Difference Between Hadoop and MongoDB
We’ve been hearing the term Big Data for quite some time now, but what exactly is this Big Data? The amount of data produced by the Internet of Things has increased dramatically over the years and it keeps increasing at an exponential rate. The processing of these massive volumes of data not suitable for traditional methods to handle is termed as Big Data. This kind of data poses challenges to the traditional RDBMS systems used for storing and processing data. The processing power needed to store and process this much data in a timely and cost effective manner is massive. In order to address this problem, new and improved Big Data solutions are required that are specifically designed for processing large unstructured data. Of the many technologies, Hadoop and MongoDB are the two popular choices when it comes to storing and processing big data. While both are fairly similar in basically what they do, but their approach to how they do it is quite different. Let’ take a look.
What is MongoDB?
MongoDB is an open-source document database which has grown to become the de facto NoSQL database with millions of users, from small startups to Fortune 500 companies. Leading enterprises and consumer IT companies leverage the capabilities of MongoDB in their products and solutions. Written in C++, MongoDB is a cross-platform, document oriented database that effectively addresses the limitations of SQL schema-based databases by providing high performance, high availability, and easy scalability solutions. It is a database designed for the modern web. Like other NoSQL databases, MongoDB does not comply with the principles of RDBMS with no concepts of tables, rows and columns. It stores its data in BSON documents where all the related data is placed together in a single document.
What is Hadoop?
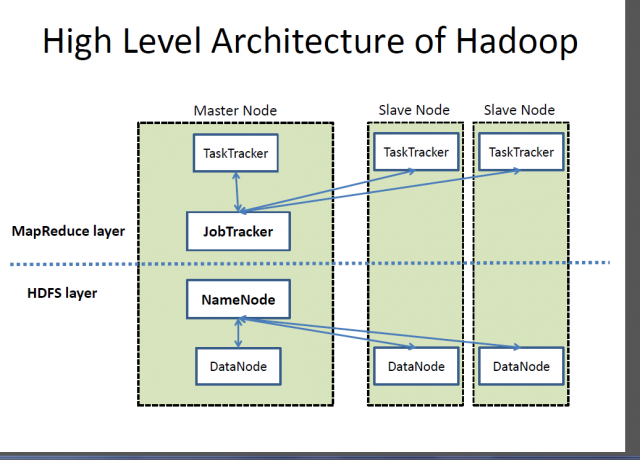
Hadoop is an open-source framework designed for storage and processing massive volumes of data across clusters of computers. It is an applications based on Java and a collection of different software that creates data processing framework. The idea is to process large scale data at reasonable cost in the least time possible. Hadoop consists of three primary resources: the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), the Google’s MapReduce programming platform, and the whole Hadoop ecosystem. The Hadoop ecosystem consists of modules that help to program the system, manage and configure the cluster, manage and store data in the cluster and perform analytic tasks. Hadoop MapReduce aids data analytics process very large amounts of both structured and unstructured data. Hadoop is a registered trademark of the Apache Software Foundaton and MapReduce is its framework for parallel processing.
Difference between Hadoop and MongoDB
Platform
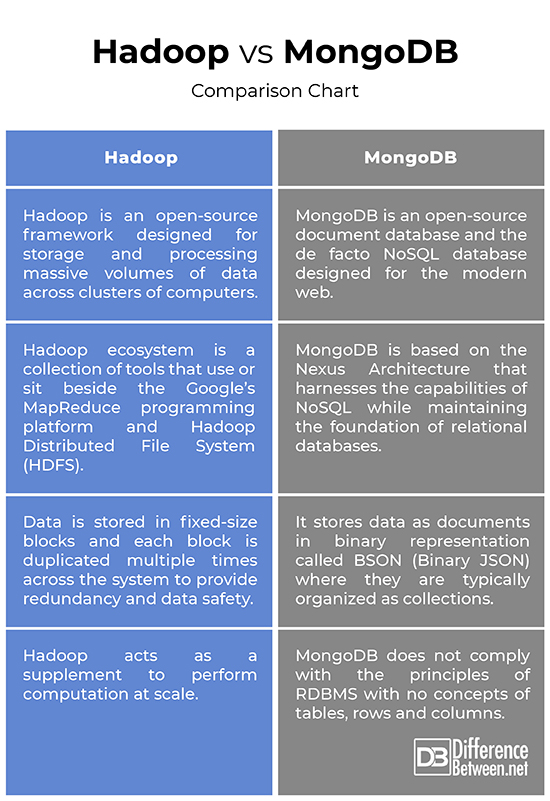
– While both are considered big data solutions, MongoDB is basically a general-purpose platform designed to replace or improve on the existing RDBMS systems. MongoDB is an open-source document database and one of the leading NoSQL databases that uses documents, instead of rows and tables, to make it flexible, scalable, and fast. Hadoop, on the other hand, is an open-source framework designed for storage and processing massive volumes of data across clusters of computers. Hadoop is not meant to replace the existing RDBMS systems; in fact, it acts as a supplement to aid data analytics process large volumes of both structured and unstructured data.
Architecture
– The Hadoop ecosystem is a collection of tools that use or sit beside the Google’s MapReduce programming platform and HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System) to store and organize data, and manage the machines that run Hadoop. HDFS is designed for streaming data access. MongoDB, on the other hand, offers a different approach; it is based on the Nexus Architecture that harnesses the capabilities of NoSQL while maintaining the foundation of relational databases. It stores data as documents in binary representation called BSON (Binary JSON) where they are typically organized as collections.
Strength
– The biggest strength of Hadoop is MapReduce. Today Hadoop is the best MapReduce framework in the market. The concept behind MapReduce is that input can be split into logical chunks, where each chunk can be independently processed by a map task. A map task can run on any compute node in the cluster and multiple map tasks can run in parallel across the cluster. MongoDB, on the other hand, is a document database that can handle loads ranging from startup MVPs and POCs to enterprise applications with hundreds of servers. MongoDB has grown from being a niche database solution to the de facto NoSQL database. Its notion of documents is really expressive and flexible.
Hadoop vs. MongoDB: Comparison Chart
Summary
While both are fairly similar in basically what they do, but their approach to how they do it is quite different. MongoDB stores data as documents in binary representation called BSON, whereas in Hadoop, the data is stored in fixed-size blocks and each block is duplicated multiple times across the system. The Hadoop ecosystem is a collection of tools that use or sit beside the Google’s MapReduce programming platform, whereas MongoDB based on the Nexus Architecture that harnesses the capabilities of NoSQL while maintaining the foundation of relational databases.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Connection_to_the_MongoDB_Shell.png
[1]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Hadoop-HighLevel_hadoop_architecture-640x460.png
[2]Edward, Shakuntala Gupta and Navin Sabharwal. Practical MongoDB: Architecting, Developing, and Administering MongoDB. New York, United States: Apress, 2015. Print
[3]Sitto, Kevin and Marshall Presser. Field Guide to Hadoop. Sebastopol, California: O’Reilly Media, 2015. Print
[4]Giamas, Alex. Mastering MongoDB 3.x. Birmingham, United Kingdom: Packt Publishing, 2017. Print
[5]Jain, V.K. Big Data and Hadoop. New Delhi, India: Khanna Book Publishing, 2017. Print
[6]Bengfort, Benjamin and Jenny Kim. Data Analytics with Hadoop: An Introduction for Data Scientists. Sebastopol, California: O’Reilly Media, 2016. Print
