Difference Between Encrypted and Unencrypted
The amount of data that we create and use is growing exponentially and the rate at which it’s growing we would be sitting on trillions of trillions gigabytes of data in the digital space by 2020. We’re living in a digital era characterized by the rapid evolution of digital technology. The data we’re generating is everywhere – in laptops, smartphones, and a dozen of online services. We’ve come way beyond the conventional use of the internet – video calls, online shopping, social media, and general browsing are some of the few things we can no longer live without.
Data and information are shared online on a daily basis which makes them more vulnerable to data breaches. Businesses are increasingly targeted by cybercriminals and hackers which make it all the more important to encrypt your data.
What is Encrypted?
Encryption is the process of safeguarding your personal data or information from unauthorized access by encoding a plaintext or any type of data in such as way that only the intended party are allowed to access it.
A simple text or data can be converted to an encoded version that can only be decoded or read by the intended recipient or the individual with the decryption key.
The key to encryption is to generate large numbers that only you can understand. When you encrypt data, you simply convert your data from plaintext into scrambled cipher text that can only be decoded or decrypted with the right decryption key.
No unauthorized person or computer can access the encrypted data. Encrypting files, documents, Emails, messages, and even your data storage prevent any unauthorized access.
There are a number of tools available for encrypting data, all of which based on having encryption and decryption keys. Most of the modern computer systems use public-key encryption, which is the most common and widely used encryption method that uses a public key to encrypt data and a private key a decrypt data.
The public key can be shared with everyone, but the private key must be kept secret. As the public key is published online, almost any sender can use the public key to encrypt messages and only the intended recipient or receiver holds the private key required to decrypt the message. The public key is never the same as the private key which makes it even harder to figure out.
What is Unencrypted?
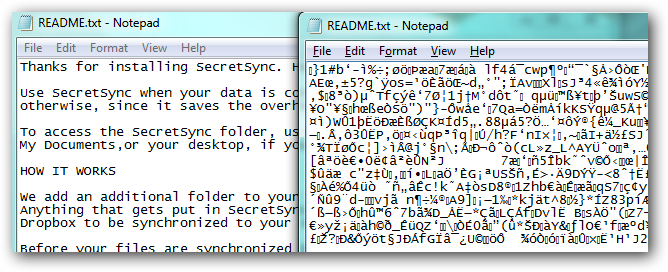
Unencrypted, on the contrary, refers to anything that is not encrypted. Unencrypted data is often referred to as a plaintext which is readable by a human or a computer. Unencrypted usually refers to data or information that is stored unprotected, without any encryption. Unencrypted data is vulnerable to online breaches. Unencrypted or plaintext, refers to data pending encryption using encryption algorithms.
When you say the data is unencrypted, it means the data – a document, message, email, file, etc. – is in an unsecured form that can be easily viewed or accessed without the need of a decryption key. This means the information is stored unprotected and almost anyone can access it at any stage. For example, an unencrypted email is more vulnerable to being hacked at any stage while on its way from sender to receiver.
Difference between Encrypted and Unencrypted
Definition of Encrypted Vs. Unencrypted
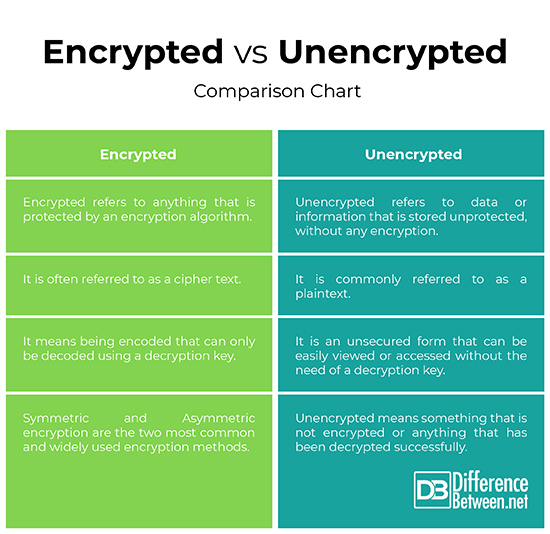
– Encrypted data is often referred to as a cipher text, whereas unencrypted data is referred to as plaintext. Encrypted means anything that is protected by an encryption algorithm to prevent unauthorized access. Encryption is the method of converting a plaintext into a cipher text so that only the authorized parties can decrypt the information and no third parties can tamper with the data.
Unencrypted usually refers to data or information that is stored unprotected, without any encryption.
Security of Encrypted Vs. Unencrypted
– Being encrypted is being in code which means it’s unreadable and secure. It is the most effective method to protect or secure your data including messages, emails, documents, files, etc. from unauthorized outside access. The most common method to encrypt data is public key encryption which protects your data by transforming data into cipher text.
Being unencrypted means something that’s not encrypted which makes it vulnerable to online breaches. Unencrypted data is prone to cyber attacks.
Tools
– There are various methods and software tools available that can be mainly used for protecting sensitive information from non-essential access.
Encryption provides security against breaches based on encryption and decryption keys both of which are related to each other. Encryption key is required to encrypt the data via encoded information and the decryption key is required to decode that information. Symmetric and Asymmetric encryption are the two most common and widely used encryption methods.
Unencrypted means information is stored without any encryption.
Encrypted vs. Unencrypted: Comparison Chart
Summary of Encrypted Vs. Unencrypted
When you say encryption, you might think this is something geeks would know of or use. You may not realize it yet but you probably use encryption. It’s just a way to protect your data or information from potential online threats or cybercriminals.
Almost everyone uses encryption to safeguard their data from online breaches. Data security is the main concern these days and by data it means your credit card information, your personal messages, emails, and all sorts of communication.
Emails have been around for as long as the internet. And even they are not completely secure and can be easily intercepted. This is why protecting your information via encryption is vital.
Unencrypted, on the contrary, is something that’s not encrypted.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Katz, Jonathan and Yehuda Lindell. Introduction to Modern Cryptography: Principles and Protocols. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, 2007. Print
[1]Fouché Gaines, Helen. Cryptanalysis: A Study of Ciphers and Their Solution. New York: Dover Publications, 1939. Print
[2]Lian, Shiguo. Multimedia Content Encryption: Techniques and Applications. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, 2008. Print
[3]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/6f/Enrypted_file.png
[4]Image credit: https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2017/06/28/10/44/laptop-2450220_960_720.jpg


pls help reset Outlook