Difference Between Fleas and Gnats
What is Fleas?
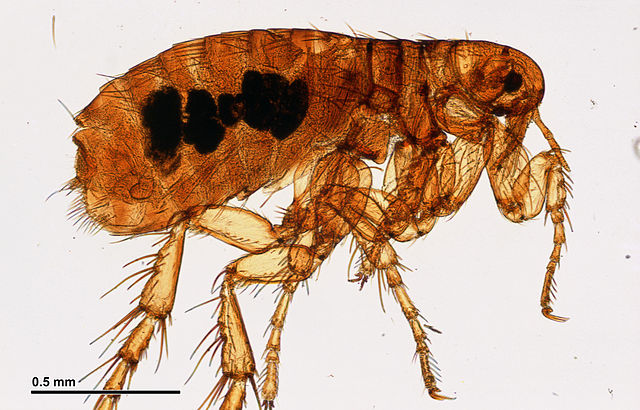
- Fleas are small wingless parasite insects form the order Siphonaptera. They are external parasites of birds and mammals. They are 1.5 to 3.5 mm long, dark in color and their mouthparts are adapted to feeding by perforation of the host’s skin and sucking blood.
- The bodies of the fleas are flattened sideways, to help them pass over the feathers or fur of their hosts. Their legs end in strong claws that help them grasp the host and prevent from falling. The fleas have strong bodies and can survive a great pressure.
- The bodies of the fleas are covered with sclerites, overgrown with short spines and hairs, directed backward.
- Fleas have simple eyespots. There are species with no eyes.
- The fleas do not have wings. Their legs are tailored for jumping at a big distance. A flea can jump more than 50 times its body length.

- Fleas lay small, oval, white eggs. Fleas’ larvae are pale, small, worm-like, covered with bristles. They do not have eyes.
- The larvae have feeding apparatus adapted for chewing and eat organic matter. Their main food is the feces of adult fleas.
- Fleas are usually a nuisance to their hosts, causing an itching sensation. Flea bite causes a swollen, slightly raised itching spot. Flea allergy dermatitis is common in many host species, including dogs and cats. As a result of frequent scratching by the animal, fleas can lead to hair loss at certain sections of the body.
- Fleas are vectors for many different viral and bacterial diseases, protozoan and helminth parasites of humans, other mammals, and birds.
What is Gnats?
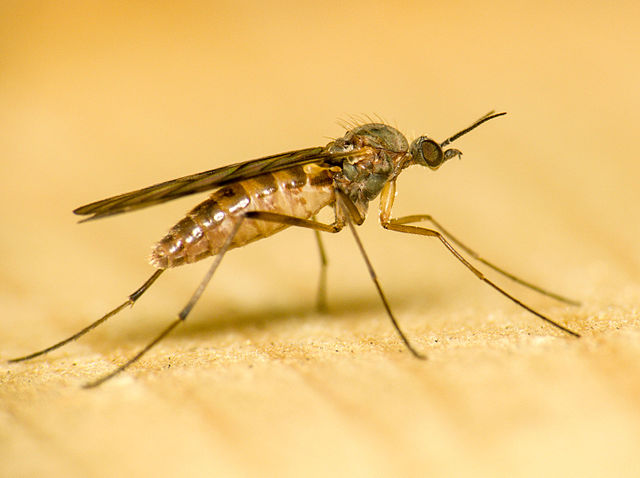
- Gnats are small flying insects in the Dipterid suborder Nematocera.
- “Gnat” is not a phylogenetic or taxonomic term and there is no scientific consensus on what species are considered gnats.
- Ranging in length from 1 to 15 mm, gnats are delicate-looking small, long-legged insects with six legs, three body parts (head, thorax, abdomen) and one pair of wings. Many of them are weak fliers.
- Depending on the species, the adult gnats feed on insects, plants, fungi, or blood. They can be plant pollinators, feed on crop pests such as scales and aphids, or be crop pests themselves.
- The species of gnats that feed on blood are extremely small. Only the females of these species feed on blood, they need it for the proper development of their eggs. The males feed on plants.
- The symptoms of a gnat bite are redness, swelling, irritation, and itchiness at the site of the bite. The biting gnats may spread diseases and parasites to animals and humans.
- The males of some gnat species assemble in large mating swarms, occurring most commonly at dusk in large fields and above streets.
- Depending on the species, gnats lay their eggs on water or land. Larvae may be mobile or immobile, terrestrial or aquatic. They are carnivorous or plant feeders, depending on the species. The larvae, feeding on plants may cause the formation of galls on the root, stem, or leaves of the host plant. Some gnat species are pests of mushrooms and potted plants.
