Difference Between Ultrabook and Notebook
Notebooks, or laptops or ultrabooks or whatever you call them, have come a long way since it first became known to people. The first computers were monstrous mainframes. Profound changes in technology in the last few decades dramatically changed the whole landscape. Personal computers were probably the biggest personal tool known to mankind. Then, laptops came to the picture and took computing to a whole new level. A few decades back, the word laptop or notebook would not have made sense. But now, laptops are high-performance, advanced machines capable of handling anything you throw at them. Today, tech companies make thousands of unique, inventive products every year and release them for the general public. Thanks to the technological evolution, we now have plethora of options when it comes to portable computers.

What is Ultrabook?
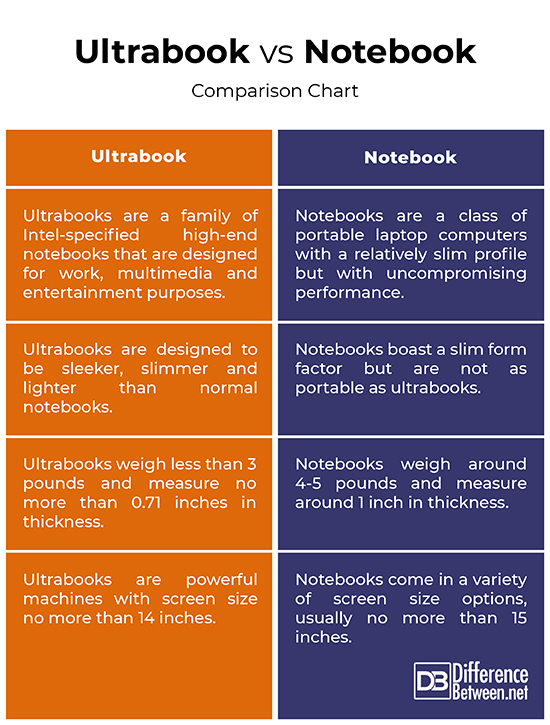
Ultrabooks have managed to garner a lot of attention in the recent years for their sleek profile. But what exactly are they? Ultrabooks are a class of Intel-specified high-end notebooks that are designed for work, multimedia and entertainment purposes. Ultrabooks are super-slim and extremely lightweight notebooks that offer a superb balance between price, mobility, and features. They are a great tread off between a full-featured laptop computer and a sleek tablet. Known for their ultra-portable form factor and super lightweight design, ultrabooks are mean machines that boast latest generation Intel processor and high performance solid state drives for better performance and reliability. Their biggest selling point is their sleek form factor, featuring a slim, lightweight design and weighing less than 4 pounds or sometimes less than 3 pounds. They are usually budget-friendly laptops but uncompromising in performance. The term ‘ultrabook’ was originally coined by Intel and the market is mostly flooded with Intel-powered processors, featuring core i3, i5 and i7 family of processors.

What is a Notebook?
Notebooks are slim laptop computers that appeal to majority of consumers, including casual and professional users. Notebooks are also laptops but with relatively slim profile and much sleeker. Notebook is a small, portable laptop computer that usually weighs less than a laptop, around 3 – 4 pounds or less and is about 1 inch thick. Notebooks come in a wide range of varying screen sizes, form factor, and display technologies. Notebooks are particularly designed for mobile users who would want carry them easily wherever they go. Notebooks use a variety of flat-panel technologies these days, ranging from good-old LCD screens to truly spectacular OLED displays for immersive experience. So, basically all ultrabooks are notebooks but with low-power Intel processors and solid state drives (SSDs). Notebooks are not necessarily powered by Intel processors; there are a ton of AMD powered notebooks as well. Notebooks are a perfect balance between portability and performance.
Difference between Ultrabook and Notebook
Chassis
– Both the terms ultrabooks and notebooks are often used interchangeably to refer to laptop computers, but there is a fine line between the two categories of portable laptop computers. Notebooks are a class of slim and lightweight laptop computers with a streamlined chassis but feature-rich in performance. Notebooks are particularly designed for mobile users who would want convenience and performance in a sleek package. Ultrabooks, on the other hand, are Intel-specified high-performance notebooks with super slim chassis and extremely lightweight design. Ultrabooks are a fine trade-off between high-performance laptops and super slim tablets.
Portability
– One of the biggest selling points of ultrabooks is portability because they are conveniently optimized for increased mobility, meaning you can carry them with ease wherever you go. Ultrabooks are designed to be sleeker, slimmer and lighter than normal notebooks. They come in a couple of options when it comes to screen sizes, but usually, they are no more than 13 inches or so and measure 0.71 inches or less with machines less than 14 inches in size. Notebooks are also portable laptops with a slim profile and lightweight chassis, but they are not as slim and lightweight as ultrabooks. Notebooks come in varying screen sizes, usually 15 inches or less and measure 1 inch or less in thickness.
Performance
– Notebooks are basically feature-rich laptops that come equipped with high-performance mobile processors that pack adequate power in a small package, complemented by high-quality displays for superior performance. Even the budget notebooks deliver enough processing power to handle your day-to-day computing requirements. Ultrabooks also come in a variety of options, ranging from low-cost Intel Core i3 notebooks to high-end ultrabooks with latest generation Core i7 processor, accompanied by up to 16 GB of RAM. Well, regardless of the name, the performance of both is determined by CPU, GPU, RAM and storage type. While ultrabooks mostly come packed with super-fast SSDs, notebooks use either SSDs or HDDs or a combination of both. Ultrabooks also come with hybrid hard disk storage.
Ultrabook vs. Notebook: Comparison Chart
Summary
All ultrabooks are basically notebooks, but not all notebooks are ultrabooks. This is because notebooks come in a wide range of screen sizes but no more than 15 inches and measure no more than 1 inch in thickness, give or take. Ultrabooks are super slim notebooks that deliver superior performance in a small form factor. So, big things indeed come in small packages. Both notebooks and ultrabooks are quite similar in terms of performance and portability. But they do have their fair share of differences as well. Well, it’s the technology that is inside that truly sets the two apart.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Sandler, Corey. Laptops for Dummies. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2008. Print
[1]Wren, Daniel A. and Arthur G. Bedeian. The Evolution of Management Thought. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2020. Print
[2]Stair, Ralph and George Reynolds. Fundamentals of Information Systems. Massachusetts, United States: Cengage, 2017. Print
[3]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Asus_UX_31_Ultrabook_PC.jpg
[4]Image credit https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Laptop-notebook-clean-hero_(23699770333).jpg
