Difference Between Hadoop and Teradata
Now, more than ever, technology plays a pivotal role in the entire process of how we gather and use data. Technology has changed the way data is produced, processed and consumed. As the big data analytics market is rapidly expanding, many enterprises and businesses start to invest in Big Data technologies to store and analyze these massive volumes of data. Today, there are many Big Data technologies on the market that are making quite an impact on the new technology stacks for handling Big Data. One such technology that has been at the center of the Big Data talks is Apache Hadoop. Hadoop is the one of the biggest names in the Big Data industry. Teradata is a relational database management system and a leading data warehousing solution that provides data management solutions for analytics. It is used to store and process large amount of structured data in a central repository. Below is a head to head comparison between the two technologies.
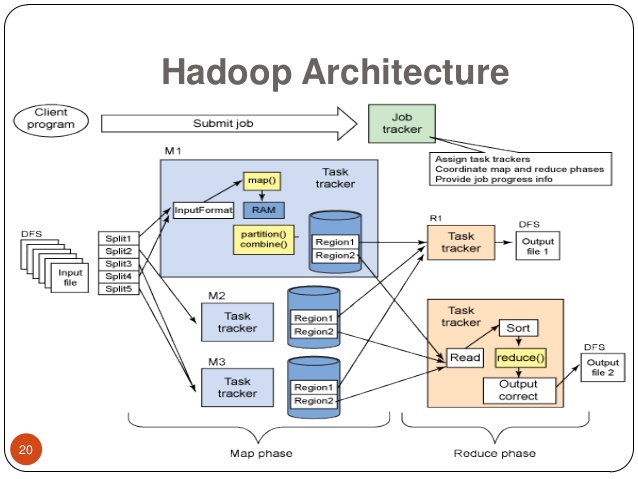
What is Hadoop?
Hadoop is the heart of Big Data. It is an open-source software framework developed by Apache Software Foundation and used to store and process diverse data types that enable data-driven enterprises to rapidly derive the complete value from all their data. Hadoop is the answer to implement a Big Data strategy. The original creators of Hadoop are Doug Cutting and Mike Cafarella. They were working on a project to create a large Web index called “Nutch”. They saw the MapReduce and GFS papers from Google, and found it useful for the project. So, they finally integrated the concepts from the papers into the project, which eventually formed the genesis of the Hadoop project. Doug gave the name “Hadoop” to his toy elephant, which he later used for his open source project. Hadoop stores terabytes and even petabytes of data inexpensively, without losing data or interrupting data analyses.

What is Teradata?
Teradata is a relational database management system like Oracle developed by a leading software company with the same name. Teradata is the world’s leading provider of business analytics solutions, data and analytics solutions, and hybrid cloud products and services. It provides the relational database management system in a single RDMS which acts as a central repository. Its RDBMS is considered to be a leading data warehousing solution that runs the world’s largest commercial databases. Teradata provides decision-support capabilities for organizations and enterprises that need to store and analyze gigabytes and even terabytes of data. The company was incorporated in 1979 and started in a garage in Brentwood, California. The name Teradata symbolized the ability to manage trillions of bytes of data. The company was actually founded by a group of people.
Difference between Hadoop and Teradata
Technology
– Hadoop is a Big Data technology developed by Apache Software Foundation to store and process Big Data applications on scalable clusters of commodity hardware. It is an open-source platform that addresses the Big Data challenges involving massive amounts of data that is too diverse and fast-changing for conventional technologies and infrastructure to address efficiently. Teradata, on the other hand, is a fully scalable relational database warehouse implemented in single RDBMS which acts as a central repository. It is a leading data warehousing solution that runs the world’s largest commercial databases.
Architecture
– Hadoop is based on a ‘Master-Slave Architecture’, where a cluster comprises of a single Master node and all the other nodes are Slave nodes. The Hadoop architecture is based on three sub-components: HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System), MapReduce, and YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator). HDFS is the storage part of the Hadoop architecture; MapReduce is the agent that distributes the work and collects the results; and YARN allocates the available resources in the system.
Teradata is a shared nothing architecture based on a massively parallel processing (MPP) system. The Teradata DBMS is linearly and predictably scalable in all dimensions of a database system workload. It acts as a single data store that can accept large number of concurrent requests from multiple client applications. The main components of Teradata are Parsing Engine, BYNET, and AMPs (Access Module Processors).
Data Type
– Hadoop is used to store and process diverse data types that enable data-driven enterprises to rapidly derive the complete value from all their data. It can process any type of data using multiple open-source tools – regardless of the data type, whether it’s structured semi-structured or unstructured data. Hadoop’s superior capabilities for processing unstructured data are unmatched. Teradata, on the other hand, is a relational data warehousing solution best used to store and process large amount of structured tabular format data. It is not good for processing semi-structured or unstructured data.
Hadoop vs. Teradata: Comparison Chart
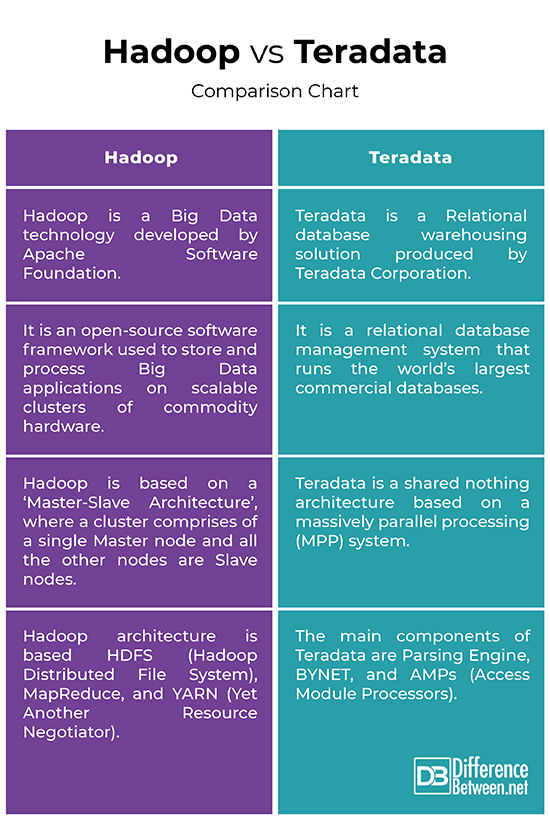
Summary of Hadoop vs. Teradata
Hadoop stores terabytes and even petabytes of data inexpensively, without losing data. . It can process any type of data using multiple open-source tools. Teradata, on the other hand, is a fully scalable relational database management solution used to store and process large amount of structured data in a central repository. Hadoop is based on a ‘Master-Slave Architecture’, where a cluster comprises of a single Master node and all the other nodes are Slave nodes, whereas Teradata is a shared nothing architecture based on a massively parallel processing (MPP) system.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Linstedt, Daniel, et al. Data Architecture: A Primer for the Data Scientist. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Academic Press, 2019. Print
[1]Singh, S.K. Database Systems: Concepts, Design and Applications. Noida, India: Pearson Education India, 2011. Print
[2]Minelli, Michael, et al. Big Data, Big Analytics: Emerging Business Intelligence and Analytic Trends for Today's Businesses. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2012. Print
[3]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Big-data-concepts-20-638.jpg
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Teradata_logo_2018.png