Difference Between Fleas and Gnats
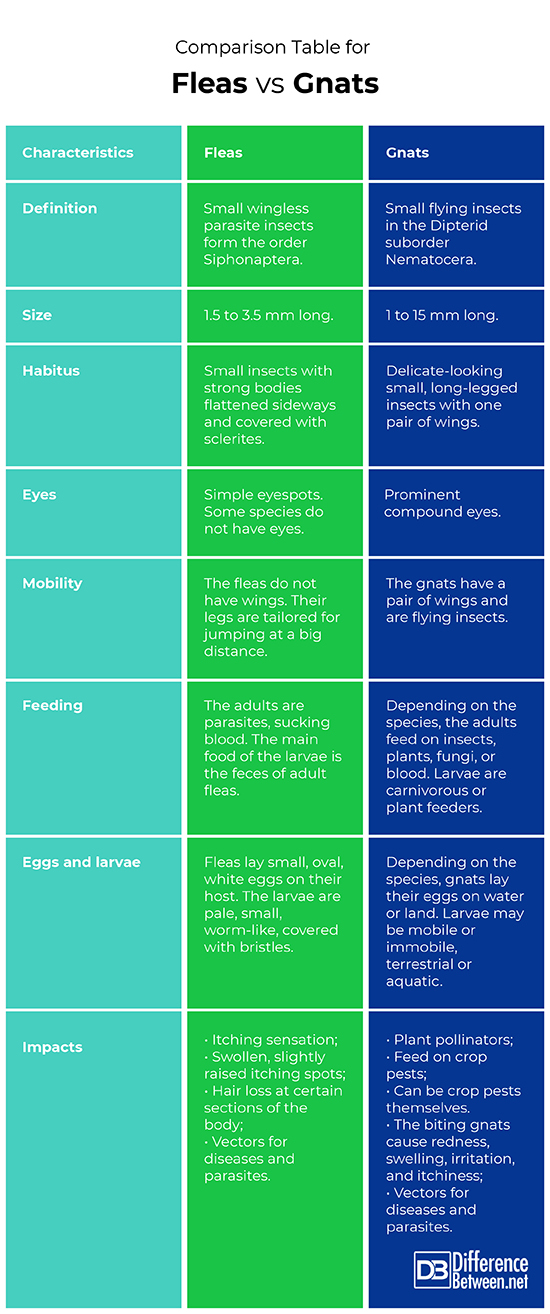
1. Definition
Fleas: Fleas are small wingless parasite insects form the order Siphonaptera.
Gnats: Gnats are small flying insects in the Dipterid suborder Nematocera.
2. Size
Fleas: The fleas are 1.5 to 3.5 mm long.
Gnats: The gnats are 1 to 15 mm long.
3. Habitus
Fleas: The fleas have strong bodies flattened sideways and covered with sclerites.
Gnats: The gnats are delicate-looking small, long-legged insects with one pair of wings.
4. Eyes
Fleas: Fleas have simple eyespots. There are species with no eyes.
Gnats: Gnats have prominent compound eyes.
5. Mobility
Fleas: The fleas do not have wings. Their legs are tailored for jumping at a big distance.
Gnats: The gnats have a pair of wings and are flying insects.
6. Feeding
Fleas: The adult fleas are parasites, feeding by perforation of the host’s skin and sucking blood. The larvae have feeding apparatus adapted for chewing. Their main food is the feces of adult fleas.
Gnats: Depending on the species, the adult gnats feed on insects, plants, fungi, or blood. Larvae are carnivorous or plant feeders.
7. Eggs and larvae
Fleas: Fleas lay small, oval, white eggs on their host. The larvae are pale, small, worm-like, covered with bristles.
Gnats: Depending on the species, gnats lay their eggs on water or land. Larvae may be mobile or immobile, terrestrial or aquatic.
8. Impacts
Fleas: Fleas are causing an itching sensation. Flea bite causes a swollen, slightly raised itching spot. As a result of frequent scratching by the animal, fleas can lead to hair loss at certain sections of the body. Fleas are vectors for viral and bacterial diseases, protozoan and helminth parasites.
Gnats: Gnats can be plant pollinators, feed on crop pests such as scales and aphids, or be crop pests themselves. The biting gnats cause redness, swelling, irritation, and itchiness at the site of the bite and may spread diseases and parasites to animals and humans.
Comparison Table for Fleas Vs. Gnats
Summary of Fleas Vs. Gnats:
- Fleas are small wingless parasite insects form the order Siphonaptera.
- Gnats are small flying insects in the Dipterid suborder Nematocera.
- The fleas are 1.5 to 3.5 mm long, while the gnats are 1 to 15 mm long.
- The fleas have strong bodies flattened sideways and covered with sclerites. The gnats are delicate-looking small, long-legged insects with one pair of wings.
- Fleas have simple eyespots. Gnats have prominent compound eyes.
- The fleas do not have wings and their legs are tailored for jumping at a big distance. The gnats have a pair of wings and are flying insects.
- The adult fleas are parasites, feeding by perforation of the host’s skin and sucking blood. Depending on the species, the adult gnats feed on insects, plants, fungi, or blood.
- The fleas’ larvae have feeding apparatus adapted for chewing and feed on the feces of the adults. The gnats’ larvae are carnivorous or plant feeders.
- Gnats can be plant pollinators, feed on crop pests, or be crop pests themselves.
- Fleas cause an itching sensation, swollen, slightly raised itching spots, hair loss at certain sections of the body. The biting gnats cause redness, swelling, irritation, and itchiness at the site of the bite.
- Fleas and biting gnats are vectors for different diseases and parasites.
- Difference Between Gallstones and Cholecystitis - September 5, 2021
- Difference Between Constipation and Cramping - August 4, 2021
- Difference Between Whole Genome Sequencing and Microarray - May 6, 2021
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
3 Comments
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7c/Flea_%28251_01%29_Aphaniptera%3B_total_preparation.jpg/640px-Flea_%28251_01%29_Aphaniptera%3B_total_preparation.jpg
[1]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4b/Wood_Gnat_%28Sylvicola%29_%2812609603704%29.jpg/640px-Wood_Gnat_%28Sylvicola%29_%2812609603704%29.jpg
[2]Askew, R. Parasitic Insects. New York: Elsevier. 1971. Print.
[3]Gullan, J., P. Cranston. The Insects: An Outline of Entomology. 5th Edition. Hoboken: John Wiley and Sons. 2014. Print.
[4]Marshall, S. Flies: The Natural History and Diversity of Diptera. Richmond Hill: Firefly Books. 2012. Print.

I have determined that I have a somewhat infestation of nats. The best way to get rid of them is?
The pictures of a flea and a gnat are transposed. Two definitions and two wrongly placed photos.
How to get rid of gnats?