes, and gout are also risk factors for bursitis.
Treatment
The treatment for gout includes using anti-inflammatory medicines and colchicine, and medicine such as febuxostat and allopurinol to reduce the amount of uric acid in the blood. The treatment for bursitis involves using anti-inflammatory medicines and corticosteroid injections, and splints to immobilize a joint.
Complications
The problem with gout is that it can lead to the development of tophi, kidney stones and kidney infections. The problem with bursitis is that sepsis can develop which can be very dangerous.
Table Comparing Gout Vs. Bursitis
Summary of Gout Vs. Bursitis
- Gout is the condition in which urate crystals are deposited in joints.
- Bursitis is the condition in which bursae, sacs found at the joints, become inflamed.
- Both conditions cause painful, red and swollen joints.
- Both gout and bursitis can cause complications which can further jeopardize your health.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Biundo, Joseph J. “Bursitis”. Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2018, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/musculoskeletal-and-connective-tissue-disorders/bursa,-muscle,-and-tendon-disorders/bursitis
[1]Edwards, N Lawrence. “Gout”. Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2018, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/musculoskeletal-and-connective-tissue-disorders/crystal-induced-arthritides/gout
[2]Ho, George, Alan D. Tice, and Stephen R. Kaplan. "Septic bursitis in the prepatellar and olecranon bursae: an analysis of 25 cases." Annals of internal medicine 89.1 (1978): 21-27.
[3]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/9/98/Bursitis_olecrani.jpg
[4]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e1/Gout_Advanced.jpg/640px-Gout_Advanced.jpg
