Difference Between Power Strip and Surge Protector
Both power strips and surge protectors are essential electronic accessories used in almost every household with electronic devices. You probably have outlets in your house or office that are most likely to accommodate two or three devices. What if you want to connect more than two devices at once? You’ll probably need a power strip, which is nothing but an extension block that powers multiple electronic devices from a single socket, all at a time. It simply plugs into your wall socket and allows you to plug in multiple devices.
A surge protector is just like a power strip almost with the same function except it also protects your electronic devices from accidental power surges. Let’s study each of them in detail and understand the difference between the two.

What is a Power Strip?
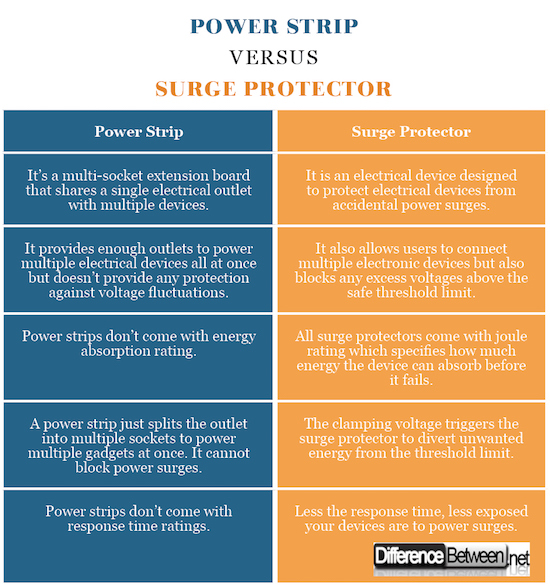
A power strip is an extension board with a block of electrical sockets that plugs into your wall outlet allowing you to power multiple electrical devices or electronic gadgets all at once. It is a simple electrical device that connects to a flexible chord at one end which goes right into your outlet and consists of several sockets on the other hand which can easily accommodate any number of devices at a time. All it does is expand the capacity of your wall outlet in terms of number of connecting devices it can power up simultaneously.
They are just extension blocks that do not provide any level of protection against accidental power spikes.
What is a Surge Protector?
A surge protector often looks just like a power strip, but not every surge protector is a power strip. It not only functions as a power strip to power multiple electrical devices simultaneously but also protect your devices from sudden voltage fluctuations and power surges. Because of the electrical sensitivity of electronic gadgets, they are more vulnerable to power spikes or power outages.
In case a power spike hits and your devices are not connected to a surge protector, it may cause potential damages. In the event of power spikes, surge protectors protect your devices by blocking or limiting any excess voltage that crosses the safe threshold limit. For example, an UPS functions as a surge protector.

Difference between Power Strip and Surge Protector
Basics of Power Strip and Surge Protector
A power strip is a power board with multiple sockets attached to the end of a flexible cable which plugs into your wall outlet. It’s simply an extension board that furnishes simple parallel wired power to accommodate multiple electronic devices at once. It is also called as a multi-socket board which can power two to a dozen gadgets all at a time. A surge protector or a surge suppressor is an electronic device designed to protect electronic devices from sudden power spikes or voltage fluctuations by limiting any excess voltage above a certain threshold.
Form Factor for Power Strip and Surge Protector
From the outside, both look just the same; in fact, the form factor of a power strip makes many people think that all power strips are surge protectors but that’s not the case. A power strip is a multi-socket board that connects to a wall outlet. It usually comes with a circuit breaker of some sort, but doesn’t provide any real protection from voltage fluctuations. A surge protector is entirely a different piece of equipment that comes with a compact form factor but offers a great level of protection to your sensitive electronic devices against accidental power surges.
Energy Absorption/Dissipation Rating
Think of energy absorption/dissipation rating as the joule rating which is measured in ‘joules’. The energy absorption rating tells you how much of a beating a surge protector can take until it fails. This joule rating suggests exactly how much energy the device can absorb before it fails. All surge protectors come with this joule rating and more the rating, greater the protection. If a surge protector is rated at 500 joules, which means it can take five 100 joules hits or a single 500 joule hit before it shorts. Generally, more the joules, the more protected you are against sudden power surges. A power strip only offers more outlets and doesn’t usually come with energy absorption rating.
Response Time in Power Strip and Surge Protector
This is another of surge protector ratings that specifies the ability of a surge protected device (SPD) to respond to a voltage threshold limit. In simple terms, the response time of a SPD determines the length of time an electronic device is exposed to the power surge. All surge protectors come with a certain response time to kick in and mitigate voltage spikes within the safe threshold limit. Response times are based on component data and less the response time, the more protected the devices are. Surge protectors respond almost immediately when they see a surge. Power strips, on the other hand, don’t have response time ratings.
Power Strip vs. Surge Protector: Comparison Chart
Summary of Power Strip vs Surge Protector
Both power strips and surge protectors are essential electronic accessories commonly found in almost every household to expand the capacity of your wall outlet. Many people think that all power strips are surge protectors, but that’s not the case. Although, they look quite similar from the outside, a surge protector is entirely a different piece of device. A surge protector also functions like a power strip; it allows users to connect multiple devices at once, but comes with an extra level of protection. A surge protector not only acts as a power strip but also protects your devices from sudden voltage fluctuations and power surges by blocking excess voltage above the certain safe threshold limit.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Sinopoli, James M. Smart Buildings Systems for Architects, Owners and Builders. Oxford, UK: Butterworth-Heinemann, 2009. Print
[1]Ivens, Kathy. Home Networking Annoyances. Sebastopol: O’Reilly Media, 2005. Print
[2]Shelly, Gary and Misty Vermaat. Discovering Computers 2009: Introductory. Boston: Cengage, 2008. Print
[3]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/fa/Belkin-Surge-Protector.jpg/640px-Belkin-Surge-Protector.jpg
[4]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/75/Schuko_Power_Strip.jpg/640px-Schuko_Power_Strip.jpg
